学习内容
JDBC:
JDBC (Java DataBase Connection) 是通过JAVA访问数据库
1.导包:
前往官网下载mysql连接包
https://www.mysql.com/cn/products/connector

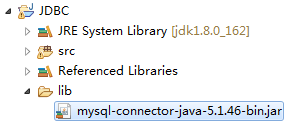
在eclipse新建一个工程,并在工程内新建一个lib文件,将下载好的连接器包解压,找到mysql-connector-java-5.1.46-bin.jar,
将其复制到lib文件夹下,右击jar文件,选择Build Path,Add to Build Path。
2.连接数据库:
(1)初始化驱动
import java.sql.Connection; //用来连接数据库 import java.sql.DriverManager; //驱动 import java.sql.SQLException; //用来捕捉异常 import java.sql.Statement; //用来执行语句 import java.sql.ResultSet; //用来查询 public class TestJDBC { public static void main(String[] args) { try { //初始化驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //Class.forName是把这个类加载到JVM中,加载的时候,就会执行其中的静态初始化块,完成驱动的初始化的相关工作。 }catch(ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
(2)建立连接
import java.sql.Connection; //用来连接数据库 import java.sql.DriverManager; //驱动 import java.sql.SQLException; //用来捕捉异常 import java.sql.Statement; //用来执行语句 import java.sql.ResultSet; //用来查询 public class TestJDBC { public static void main(String[] args) { try { //初始化驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //Class.forName是把这个类加载到JVM中,加载的时候,就会执行其中的静态初始化块,完成驱动的初始化的相关工作。 }catch(ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try(Connection c = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/JDBC?characterEncoding=UTF-8","root","123456"); Statement s = c.createStatement();//使用try-with-resource的方式自动关闭连接 ){ //连接数据库 //"jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/数据库名?characterEncoding=默认字符集","账户名","密码" }catch(SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
(3)关闭连接
上面代码使用的使用try-with-resource的方式自动关闭连接是JDK1.7的特性,之前版本要用finally关闭
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; public class TestJDBC { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection c = null; Statement s = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); c = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/how2java?characterEncoding=UTF-8", "root","admin"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 数据库的连接时有限资源,相关操作结束后,养成关闭数据库的好习惯 // 先关闭Statement if (s != null) try { s.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // 后关闭Connection if (c != null) try { c.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
3.增删改查
import java.sql.Connection; //用来连接数据库
import java.sql.DriverManager; //驱动 import java.sql.SQLException; //用来捕捉异常 import java.sql.Statement; //用来执行语句 import java.sql.ResultSet; //用来查询 public class TestJDBC { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); }catch(ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try( Connection c = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/JDBC?characterEncoding=UTF-8","root","123456"); Statement s = c.createStatement(); ){//Statement是用于执行SQL语句的,比如增加,删除 // 注意: 字符串要用单引号' String sql = "insert into hero values(1,"+"'提莫'"+","+313.0f+","+50+")"; String sql2 = "insert into hero values(2,"+"'盖伦'"+","+405.0f+","+50+")"; String sql3 = "insert into hero values("+3+","+"'剑姬'"+","+315.0f+","+80+")"; String sql4 = "insert into hero values(4,'盲僧',370.0,65)";//增 最简洁,执行无误 String sql5 = "delete from hero where id = 2"; //删 String sql6 = "update hero set damage=65 where id = 1"; //改 String sql7 = "select * from hero"; //查 要把结果返回给ResultSet //s.execute(sql); //s.execute(sql2); //s.execute(sql3); //s.execute(sql4); //s.execute(sql5); //s.execute(sql6); ResultSet rs = s.executeQuery(sql7);//executeQuery返回ResultSet对象集 //int row = s.executeUpdate(sql1);//返回有几条语句受到影响 //System.out.println(row); while(rs.next()) {//遍历rs,next()将光标从当前位置向前移动一行,即从第一行向下移动,返回布尔值 int id = rs.getInt("id");//使用字段名 String name = rs.getString(2);//也可以使用字段顺序,字段顺序基1 float hp = rs.getFloat("hp"); int damage = rs.getInt(4); System.out.printf("%d %s %f %d%n", id, name, hp, damage); } }catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
注意ResultSet的next方法,如果用同一个ResultSet建立两个while循环,第二个while循环并不会从头开始,会从第一个while循环的的下一次开始,这是next方法的特性!
4.注入与PreparedStatement
(1)注入
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.Statement; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.ResultSet; public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_JDBC?characterEncoding=UTF-8"; String user = "root"; String pwd = "123456"; try(Connection c = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd); Statement s = c.createStatement(); ) { String sql = "select * from users where username='张三' and pwd=123456 or 1=1"; //因为1=1恒等,所以即使前面的and语句内用户名和密码不匹配也可以查询到该表的所有内容,有风险 ResultSet rs = s.executeQuery(sql); while(rs.next()) { int id = rs.getInt(1); String username = rs.getString(2); String pwdd = rs.getString(3); System.out.printf("%d %s %s",id,username,pwdd); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
(2)PreparedStatement
预编译语句,可防止注入
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; public class Prepared { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } String sql = "select * from users where username=? and pwd=?";//用占位符?替换查询字段 String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_JDBC?characterEncoding=UTF-8"; String user = "root"; String pwd = "123456"; try(Connection c = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd); PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql); ) { ps.setString(1, "张三");//占位符次序,基1 ps.setString(2, "123456 or 1=1");//查询不出结果,反注入 ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();//不用传参 while(rs.next()) { int id = rs.getInt(1); String username = rs.getString(2); String pwdd = rs.getString(3); System.out.printf("%d %s %s%n",id,username,pwdd); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
5.DAO
DAO=Data Access Object
数据库访问对象 ,就是把数据库相关的操作都封装在这个类里面,其他地方看不到JDBC的代码
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.Statement; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.ResultSet; public class DB {private static Connection conn;
//初始化驱动、建立连接都放在静态代码块内执行 static{ try{ Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_JDBC?characterEncoding=UTF-8"; String username="root"; String password="123456"; conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); }catch(Exception ex){ throw new RuntimeException(ex+"数据库连接失败"); } }
//返回一个Connection对象 public static Connection getConn(){ return conn; }
//多种关闭方法 public static void close(Connection conn,Statement sta,ResultSet rs){ if(rs!=null){ try{ rs.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } if(sta!=null){ try{ sta.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } if(conn!=null){ try{ conn.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } } public static void close(Connection conn,Statement sta){ if(sta!=null){ try{ sta.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } if(conn!=null){ try{ conn.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } } public static void close(Connection conn){ if(conn!=null){ try{ conn.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } } }
应用:简单的商店库存管理系统,具备增删改查功能
Store类内有所有的数据库操作方法,其中增删改功能有操作成功提示以及操作成功后自动显示所有库存的功能:
package edu.jdbc.store; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Store { private int sid; private String brands; private int size; private double price; private int counts; public static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); public int getSid() { return sid; } public void setSid(int sid) { this.sid = sid; } public String getBrands() { return brands; } public void setBrands(String brands) { this.brands = brands; } public int getSize() { return size; } public void setSize(int size) { this.size = size; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public int getCounts() { return counts; } public void setCounts(int counts) { this.counts = counts; } private static Connection c; static{ try{ Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo_JDBC?characterEncoding=UTF-8"; String username="root"; String password="123456"; c=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); }catch(Exception ex){ throw new RuntimeException(ex+"数据库连接失败"); } } public static Connection getConn(){ return c; } public static void close(Connection conn,Statement sta,ResultSet rs){ if(rs!=null){ try{ rs.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } if(sta!=null){ try{ sta.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } if(conn!=null){ try{ conn.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } } public static void close(Connection conn,Statement sta){ if(sta!=null){ try{ sta.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } if(conn!=null){ try{ conn.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } } public static void close(){ if(c!=null){ try{ c.close(); }catch(SQLException ex){} } } public static void select(ArrayList<Store> a) { c = Store.getConn(); String sql = "select * from store"; try(PreparedStatement ps= c.prepareStatement(sql); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();) { while(rs.next()) { Store s = new Store(); s.setSid(rs.getInt("sid")); s.setBrands(rs.getString("brands")); s.setSize(rs.getInt("size")); s.setPrice(rs.getDouble("price")); s.setCounts(rs.getInt("counts")); a.add(s); } System.out.println("商品编号 商品品牌 商品尺寸 商品价格 商品数量"); for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++) { System.out.printf("%d %s %d %f %d%n" ,a.get(i).getSid(),a.get(i).getBrands(),a.get(i).getSize(),a.get(i).getPrice(),a.get(i).getCounts()); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void add(ArrayList<Store> a) { select(a); c = Store.getConn(); String sql = "insert into store values(?,?,?,?,?)"; System.out.println("请输入商品编号:"); int id = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入商品品牌:"); String brands = sc.next(); System.out.println("请输入商品尺寸"); int size = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入商品价格:"); double price = sc.nextDouble(); System.out.println("请输入商品数量:"); int counts= sc.nextInt(); try(PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);){ ps.setInt(1, id); ps.setString(2, brands); ps.setInt(3, size); ps.setDouble(4, price); ps.setInt(5, counts); int j = ps.executeUpdate(); if(j>0) { System.out.println("添加成功!"); select(a); }else { System.out.println("添加失败!"); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void update(ArrayList<Store> a) { select(a); c = Store.getConn(); String sql = "update store set sid= ?,brands= ? , size = ? ,price= ?,counts= ? where sid = ?"; System.out.println("请输入要修改的商品编号:"); int id = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入修改后的商品编号:"); int cid = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入修改后的商品品牌:"); String brands = sc.next(); System.out.println("请输入修改后的商品尺寸"); int size = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入修改后的商品价格:"); double price = sc.nextDouble(); System.out.println("请输入修改后的商品数量:"); int counts= sc.nextInt(); try(PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);){ ps.setInt(1, cid); ps.setString(2, brands); ps.setInt(3, size); ps.setDouble(4, price); ps.setInt(5, counts); ps.setInt(6, id); int j = ps.executeUpdate(); if(j>0) { System.out.println("修改成功!"); select(a); }else { System.out.println("修改失败!"); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void delete(ArrayList<Store> a) { select(a); c = Store.getConn(); String sql = "delete from store where sid = ?"; System.out.println("请输入要删除的商品编号:"); int id = sc.nextInt(); try(PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);){ ps.setInt(1, id); int j = ps.executeUpdate(); if(j>0) { System.out.println("删除成功!"); select(a); }else { System.out.println("删除失败!"); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
StoreApp类继承Store类,直接调用方法即可:
package edu.jdbc.store; import java.util.ArrayList; public class StoreApp extends Store{ public static int show() { System.out.println("------------商城管理系统------------"); System.out.println("1.查询所有商品信息"); System.out.println("2.新增商品信息"); System.out.println("3.修改商品信息"); System.out.println("4.删除商品信息"); System.out.println("5.退出"); System.out.println("请选择功能序号:"); return sc.nextInt(); } public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Store> a = new ArrayList<Store>(); while(true) { switch(show()) { case 1: select(a); break; case 2: add(a); break; case 3: update(a); break; case 4: delete(a); break; case 5: System.out.println("欢迎下次使用!"); sc.close(); Store.close(); return; default: System.out.println("选择有误,请重新选择功能!"); } } } }