【LeetCode & 剑指offer 刷题笔记】目录(持续更新中...)
68 树中两个节点的最低公共祖先
题目:
求树中两个结点的最低公共祖先
思路:
考虑一下几种情况:
1、该树为二叉搜索树
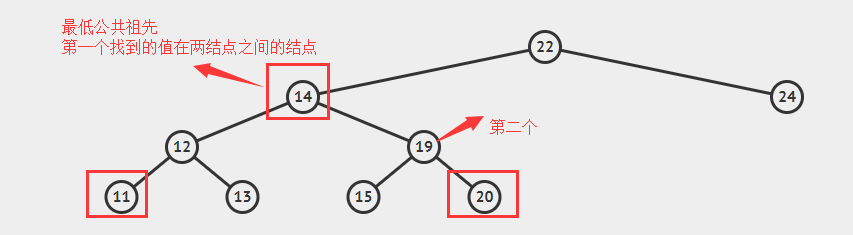
二叉搜索树是排序树,位于左子树点的结点都比父结点小,而位于右子树的结点都比父结点大,只需要从树的根结点开始和两个输入的结点进行比较。
如果当前结点的值比两个结点的值都大,那么最低的公共父结点一定在左子树,下一步就是遍历左子树;
如果当前结点的值比两个结点的值都小,那么最低的公共父结点一定在右子树;下一步就是遍历右子树;
如果当前结点的值介于两个结点的值之间,那么它就是两个结点的公共父结点,第一个找到的就是最低的公共父结点。

235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
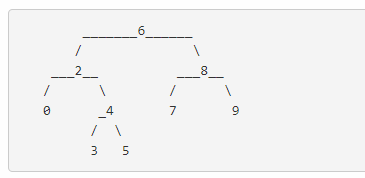
Given binary search tree: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]

Example 1:
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
Output: 6
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6.
Example 2:
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
Output: 2
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself
according to the LCA definition.
Note:
-
All of the nodes' values will be unique.
-
p and q are different and both values will exist in the BST.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
/*
问题:二叉搜索树的最低公共祖先
方法:递归法
如果根节点的值大于p和q之间的较大值,说明p和q都在左子树中,那么此时我们就进入根节点的左子节点继续递归,如果根节点小于p和q之间的较小值,说明p和q都在右子树中,那么此时我们就进入根节点的右子节点继续递归,如果都不是,则说明当前根节点就是最小共同父节点,直接返回即可
*/
class Solution
{
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
{
if (!root) //空结点时返回空
return nullptr;
//从根结点开始递归
if (root->val > max(p->val, q->val)) //如果p,q在当前结点左子树,则对左子树遍历
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
else if (root->val < min(p->val, q->val)) //如果p,q在当前结点右子树,则对右子树遍历
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
else //如果当前结点在p,q之间,则为最低公共父结点(因为从上往下在遍历,故遇到的第一个满足此条件的就是)
return root;
}
};
2、该树为二叉树,结点中有指向父结点的指针
有了父结点,就可以找到任意结点到根结点的路径;因此:
分别找到从两个结点开始到根结点的路径,即两个链表;
然后找到两个链表的第一个公共结点,就是最低的公共父结点;
3、该树为普通的树
从根结点开始,dfs,分别找到到达两个结点的路径;
然后找到两条路径的最后一个公共结点,就是最低的公共父结点;
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
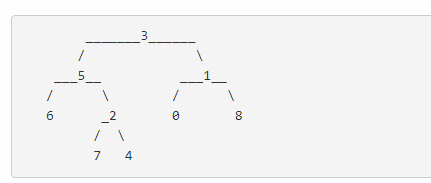
Given the following binary tree: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]

Example 1:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
Output: 3
Explanation: The LCA of of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
Output: 5
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself
according to the LCA definition.
Note:
-
All of the nodes' values will be unique.
-
p and q are different and both values will exist in the binary tree.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
/*
问题:普通二叉树的最低公共祖先
方法:递归法
这道题是普通是二叉树,不是二叉搜索树,所以就不能利用其特有的性质,所以我们只能在二叉树中来搜索p和q,从左右子树中分别找p,q,如果对于某个结点,左右分别有p,q,则说明该结点为最低公共祖先
题目中没有明确说明p和q是否是树中的节点,如果不是,应该返回NULL,而下面的方法就不正确了
不好理解
*/
class Solution
{
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
{
if (root == nullptr || p == root || q == root) //如果p==root或者q==root,说明找到了p和q
return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); //找左子树中是否存在p或q,存在时返回p或q或者p,q的祖先结点,不存在时返回nullptr
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p , q); //找右子树中是否存在p或q
if (left && right) //left和right分别有p或q,则其父结点root为p,q的最低公共祖先
return root;
else
return left ? left : right; //left同时有p,q,则left为公共祖先,(若left为空,则right为公共祖先)
}
};
/*
改进:在找完左子树的共同父节点时如果结果存在,且不是p或q,
那么不用再找右子树了,直接返回这个结果即可,同理,对找完右子树的结果做同样处理,参见代码如下:
*/
class Solution
{
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
{
if (!root || p == root || q == root)
return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
if (left && left != p && left != q) return left; //如果left不为空且不是p或q,则其为公共祖先
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p , q);
if (right && right != p && right != q) return right;
if(left && right) //left和right分别有p或q,则其父结点root为p,q的最低公共祖先
return root;
else
return left ? left : right;
}
};