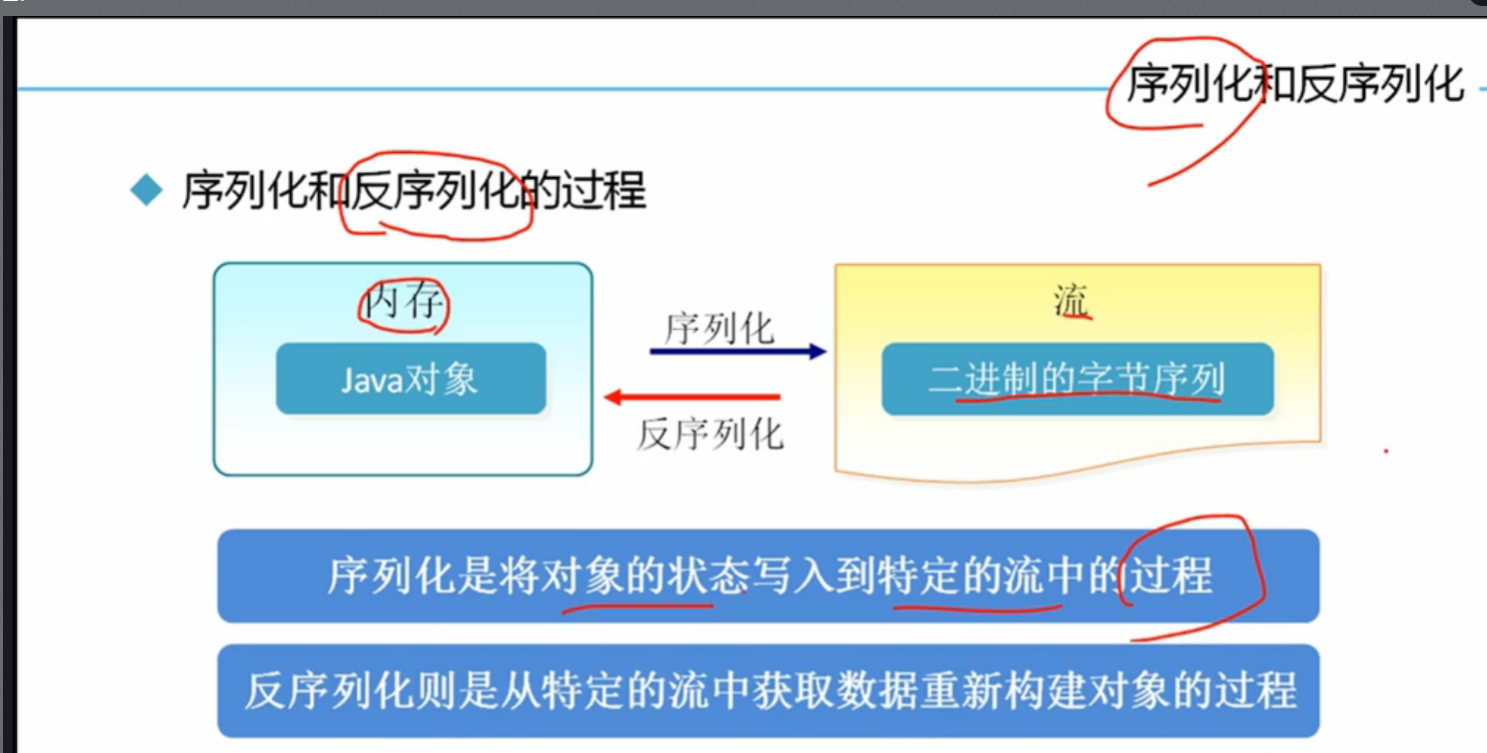
序列化是将对象的状态写入到特定的流的过程
反序列化则是从特定的流中获取数据重新构建对象的过程
使用集合保存对象,可以将集合中的所有对象序列化
//创建上student类
package xulie;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class student implements Serializable {
// 学生的姓名
public String nameString;
// 学生的年龄
public int Age;
// 学生的性别
public String Sex;
public student(String namString, int age, String sex) {
this.nameString = namString;
this.Age = age;
this.Sex = sex;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("学生 的姓名" + nameString + " 学生的年龄" + Age + "学生的性别"
+ Sex);
}
}
//序列化的的代码 和反序列化
package xulie;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个序列化 的 学生对象
student stu = new student("呵呵", 12, "男");
// 创建一个对象输出流
FileOutputStream file = null;
ObjectOutputStream out = null;
// 创建对象输入流
FileInputStream file1 = null;
ObjectInputStream out1 = null;
try {
file = new FileOutputStream("F:\java IO\序列化和反序列化\新建文本文档.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
out = new ObjectOutputStream(file);
out.writeObject(stu);
System.err.println("创建成功");
file1 = new FileInputStream("F:\java IO\序列化和反序列化\新建文本文档.txt");
out1 = new ObjectInputStream(file1);
try {
student s2 = (student) out1.readObject();
System.err.println(s2.Age + "" + s2.nameString + "" + s2.Sex);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
实现接口 Serializable 这个接口
transient 可以不用序列化