Redis技术交流群 481804090
Redis:https://github.com/zwjlpeng/Redis_Deep_Read
Redis中采用两种算法进行内存回收,引用计数算法以及LRU算法,在操作系统内存管理一节中,我们都学习过LRU算法(最近最久未使用算法),那么什么是LRU算法呢
LRU算法作为内存管理的一种有效算法,其含义是在内存有限的情况下,当内存容量不足时,为了保证程序的运行,这时就不得不淘汰内存中的一些对象,释放这些对象占用的空间,那么选择淘汰哪些对象呢?LRU算法就提供了一种策略,告诉我们选择最近一段时间内,最久未使用的对象将其淘汰,至于为什么要选择最久未使用的,可以想想,最近一段时间内使用的东西,我们是不是可能一会又要用到呢~,而很长一段时间内都没有使用过的东西,也许永远都不会再使用~
在操作系统中LRU算法淘汰的不是内存中的对象,而是页,当内存中数据不足时,通过LRU算法,选择一页(一般是4KB)将其交换到虚拟内存区(Swap区)
LRU算法演示
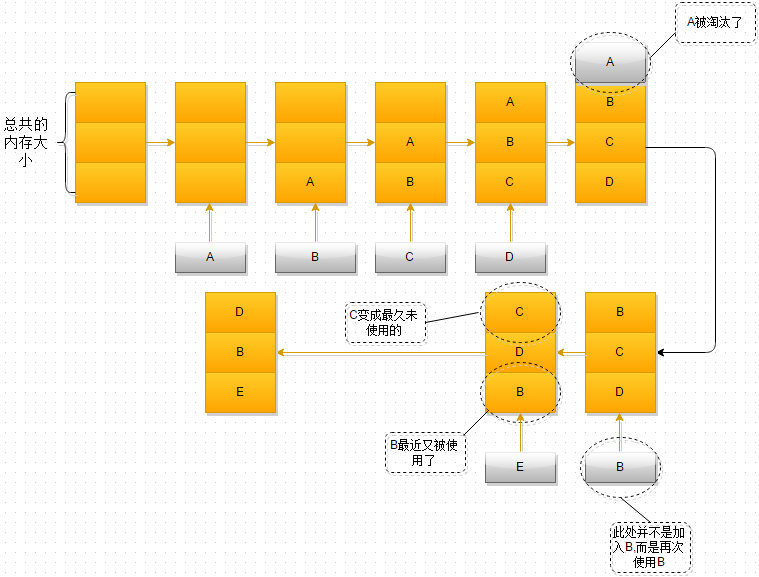
这张图应该画的还行吧,用的是www.draw.io,解释如下,假设前提,只有三块内存空间可以使用,每一块内存空间只能存放一个对象,如A、B、C...
1、最开始时,内存空间是空的,因此依次进入A、B、C是没有问题的
2、当加入D时,就出现了问题,内存空间不够了,因此根据LRU算法,内存空间中A待的时间最为久远,选择A,将其淘汰
3、当再次引用B时,内存空间中的B又处于活跃状态,而C则变成了内存空间中,近段时间最久未使用的
4、当再次向内存空间加入E时,这时内存空间又不足了,选择在内存空间中待的最久的C将其淘汰出内存,这时的内存空间存放的对象就是E->B->D
LRU算法的整体思路就是这样的
算法实现应该采用怎样的数据结构
队列?那不就是FIFO算法嘛~,LRU算法最为精典的实现,就是HashMap+Double LinkedList,时间复杂度为O(1),具体可以参考相关代码
REDIS中LRU算法的实际应用,在Redis 1.0中并未引入LRU算法,只是简单的使用引用计数法,去掉内存中不再引用的对象以及运行一个定时任务serverCron去掉内存中已经过期的对象占用的内存空间,以下是Redis 1.0中CT任务的释放内存中的部份代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
//去掉一些过期的KEYSfor (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) { redisDb *db = server.db+j; int num = dictSize(db->expires);//计算hash表中过期Key的数目 if (num) { time_t now = time(NULL); //#define REDIS_EXPIRELOOKUPS_PER_CRON 100 if (num > REDIS_EXPIRELOOKUPS_PER_CRON) num = REDIS_EXPIRELOOKUPS_PER_CRON; //循环100次,从过期Hash表中随机挑选出100个Key,判断Key是否过期,如果过期了,执行删除操作 while (num--) { dictEntry *de; time_t t; //随机获取Key值(db->expires里面存储的均是即将过期的Keys) if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break; t = (time_t) dictGetEntryVal(de); if (now > t) { //不仅要从存放过期keys的Hash表中删除数据,还要从存放实际数据的Hash表中删除数据 deleteKey(db,dictGetEntryKey(de)); } } }} |
如果没有看过Redis 1.0源码,理解起来可能有些困难,但看看1.0源码中的这个结构体,估计有点数据结构基础的人,都明白上面这几行代码的意思了(注释部份我也已经写的很清楚了)~
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
typedef struct redisDb { dict *dict;//用来存放实际Key->Value数据的位置 dict *expires;//用于记录Key的过期时间 int id;//表示选择的是第几个redis库} redisDb; |
没有查证是从什么版本开始,Redis增加了LRU算法,以下是分析Redis 2.9.11代码中的LRU算法淘汰策略,在2.9.11版本中与LRU算法相关的代码主要位于object.c以及redis.c两个源文件中, 再分析这两个文件关于LRU源代码之前,让我们先看一下,Redis 2.9.11版本中关于LRU算法的配置,配置文件在redis.conf文件中,如下所示
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
# maxmemory <bytes># MAXMEMORY POLICY: how Redis will select what to remove when maxmemory# is reached. You can select among five behaviors:# # volatile-lru -> remove the key with an expire set using an LRU algorithm# allkeys-lru -> remove any key accordingly to the LRU algorithm# volatile-random -> remove a random key with an expire set# allkeys-random -> remove a random key, any key# volatile-ttl -> remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL)# noeviction -> don't expire at all, just return an error on write operations# # Note: with any of the above policies, Redis will return an error on write# operations, when there are not suitable keys for eviction.## At the date of writing this commands are: set setnx setex append# incr decr rpush lpush rpushx lpushx linsert lset rpoplpush sadd# sinter sinterstore sunion sunionstore sdiff sdiffstore zadd zincrby# zunionstore zinterstore hset hsetnx hmset hincrby incrby decrby# getset mset msetnx exec sort## The default is:## maxmemory-policy noeviction# LRU and minimal TTL algorithms are not precise algorithms but approximated# algorithms (in order to save memory), so you can tune it for speed or# accuracy. For default Redis will check five keys and pick the one that was# used less recently, you can change the sample size using the following# configuration directive.## The default of 5 produces good enough results. 10 Approximates very closely# true LRU but costs a bit more CPU. 3 is very fast but not very accurate.## maxmemory-samples 5 |
从上面的配置中,可以看出,高版本的Redis中当内存达到极限时,内存淘汰策略主要采用了6种方式进行内存对象的释放操作
1.volatile-lru:从设置了过期时间的数据集中,选择最近最久未使用的数据释放
2.allkeys-lru:从数据集中(包括设置过期时间以及未设置过期时间的数据集中),选择最近最久未使用的数据释放
3.volatile-random:从设置了过期时间的数据集中,随机选择一个数据进行释放
4.allkeys-random:从数据集中(包括了设置过期时间以及未设置过期时间)随机选择一个数据进行入释放
5.volatile-ttl:从设置了过期时间的数据集中,选择马上就要过期的数据进行释放操作
6.noeviction:不删除任意数据(但redis还会根据引用计数器进行释放呦~),这时如果内存不够时,会直接返回错误
默认的内存策略是noeviction,在Redis中LRU算法是一个近似算法,默认情况下,Redis随机挑选5个键,并且从中选取一个最近最久未使用的key进行淘汰,在配置文件中可以通过maxmemory-samples的值来设置redis需要检查key的个数,但是栓查的越多,耗费的时间也就越久,但是结构越精确(也就是Redis从内存中淘汰的对象未使用的时间也就越久~),设置多少,综合权衡吧~~~
在redis.h中声明的redisObj定义的如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#define REDIS_LRU_BITS 24#define REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_MAX ((1<<REDIS_LRU_BITS)-1) /* Max value of obj->lru */#define REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION 1000 /* LRU clock resolution in ms */typedef struct redisObject {<br> //存放的对象类型 unsigned type:4; //内容编码 unsigned encoding:4; //与server.lruclock的时间差值 unsigned lru:REDIS_LRU_BITS; /* lru time (relative to server.lruclock) */ //引用计数算法使用的引用计数器 int refcount; //数据指针 void *ptr;} robj; |
从redisObject结构体的定义中可以看出,在Redis中存放的对象不仅会有一个引用计数器,还会存在一个server.lruclock,这个变量会在定时器中每次刷新时,调用getLRUClock获取当前系统的毫秒数,作为LRU时钟数,该计数器总共占用24位,最大可以表示的值为24个1即((1<<REDIS_LRU_BITS) - 1)=2^24 - 1,单位是毫秒,你可以算一下这么多毫秒,可以表示多少年~~
server.lruclock在redis.c中运行的定时器中进行更新操作,代码如下(redis.c中的定时器被配置中100ms执行一次)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) { ..... run_with_period(100) trackOperationsPerSecond(); /* We have just REDIS_LRU_BITS bits per object for LRU information. * So we use an (eventually wrapping) LRU clock. * * Note that even if the counter wraps it's not a big problem, * everything will still work but some object will appear younger * to Redis. However for this to happen a given object should never be * touched for all the time needed to the counter to wrap, which is * not likely. * * Note that you can change the resolution altering the * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION define. */ server.lruclock = getLRUClock(); .... return 1000/server.hz;} |
看到这,再看看Redis中创建对象时,如何对redisObj中的unsigned lru进行赋值操作的,代码位于object.c中,如下所示
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
robj *createObject(int type, void *ptr) { robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(*o)); o->type = type; o->encoding = REDIS_ENCODING_RAW; o->ptr = ptr; o->refcount = 1; //很关键的一步,Redis中创建的每一个对象,都记录下该对象的LRU时钟 /* Set the LRU to the current lruclock (minutes resolution). */ o->lru = LRU_CLOCK(); return o;} |
该代码中最为关键的一句就是o->lru=LRU_CLOCK(),这是一个定义,看一下这个宏定义的实现,代码如下所示
|
1
|
#define LRU_CLOCK() ((1000/server.hz <= REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION) ? server.lruclock : getLRUClock()) |
其中REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION为1000,可以自已在配置文件中进行配置,表示的是LRU算法的精度,在这里我们就可以看到server.lruclock的用处了,如果定时器执行的频率高于LRU算法的精度时,可以直接将server.lruclock直接在对象创建时赋值过去,避免了函数调用的内存开销以及时间开销~
有了上述的基础,下面就是最为关键的部份了,REDIS中LRU算法,这里以volatile-lru为例(选择有过期时间的数据集进行淘汰),在Redis中命令的处理时,会调用processCommand函数,在ProcessCommand函数中,当在配置文件中配置了maxmemory时,会调用freeMemoryIfNeeded函数,释放不用的内存空间
以下是freeMemoryIfNeeded函数的关于LRU相关部份的源代码,其他代码类似
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
//不同的策略,操作的数据集不同if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU || server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM){ dict = server.db[j].dict;} else {//操作的是设置了过期时间的key集 dict = server.db[j].expires;}if (dictSize(dict) == 0) continue;/* volatile-random and allkeys-random policy *///随机选择进行淘汰if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM || server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_RANDOM){ de = dictGetRandomKey(dict); bestkey = dictGetKey(de);}/* volatile-lru and allkeys-lru policy *///具体的LRU算法else if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU || server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU){ struct evictionPoolEntry *pool = db->eviction_pool; while(bestkey == NULL) { //选择随机样式,并从样本中作用LRU算法选择需要淘汰的数据 evictionPoolPopulate(dict, db->dict, db->eviction_pool); /* Go backward from best to worst element to evict. */ for (k = REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1; k >= 0; k--) { if (pool[k].key == NULL) continue; de = dictFind(dict,pool[k].key); sdsfree(pool[k].key); //将pool+k+1之后的元素向前平移一个单位 memmove(pool+k,pool+k+1, sizeof(pool[0])*(REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-k-1)); /* Clear the element on the right which is empty * since we shifted one position to the left. */ pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key = NULL; pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].idle = 0; //选择了需要淘汰的数据 if (de) { bestkey = dictGetKey(de); break; } else { /* Ghost... */ continue; } } }} |
看了上面的代码,也许你还在奇怪,说好的,LRU算法去哪去了呢,再看看这个函数evictionPoolPopulate的实现吧
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
#define EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE 16void evictionPoolPopulate(dict *sampledict, dict *keydict, struct evictionPoolEntry *pool) { int j, k, count; //EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE最大样本数,默认16 dictEntry *_samples[EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE]; dictEntry **samples; //如果我们在配置文件中配置的samples小于16,则直接使用EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE if (server.maxmemory_samples <= EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE) { samples = _samples; } else { samples = zmalloc(sizeof(samples[0])*server.maxmemory_samples); }#if 1 /* Use bulk get by default. */ //从样本集中随机获取server.maxmemory_samples个数据,存放在 count = dictGetRandomKeys(sampledict,samples,server.maxmemory_samples);#else count = server.maxmemory_samples; for (j = 0; j < count; j++) samples[j] = dictGetRandomKey(sampledict);#endif for (j = 0; j < count; j++) { unsigned long long idle; sds key; robj *o; dictEntry *de; de = samples[j]; key = dictGetKey(de); if (sampledict != keydict) de = dictFind(keydict, key); o = dictGetVal(de); //计算LRU时间 idle = estimateObjectIdleTime(o); k = 0; //选择de在pool中的正确位置,按升序进行排序,升序的依据是其idle时间 while (k < REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE && pool[k].key && pool[k].idle < idle) k++; if (k == 0 && pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key != NULL) { /* Can't insert if the element is < the worst element we have * and there are no empty buckets. */ continue; } else if (k < REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE && pool[k].key == NULL) { /* Inserting into empty position. No setup needed before insert. */ } else { //移动元素,memmove,还有空间可以插入新元素 if (pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key == NULL) { memmove(pool+k+1,pool+k, sizeof(pool[0])*(REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-k-1)); } else {//已经没有空间插入新元素时,将第一个元素删除 /* No free space on right? Insert at k-1 */ k--; /* Shift all elements on the left of k (included) to the * left, so we discard the element with smaller idle time. */ //以下操作突出了第K个位置 sdsfree(pool[0].key); memmove(pool,pool+1,sizeof(pool[0])*k); } } //在第K个位置插入 pool[k].key = sdsdup(key); pool[k].idle = idle; } //执行到此之后,pool中存放的就是按idle time升序排序 if (samples != _samples) zfree(samples);} |
看了上面的代码,LRU时钟的计算并没有包括在内,那么在看一下LRU算法的时钟计算代码吧,LRU时钟计算代码在object.c中的estimateObjectIdleTime这个函数中,代码如下~~
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
//精略估计LRU时间 unsigned long long estimateObjectIdleTime(robj *o) { unsigned long long lruclock = LRU_CLOCK(); if (lruclock >= o->lru) { return (lruclock - o->lru) * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION; } else {//这种情况一般不会发生,发生时证明redis中键的保存时间已经wrap了 return (lruclock + (REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_MAX - o->lru)) * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION; }} |
好了,先到此吧~~~