一、CAS和synchronized适用场景
1、对于资源竞争较少的情况,使用synchronized同步锁进行线程阻塞和唤醒切换以及用户态内核态间的切换操作额外浪费消耗cpu资源;而CAS基于硬件实现,不需要进入内核,不需要切换线程,操作自旋几率较少,因此可以获得更高的性能。
2、对于资源竞争严重的情况,CAS自旋的概率会比较大,从而浪费更多的CPU资源,效率低于synchronized。以java.util.concurrent.atomic包中AtomicInteger类为例,其getAndIncrement()方法实现如下:
public final int getAndIncrement() {
for (;;) {
int current = get();
int next = current + 1;
if (compareAndSet(current, next))
return current;
}
}
如果compareAndSet(current, next)方法成功执行,则直接返回;如果线程竞争激烈,导致compareAndSet(current, next)方法一直不能成功执行,则会一直循环等待,直到耗尽cpu分配给该线程的时间片,从而大幅降低效率。
二、CAS错误的使用场景
1 public class CASDemo {
2 private final int THREAD_NUM = 1000;
3 private final int MAX_VALUE = 20000000;
4 private AtomicInteger casI = new AtomicInteger(0);
5 private int syncI = 0;
6 private String path = "/Users/pingping/DataCenter/Books/Linux/Linux常用命令详解.txt";
7
8 public void casAdd() throws InterruptedException {
9 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
10 Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_NUM];
11 for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) {
12 threads[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() {
13 public void run() {
14 while (casI.get() < MAX_VALUE) {
15 casI.getAndIncrement();
16 }
17 }
18 });
19 threads[i].start();
20 }
21 for (int j = 0; j < THREAD_NUM; j++) {
22 threads[j].join();
23 }
24 System.out.println("CAS costs time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));
25 }
26
27 public void syncAdd() throws InterruptedException {
28 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
29 Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_NUM];
30 for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) {
31 threads[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() {
32 public void run() {
33 while (syncI < MAX_VALUE) {
34 synchronized ("syncI") {
35 ++syncI;
36 }
37 }
38 }
39 });
40 threads[i].start();
41 }
42 for (int j = 0; j < THREAD_NUM; j++)
43 threads[j].join();
44 System.out.println("sync costs time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));
45 }
46 }
在我的双核cpu上运行,结果如下:
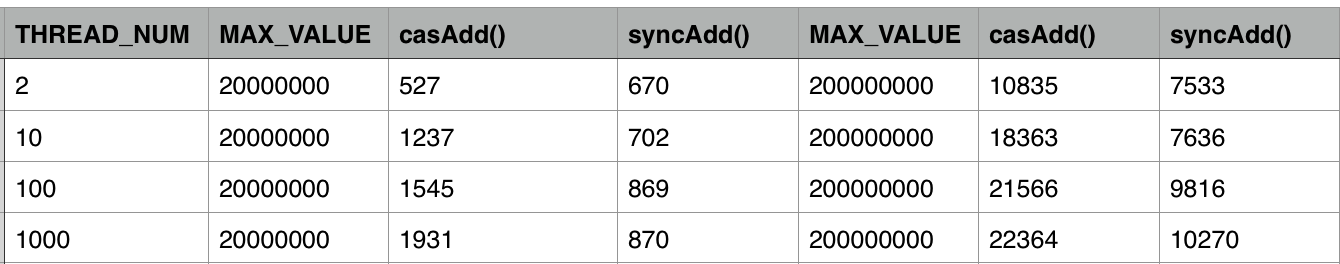
可见在不同的线程下,采用CAS计算消耗的时间远多于使用synchronized方式。原因在于第15行
14 while (casI.get() < MAX_VALUE) {
15 casI.getAndIncrement();
16 }
的操作是一个耗时非常少的操作,15行执行完之后会立刻进入循环,继续执行,从而导致线程冲突严重。
三、改进的CAS使用场景
为了解决上述问题,只需要让每一次循环执行的时间变长,即可以大幅减少线程冲突。修改代码如下:
1 public class CASDemo {
2 private final int THREAD_NUM = 1000;
3 private final int MAX_VALUE = 1000;
4 private AtomicInteger casI = new AtomicInteger(0);
5 private int syncI = 0;
6 private String path = "/Users/pingping/DataCenter/Books/Linux/Linux常用命令详解.txt";
7
8 public void casAdd2() throws InterruptedException {
9 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
10 Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_NUM];
11 for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) {
12 threads[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() {
13 public void run() {
14 while (casI.get() < MAX_VALUE) {
15 casI.getAndIncrement();
16 try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(new File(path))) {
17 while (in.read() != -1);
18 } catch (IOException e) {
19 e.printStackTrace();
20 }
21 }
22 }
23 });
24 threads[i].start();
25 }
26 for (int j = 0; j < THREAD_NUM; j++)
27 threads[j].join();
28 System.out.println("CAS Random costs time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));
29 }
30
31 public void syncAdd2() throws InterruptedException {
32 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
33 Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_NUM];
34 for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) {
35 threads[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() {
36 public void run() {
37 while (syncI < MAX_VALUE) {
38 synchronized ("syncI") {
39 ++syncI;
40 }
41 try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(new File(path))) {
42 while (in.read() != -1);
43 } catch (IOException e) {
44 e.printStackTrace();
45 }
46 }
47 }
48 });
49 threads[i].start();
50 }
51 for (int j = 0; j < THREAD_NUM; j++)
52 threads[j].join();
53 System.out.println("sync costs time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));
54 }
55 }
在while循环中,增加了一个读取文件内容的操作,该操作大概需要耗时40ms,从而可以减少线程冲突。测试结果如下:
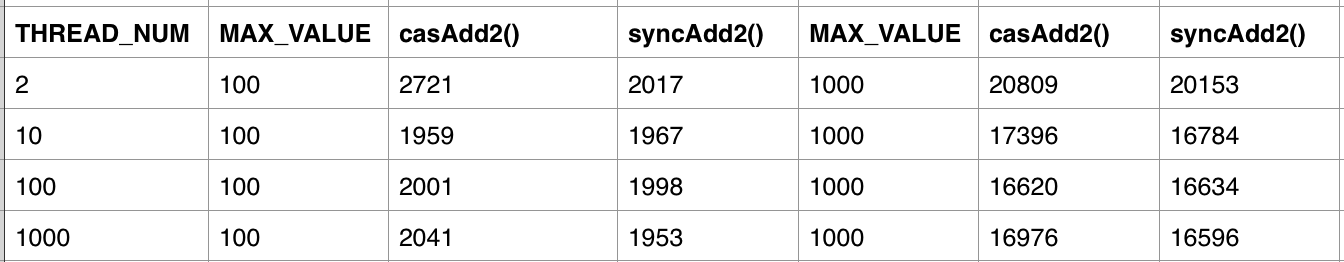
可见在资源冲突比较小的情况下,采用CAS方式和synchronized同步效率差不多。为什么CAS相比synchronized没有获得更高的性能呢?
测试使用的jdk为1.7,而从jdk1.6开始,对锁的实现引入了大量的优化,如锁粗化(Lock Coarsening)、锁消除(Lock Elimination)、轻量级锁(Lightweight Locking)、偏向锁(Biased Locking)、适应性自旋(Adaptive Spinning)等技术来减少锁操作的开销。而其中自旋锁的原理,类似于CAS自旋,甚至比CAS自旋更为优化。具体内容请参考 深入JVM锁机制1-synchronized。
传送门:http://blog.csdn.net/chen77716/article/details/6618779
四、总结
1、使用CAS在线程冲突严重时,会大幅降低程序性能;CAS只适合于线程冲突较少的情况使用。
2、synchronized在jdk1.6之后,已经改进优化。synchronized的底层实现主要依靠Lock-Free的队列,基本思路是自旋后阻塞,竞争切换后继续竞争锁,稍微牺牲了公平性,但获得了高吞吐量。在线程冲突较少的情况下,可以获得和CAS类似的性能;而线程冲突严重的情况下,性能远高于CAS。
