dhttp://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/6083427.html
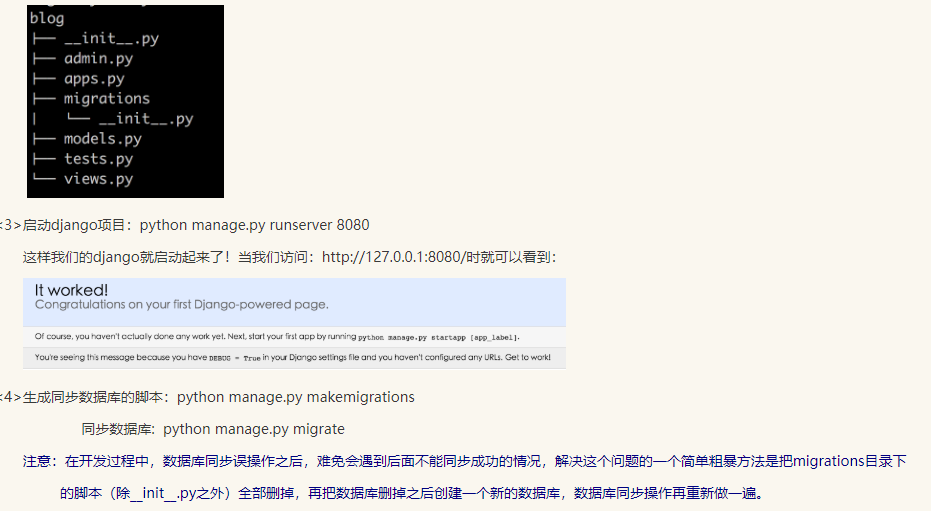
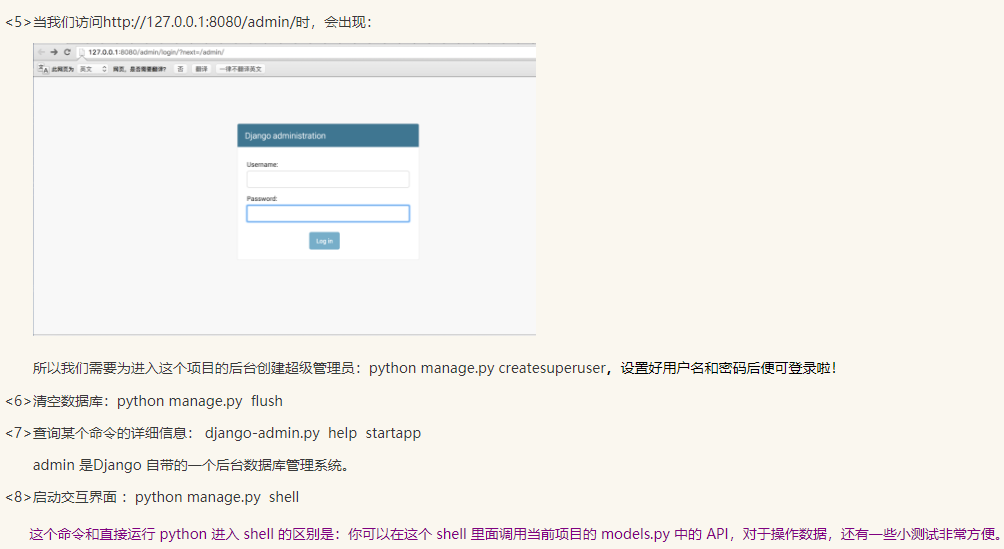
django #安装: pip3 install django 添加环境变量 #1 创建project django-admin startproject mysite ---mysite ---settings.py ---url.py ---wsgi.py ---- manage.py(启动文件) #2 创建APP python mannage.py startapp app01 #3 settings配置 TEMPLATES STATICFILES_DIRS=( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,"statics"), ) STATIC_URL = '/static/' # 我们只能用 STATIC_URL,但STATIC_URL会按着你的STATICFILES_DIRS去找#4 根据需求设计代码 url.py view.py #5 使用模版 render(req,"index.html") #6 启动项目 python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8090 #7 连接数据库,操作数据 model.py


提交数据展示
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>创建个人信息</h1> <form action="/userInfor/" method="post"> <p>姓名<input type="text" name="username"></p> <p>性别<input type="text" name="sex"></p> <p>邮箱<input type="text" name="email"></p> <p><input type="submit" value="submit"></p> </form> <hr> <h1>信息展示</h1> <table border="1"> <tr> <td>姓名</td> <td>性别</td> <td>邮箱</td> </tr> {% for i in info_list %} <tr> <td>{{ i.username }}</td> <td>{{ i.sex }}</td> <td>{{ i.email }}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </table> </body> </html> -----------------------url.py--------------------------------------- url(r'^userInfor/', views.userInfor) -----------------------views.py-------------------------------------- info_list=[] def userInfor(req): if req.method=="POST": username=req.POST.get("username",None) sex=req.POST.get("sex",None) email=req.POST.get("email",None) info={"username":username,"sex":sex,"email":email} info_list.append(info) return render(req,"userInfor.html",{"info_list":info_list})
提交数据展示----数据库
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>创建个人信息</h1> <form action="/userInfor/" method="post"> <p>姓名<input type="text" name="username"></p> <p>性别<input type="text" name="sex"></p> <p>邮箱<input type="text" name="email"></p> <p><input type="submit" value="submit"></p> </form> <hr> <h1>信息展示</h1> <table border="1"> <tr> <td>姓名</td> <td>性别</td> <td>邮箱</td> </tr> {% for i in info_list %} <tr> <td>{{ i.username }}</td> <td>{{ i.sex }}</td> <td>{{ i.email }}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </table> </body> </html> ----------------------------------------------models.py from django.db import models # Create your models here. class UserInfor(models.Model): username=models.CharField(max_length=64) sex=models.CharField(max_length=64) email=models.CharField(max_length=64) ----------------------------------------------views.py from django.shortcuts import render from app01 import models # Create your views here. def userInfor(req): if req.method=="POST": u=req.POST.get("username",None) s=req.POST.get("sex",None) e=req.POST.get("email",None) #---------表中插入数据方式一 # info={"username":u,"sex":e,"email":e} # models.UserInfor.objects.create(**info) #---------表中插入数据方式二 models.UserInfor.objects.create( username=u, sex=s, email=e ) info_list=models.UserInfor.objects.all() return render(req,"userInfor.html",{"info_list":info_list}) return render(req,"userInfor.html")
一、概述:(django静态文件配置) #静态文件交由Web服务器处理,Django本身不处理静态文件。简单的处理逻辑如下(以nginx为例): # URI请求-----> 按照Web服务器里面的配置规则先处理,以nginx为例,主要求配置在nginx. #conf里的location |---------->如果是静态文件,则由nginx直接处理 |---------->如果不是则交由Django处理,Django根据urls.py里面的规则进行匹配 # 以上是部署到Web服务器后的处理方式,为了便于开发,Django提供了在开发环境的对静态文件的处理机制,方法是这样: #1、在INSTALLED_APPS里面加入'django.contrib.staticfiles', #2、在urls.py里面加入 if settings.DEBUG: urlpatterns += patterns('', url(r'^media/(?P<path>.*)$', 'django.views.static.serve', {'document_root': settings.MEDIA_ROOT }), url(r'^static/(?P<path>.*)$', 'django.views.static.serve',{'document_root':settings.STATIC_ROOT}), ) # 3、这样就可以在开发阶段直接使用静态文件了。 二、MEDIA_ROOT和MEDIA_URL #而静态文件的处理又包括STATIC和MEDIA两类,这往往容易混淆,在Django里面是这样定义的: #MEDIA:指用户上传的文件,比如在Model里面的FileFIeld,ImageField上传的文件。如果你定义 #MEDIA_ROOT=c: empmedia,那么File=models.FileField(upload_to="abc/")#,上传的文件就会被保存到c: empmediaabc #eg: class blog(models.Model): Title=models.charField(max_length=64) Photo=models.ImageField(upload_to="photo") # 上传的图片就上传到c: empmediaphoto,而在模板中要显示该文件,则在这样写 #在settings里面设置的MEDIA_ROOT必须是本地路径的绝对路径,一般是这样写: BASE_DIR= os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) MEDIA_ROOT=os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'media/').replace('\','/') #MEDIA_URL是指从浏览器访问时的地址前缀,举个例子: MEDIA_ROOT=c: empmediaphoto MEDIA_URL="/data/" #在开发阶段,media的处理由django处理: # 访问http://localhost/data/abc/a.png就是访问c: empmediaphotoabca.png # 在模板里面这样写<img src="{{MEDIA_URL}}abc/a.png"> # 在部署阶段最大的不同在于你必须让web服务器来处理media文件,因此你必须在web服务器中配置, # 以便能让web服务器能访问media文件 # 以nginx为例,可以在nginx.conf里面这样: location ~/media/{ root/temp/ break; } # 具体可以参考如何在nginx部署django的资料。 三、STATIC_ROOT和STATIC_URL、 STATIC主要指的是如css,js,images这样文件,在settings里面可以配置STATIC_ROOT和STATIC_URL, 配置方式与MEDIA_ROOT是一样的,但是要注意 #STATIC文件一般保存在以下位置: #1、STATIC_ROOT:在settings里面设置,一般用来放一些公共的js,css,images等。 #2、app的static文件夹,在每个app所在文夹均可以建立一个static文件夹,然后当运行collectstatic时, # Django会遍历INSTALL_APPS里面所有app的static文件夹,将里面所有的文件复制到STATIC_ROOT。因此, # 如果你要建立可复用的app,那么你要将该app所需要的静态文件放在static文件夹中。 # 也就是说一个项目引用了很多app,那么这个项目所需要的css,images等静态文件是分散在各个app的static文件的,比 # 较典型的是admin应用。当你要发布时,需要将这些分散的static文件收集到一个地方就是STATIC_ROOT。 #3、STATIC文件还可以配置STATICFILES_DIRS,指定额外的静态文件存储位置。 # STATIC_URL的含义与MEDIA_URL类似。 # ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- #注意1: #为了后端的更改不会影响前端的引入,避免造成前端大量修改 STATIC_URL = '/static/' #引用名 STATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,"statics") #实际名 ,即实际文件夹的名字 ) #django对引用名和实际名进行映射,引用时,只能按照引用名来,不能按实际名去找 #<script src="/statics/jquery-3.1.1.js"></script> #------error-----不能直接用,必须用STATIC_URL = '/static/': #<script src="/static/jquery-3.1.1.js"></script> #注意2(statics文件夹写在不同的app下,静态文件的调用): STATIC_URL = '/static/' STATICFILES_DIRS=( ('hello',os.path.join(BASE_DIR,"app01","statics")) , ) #<script src="/static/hello/jquery-1.8.2.min.js"></script> #注意3: STATIC_URL = '/static/' {% load staticfiles %} # <script src={% static "jquery-1.8.2.min.js" %}></script>
其他文件配置
APPEND_SLASH Default: True When set to True, if the request URL does not match any of the patterns in the URLconf and it doesn’t end in a slash, an HTTP redirect is issued to the same URL with a slash appended. Note that the redirect may cause any data submitted in a POST request to be lost.