1.glog的主要接口如下。
#define LOG(severity) COMPACT_GOOGLE_LOG_ ## severity.stream()
#define SYSLOG(severity) SYSLOG_ ## severity(0).stream()
// Initialize.
GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void InitGoogleLogging(const char* argv0);
// Shutdown
GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void ShutdownGoogleLogging();
// 设置回调接口,如果失败调用接口.
GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void InstallFailureFunction(void (*fail_func)());
// Add or remove a LogSink as a consumer of logging data. Thread-safe. GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void AddLogSink(LogSink *destination); GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void RemoveLogSink(LogSink *destination); //设置日志扩展名称,thread-safe。 GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void SetLogFilenameExtension( const char* filename_extension); // // 设置某种等级的日志标准输出,thread-safe. // GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void SetStderrLogging(LogSeverity min_severity); // // 设置所有的日志标准输出. Thread-safe. // GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void LogToStderr(); // // Make it so that all log messages of at least a particular severity are // logged via email to a list of addresses (in addition to logging to the // usual log file(s)). The list of addresses is just a string containing // the email addresses to send to (separated by spaces, say). Thread-safe. // GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void SetEmailLogging(LogSeverity min_severity, const char* addresses); // A simple function that sends email. dest is a commma-separated // list of addressess. Thread-safe. GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL bool SendEmail(const char *dest, const char *subject, const char *body); GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL const std::vector<std::string>& GetLoggingDirectories(); // For tests only: Clear the internal [cached] list of logging directories to // force a refresh the next time GetLoggingDirectories is called. // Thread-hostile. void TestOnly_ClearLoggingDirectoriesList(); // Returns a set of existing temporary directories, which will be a // subset of the directories returned by GetLogginDirectories(). // Thread-safe. GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void GetExistingTempDirectories( std::vector<std::string>* list); // Print any fatal message again -- useful to call from signal handler // so that the last thing in the output is the fatal message. // Thread-hostile, but a race is unlikely. GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void ReprintFatalMessage(); // Truncate a log file that may be the append-only output of multiple // processes and hence can't simply be renamed/reopened (typically a // stdout/stderr). If the file "path" is > "limit" bytes, copy the // last "keep" bytes to offset 0 and truncate the rest. Since we could // be racing with other writers, this approach has the potential to // lose very small amounts of data. For security, only follow symlinks // if the path is /proc/self/fd/* GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void TruncateLogFile(const char *path, int64 limit, int64 keep); // Truncate stdout and stderr if they are over the value specified by // --max_log_size; keep the final 1MB. This function has the same // race condition as TruncateLogFile. GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL void TruncateStdoutStderr(); // Return the string representation of the provided LogSeverity level. // Thread-safe. GOOGLE_GLOG_DLL_DECL const char* GetLogSeverityName(LogSeverity severity);
使用方法如下:
(1)初始化
(2)logdestination提供文件地址,文件前缀名,输出属性的设置接口。
(3)logmessage提供日志内容的具体输出接口,封装为LOG(…)。
(4)shutdown,析构
2.直接用到的类。
从上述接口分析,我们可以得到我们直接接触到的类和文件。
2.1
LogMessage:This class more or less represents a particular log message. You create an instance of LogMessage and then stream stuff to it. When you finish streaming to it, ~LogMessage is called and the full message gets streamed to the appropriate destination.从日志中我们可以看出,日志信息的输出主要看这个类,创建LogMessage的实例,获得数据流,结束后,调用析构函数~LogMessage(),然后stream流向目的文件。
LogMessage的主要成员说明,由于一些参数太长我就省略掉了,大家可以参考具体的文档。
| LogMessage |
|
Public: class LogStream : public std::ostream //流 LogMessage(***);//构造函数 ~LogMessage();//析构函数 void Flush(); void SendToLog(); void SendToSyslogAndLog(); static void __declspec(noreturn) Fail(); std::ostream& stream(); |
|
Private: void SendToSinkAndLog(); void SendToSink(); void WriteToStringAndLog(); void SaveOrSendToLog(); void Init(……); LogMessageData* allocated_; LogMessageData* data_; friend class LogDestination; LogMessage(const LogMessage&); void operator=(const LogMessage&); |
日志内容的具体输出接口为LOG(***);其实是LogMessage封装后的接口,##起到连接的作用。 LOG(INFO) << str;其实替换过去就是COMPACT_GOOGLE_LOG_INFO.stream()<<str;最终调用的还是LogMessage的构造函数。
1 #define LOG(severity) COMPACT_GOOGLE_LOG_ ## severity.stream() 2 #define SYSLOG(severity) SYSLOG_ ## severity(0).stream() 3 4 #if GOOGLE_STRIP_LOG == 0 5 #define COMPACT_GOOGLE_LOG_INFO google::LogMessage( 6 __FILE__, __LINE__) 7 #define LOG_TO_STRING_INFO(message) google::LogMessage( 8 __FILE__, __LINE__, google::GLOG_INFO, message) 9 #else 10 #define COMPACT_GOOGLE_LOG_INFO google::NullStream() 11 #define LOG_TO_STRING_INFO(message) google::NullStream() 12 #endif
下面我们看看构造函数的内容,就是初始化了一些东西,文件名称,Log等级,行号等参数。
1 LogMessage::LogMessage(const char* file, int line) 2 : allocated_(NULL) { 3 Init(file, line, GLOG_INFO, &LogMessage::SendToLog); 4 } 5 6 void LogMessage::Init(const char* file,int line,LogSeverity severity,void (LogMessage::*send_method)()) {/*do something*/ }
析构函数:
1 LogMessage::~LogMessage() { 2 Flush();//写数据 3 } 4 // Flush buffered message, called by the destructor, or any other function 5 // that needs to synchronize the log. 6 void LogMessage::Flush() {/*flush*/}
LogMessage中有一个友类,LogDestination,接下来我们看一下这个类。
2.2
LogDestination
| LogDestination |
|
Public: friend class LogMessage; friend void ReprintFatalMessage(); friend base::Logger* base::GetLogger(LogSeverity); friend void base::SetLogger(LogSeverity, base::Logger*); static void SetLogDestination(LogSeverity severity, const char* base_filename); static void SetLogSymlink(LogSeverity severity, const char* symlink_basename); static void AddLogSink(LogSink *destination); static void RemoveLogSink(LogSink *destination); static void SetLogFilenameExtension(const char* filename_extension); static void SetStderrLogging(LogSeverity min_severity); static void SetEmailLogging(LogSeverity min_severity, const char* addresses); static void LogToStderr(); static void FlushLogFiles(int min_severity); static void FlushLogFilesUnsafe(int min_severity); static const int kNetworkBytes = 1400; static const string& hostname(); static const bool& terminal_supports_color(); static void DeleteLogDestinations(); |
|
Private: LogDestination(LogSeverity severity, const char* base_filename); ~LogDestination() { } static vector<LogSink*>* sinks_; static Mutex sink_mutex_; LogDestination(const LogDestination&); LogDestination& operator=(const LogDestination&); |
LogDestination主要提供了日志文件的名称设置接口和日志的书写方式。我们看个例子:
SetLogFilenameExtension:文件后缀名设置
效果如图
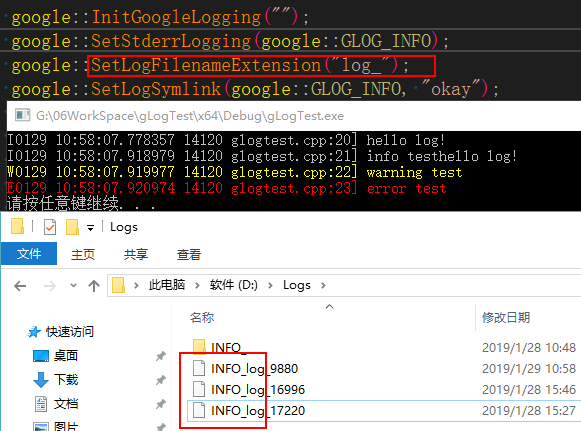
具体代码:
1 inline void LogDestination::SetLogFilenameExtension(const char* ext) { 2 // Prevent any subtle race conditions by wrapping a mutex lock around 3 // all this stuff. 4 MutexLock l(&log_mutex); 5 for ( int severity = 0; severity < NUM_SEVERITIES; ++severity ) { 6 log_destination(severity)->fileobject_.SetExtension(ext); 7 } 8 }
而SetExtension来自类LogFileObject,此处先不展开。我们看setExtension
1 /* 2 string filename_extension_; // option users can specify (eg to add port#) 3 */ 4 void LogFileObject::SetExtension(const char* ext) { 5 MutexLock l(&lock_); 6 if (filename_extension_ != ext) { 7 // Get rid of old log file since we are changing names 8 if (file_ != NULL) { 9 fclose(file_); 10 file_ = NULL; 11 rollover_attempt_ = kRolloverAttemptFrequency-1; 12 } 13 filename_extension_ = ext; 14 } 15 }
可以看出LogDestination其实只是一个壳,负责和LogMessage以及其他的一些类进行互动。真正实现还得看LogFileObject类。
2.3
LogFileObject
| LogFileObject : public base::Logger |
|
LogFileObject(LogSeverity severity, const char* base_filename);
|
| Mutex lock_; bool base_filename_selected_; string base_filename_; string symlink_basename_; string filename_extension_; // option users can specify (eg to add port#) FILE* file_; LogSeverity severity_; uint32 bytes_since_flush_; uint32 dropped_mem_length_; uint32 file_length_; unsigned int rollover_attempt_; int64 next_flush_time_; |
关于这个类,我们看一个函数:
1 void LogFileObject::Write(bool force_flush, 2 time_t timestamp, 3 const char* message, 4 int message_len) { 5 MutexLock l(&lock_); 6 7 //条件判断,不符合直接return 8 if (base_filename_selected_ && base_filename_.empty()) { 9 return; 10 } 11 12 13 if (base_filename_selected_) 14 { 15 /*如果没有创建日志文件,return*/ 16 if (!CreateLogfile(time_pid_string)) { 17 perror("Could not create log file"); 18 fprintf(stderr, "COULD NOT CREATE LOGFILE '%s'! ", 19 time_pid_string.c_str()); 20 return; 21 } 22 } 23 else 24 { 25 ostringstream file_header_stream; 26 file_header_stream.fill('0'); 27 28 file_header_stream << "Log file created at: " 29 << 1900+tm_time.tm_year << '/' 30 << setw(2) << 1+tm_time.tm_mon << '/' 31 << setw(2) << tm_time.tm_mday 32 << ' ' 33 << setw(2) << tm_time.tm_hour << ':' 34 << setw(2) << tm_time.tm_min << ':' 35 << setw(2) << tm_time.tm_sec << ' ' 36 << "Running on machine: " 37 << LogDestination::hostname() << ' ' 38 << "Log line format: [IWEF]mmdd hh:mm:ss.uuuuuu " 39 << "threadid file:line] msg" << ' '; 40 const string& file_header_string = file_header_stream.str(); 41 42 const int header_len = file_header_string.size(); 43 fwrite(file_header_string.data(), 1, header_len, file_); 44 file_length_ += header_len; 45 bytes_since_flush_ += header_len; 46 } 47 /*写满了怎么办?*/ 48 // Write to LOG file 49 if ( !stop_writing ) { 50 // fwrite() doesn't return an error when the disk is full, for 51 // messages that are less than 4096 bytes. When the disk is full, 52 // it returns the message length for messages that are less than 53 // 4096 bytes. fwrite() returns 4096 for message lengths that are 54 // greater than 4096, thereby indicating an error. 55 errno = 0; 56 fwrite(message, 1, message_len, file_); 57 if ( FLAGS_stop_logging_if_full_disk && 58 errno == ENOSPC ) { // disk full, stop writing to disk 59 stop_writing = true; // until the disk is 60 return; 61 } else { 62 file_length_ += message_len; 63 bytes_since_flush_ += message_len; 64 } 65 } 66 else { 67 if ( CycleClock_Now() >= next_flush_time_ ) 68 stop_writing = false; // check to see if disk has free space. 69 return; // no need to flush 70 } 71 /*do otherthings*/ 72 }
对应的就是以下内容
Log file created at: 2019/01/28 15:27:56
Running on machine: HostName
Log line format: [IWEF]mmdd hh:mm:ss.uuuuuu threadid file:line] msg
I0128 15:27:56.937649 16208 glogtest.cpp:20] hello log!
I0128 15:27:56.958592 16208 glogtest.cpp:21] info testhello log!
W0128 15:27:56.958592 16208 glogtest.cpp:22] warning test
E0128 15:27:56.958592 16208 glogtest.cpp:23] error test
我们再看一个函数:可以看出这个函数的功能就是创建文件名称。如果我们可以修改time_pid_string这个值,或者直接修改string_filename的值,就可以直接修改文件的名字,因为原始的名字真的是太长了,而且不便查找。
1 bool LogFileObject::CreateLogfile(const string& time_pid_string) { 2 string string_filename = base_filename_+filename_extension_+ 3 time_pid_string; 4 const char* filename = string_filename.c_str(); 5 int fd = open(filename, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, FLAGS_logfile_mode); 6 if (fd == -1) return false; 7 #ifdef HAVE_FCNTL 8 // Mark the file close-on-exec. We don't really care if this fails 9 fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC); 10 #endif 11 12 file_ = fdopen(fd, "a"); // Make a FILE*. 13 if (file_ == NULL) { // Man, we're screwed! 14 close(fd); 15 unlink(filename); // Erase the half-baked evidence: an unusable log file 16 return false; 17 } 18 19 // We try to create a symlink called <program_name>.<severity>, 20 // which is easier to use. (Every time we create a new logfile, 21 // we destroy the old symlink and create a new one, so it always 22 // points to the latest logfile.) If it fails, we're sad but it's 23 // no error. 24 /*do something*/ 25 26 return true; // Everything worked 27 }
3.太深了……写不动了
参考网站:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianyajuanke/archive/2013/02/22/2921850.html