TVMC介绍
TVMC,是TVM的命令行驱动程序,TVMC是一种通过命令行界面公开TVM功能的工具,例如uto-tuning/compiling/profiling和通过命令行接口运行模型
在完成本节内容后,将使用 TVMC 来完成以下任务:
为 TVM 运行时编译预训练 ResNet-50 v2 模型。
通过编译后的模型运行真实图像,并解释输出和模型的性能。
使用 TVM 在 CPU 上调优模型。
使用 TVM 收集的调优数据重新编译优化模型。
通过优化后的模型运行图像,并比较输出和模型的性能。
可通过ython -m tvm.driver.tvmc 访问命令行驱动功能,但为方便使用,这里对它进行了重命名
修改别名:
alias tvmc='python3 -m tvm.driver.tvmc'
通过tvmc --help查看命令帮助:
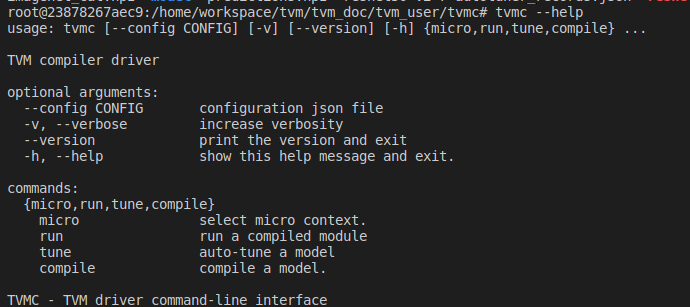
可看到,tvmc可用的TVM的主要功能来自子命令compile和run,以及tune,可使用tvmc <subcommand> --help查看详细使用
获得模型
ResNet-50 是卷积神经网络,有 50 层深度,设计用于图像分类。将使用的模型已经在超过一百万张图片上进行了预训练,有 1000 种不同的分类。该网络输入图像大小为 224x224。
wget https://github.com/onnx/models/raw/b9a54e89508f101a1611cd64f4ef56b9cb62c7cf/vision/classification/resnet/model/resnet50-v2-7.onnx
可通过https://netron.app/ 对onnx模型进行可视化展示:
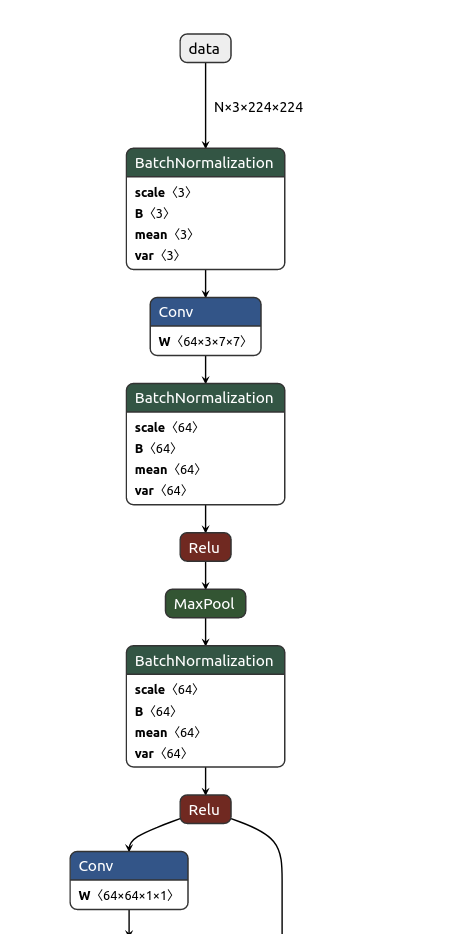
Compiling an ONNX Model to the TVM Runtime
拿到ResNet-50 模型后,就可以开始编译它,为了完成编译,我们需要使用tvmc compile。从编译过程中得到的输出是模型的 TAR 包,它被编译成目标平台的动态库。可以使用 TVM 运行时在目标设备上运行该模型。
tvmc compile \
--target "llvm" \
--input-shapes "data:[1,3,224,224]" \
--output resnet50-v2-7-tvm.tar \
resnet50-v2-7.onnx
我们对生成的resnet50-v2-7-tvm.tar 包进行解压,可看到里面主要有三个文件:
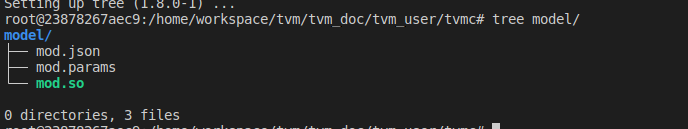
- mod.so 是模型,表示为 C++ 库,可以被 TVM 运行时加载。
- mod.json 是 TVM Relay 计算图的文本表示。
- mod.params 是包含预训练模型参数的文件。
Running the Model from The Compiled Module with TVMC
上面已经将模型编译成了模块,便可使用tvm runtime使用它进行预测。
TVMC 内置了 TVM runtime,允许使用已编译的 TVM 模型。要使用 TVMC 运行模型并进行预测,我们需要两件事:
-
- 编译好的模块,这个刚刚已处理过了
-
- 要对其进行预测的模型的有效输入。
当涉及到预期的张量形状、格式和数据类型时,每个模型都很独特的。因此,大多数模型需要一些预处理和后处理,以确保输入有效并解释输出。TVMC采用NumPy的.npz格式进行输入和输出数据。这是一种支持良好的NumPy格式,用于将多个数组序列化为一个文件。
Input pre-processing
对于 ResNet-50 v2 模型,预期输入是 ImageNet 格式的。下面是为 ResNet-50 v2 预处理图像的脚本例子。
#!python ./preprocess.py
from tvm.contrib.download import download_testdata
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
img_url = "https://s3.amazonaws.com/model-server/inputs/kitten.jpg"
img_path = download_testdata(img_url, "imagenet_cat.png", module="data")
# Resize it to 224x224
resized_image = Image.open(img_path).resize((224, 224))
img_data = np.asarray(resized_image).astype("float32")
# ONNX expects NCHW input, so convert the array
img_data = np.transpose(img_data, (2, 0, 1))
# Normalize according to ImageNet
imagenet_mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
imagenet_stddev = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
norm_img_data = np.zeros(img_data.shape).astype("float32")
for i in range(img_data.shape[0]):
norm_img_data[i, :, :] = (img_data[i, :, :] / 255 - imagenet_mean[i]) / imagenet_stddev[i]
# Add batch dimension
img_data = np.expand_dims(norm_img_data, axis=0)
# Save to .npz (outputs imagenet_cat.npz)
np.savez("imagenet_cat", data=img_data)
Running the Compiled Module
有了模型与数据,便可使用TVMC做预测了
tvmc run \
--inputs imagenet_cat.npz \
--output predictions.npz \
resnet50-v2-7-tvm.tar
.tar 模型文件包括 C++ 库,Relay 模型的描述,以及模型的参数。TVMC包含了TVM runtime,它可以加载模型并根据输入做预测。当运行上述命令时,TVMC 会输出新文件predictions.npz,其中包含 NumPy 格式的模型输出张量。
Output Post-Processing
在我们的例子中,我们需要运行一些后处理,使用为模型提供的查找表将ResNet-50 v2的输出呈现为更人性化的形式。
下面的脚本显示了从已编译模块的输出中提取标签的后处理示例。
#!python ./postprocess.py
import os.path
import numpy as np
from scipy.special import softmax
from tvm.contrib.download import download_testdata
# Download a list of labels
labels_url = "https://s3.amazonaws.com/onnx-model-zoo/synset.txt"
labels_path = download_testdata(labels_url, "synset.txt", module="data")
with open(labels_path, "r") as f:
labels = [l.rstrip() for l in f]
output_file = "predictions.npz"
# Open the output and read the output tensor
if os.path.exists(output_file):
with np.load(output_file) as data:
scores = softmax(data["output_0"])
scores = np.squeeze(scores)
ranks = np.argsort(scores)[::-1]
for rank in ranks[0:5]:
print("class='%s' with probability=%f" % (labels[rank], scores[rank]))
运行结果:
class = 'n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probabilty = 0.621104
class = 'n02123159 tiger cat' with probabilty = 0.356378
class = 'n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probabilty = 0.019712
class = 'n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probabilty = 0.001215
class = 'n04040759 radiator' with probabilty = 0.000262
Automatically Tuning the ResNet Model
之前编译好的模型可运行在TVM runtime上,但它并没有包含任何特定平台的优化。在本节中,将展示如何使用 TVMC 建立针对你工作平台的优化模型。
在某些情况下,使用编译的模块运行推理时,我们可能无法获得预期的性能。在这种情况下,我们可以利用auto-tuner,为我们的模型找到更好的配置,并提高性能。在 TVM 中进行Tuning 是指优化模型以在给定目标上更快地运行的过程。这与训练或微调的不同之处在于,它不会影响模型的准确性,而只影响运行时性能。作为调整过程的一部分,TVM 将尝试运行许多不同的算子实现变体,以验证哪种性能最佳。这些运行的结果存储在优化记录文件中,该文件最终是 tune 子命令的输出。
在最简单的形式中,tuning需要提供三件事:
- 打算在其上运行此模型的设备的目标规格
- 最后将在其中存储tune记录的输出文件的路径
- 一个要调优的模型路径
首先需要安装xgboost和cloudpickle
xgboost: The default search algorithm requires xgboost, see below for further
cloudpickle 库进行数据的序列化和反序列化
pip install xgboost cloudpickle
接下来,开始运行:
tvmc tune \
--target "llvm" \
--input-shapes "data:[1,3,224,224]" \
--output resnet50-v2-7-autotuner_records.json \
resnet50-v2-7.onnx
运行结果如下:
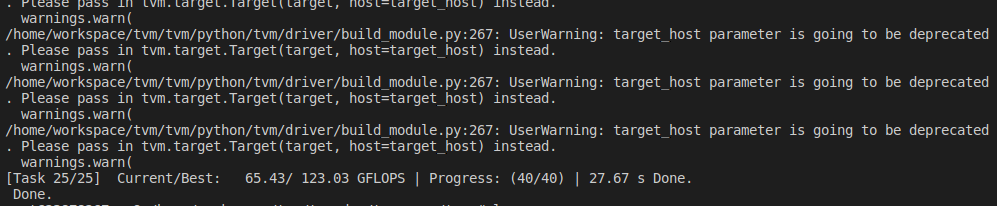
Compiling an Optimized Model with Tuning Data
经过上面的调优操作,获得了调优记录保存在resnet50-v2-7-autotuner_records.json中,这个文件有两种用途:
- 作为进一步调优的输入(通过vmc tune --tuning-records)
- 作为编译的输入
编译器将使用结果为指定目标上的模型生成高性能代码。为此,我们可以使用tvmc compile --tuning-records,可通过tvmc compile --help获取更多信息
现在已经收集了模型的调优数据,我们可以使用优化的运算符重新编译模型,以加快计算速度。
tvmc compile \
--target "llvm" \
--input-shapes "data:[1,3,224,224]" \
--tuning-records resnet50-v2-7-autotuner_records.json \
--output resnet50-v2-7-tvm_autotuned.tar \
resnet50-v2-7.onnx
验证优化后的模型,并通过前面的postprocess.py就脚本进行验证
tvmc run \
--inputs imagenet_cat.npz \
--output predictions.npz \
resnet50-v2-7-tvm_autotuned.tar
运行结果如下:
class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.621103
class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.356379
class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019712
class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001215
class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000262
Comparing the Tuned and Untuned Models
优化后的模型:
tvmc run \
--inputs imagenet_cat.npz \
--output predictions.npz \
--print-time \
--repeat 100 \
resnet50-v2-7-tvm_autotuned.tar
结果:
Execution time summary:
mean (ms) median (ms) max (ms) min (ms) std (ms)
39.6959 39.4101 49.5312 37.6119 1.4940
优化前的模型:
tvmc run \
--inputs imagenet_cat.npz \
--output predictions.npz \
--print-time \
--repeat 100 \
resnet50-v2-7-tvm.tar
结果:
Execution time summary:
mean (ms) median (ms) max (ms) min (ms) std (ms)
46.6606 46.5010 59.2688 43.4401 1.8296
优化后的模型,的确提升了不少,但也并没有想示例中提升47%恐怖的提升,也许是各自运行环境的问题,总的来说,TVMC优化后的模型,预测的精准度几乎没有变化,运行时间缩短了不少
参考:https://tvm.apache.org/docs/tutorial/tvmc_command_line_driver.html