package UDP;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.util.Scanner;
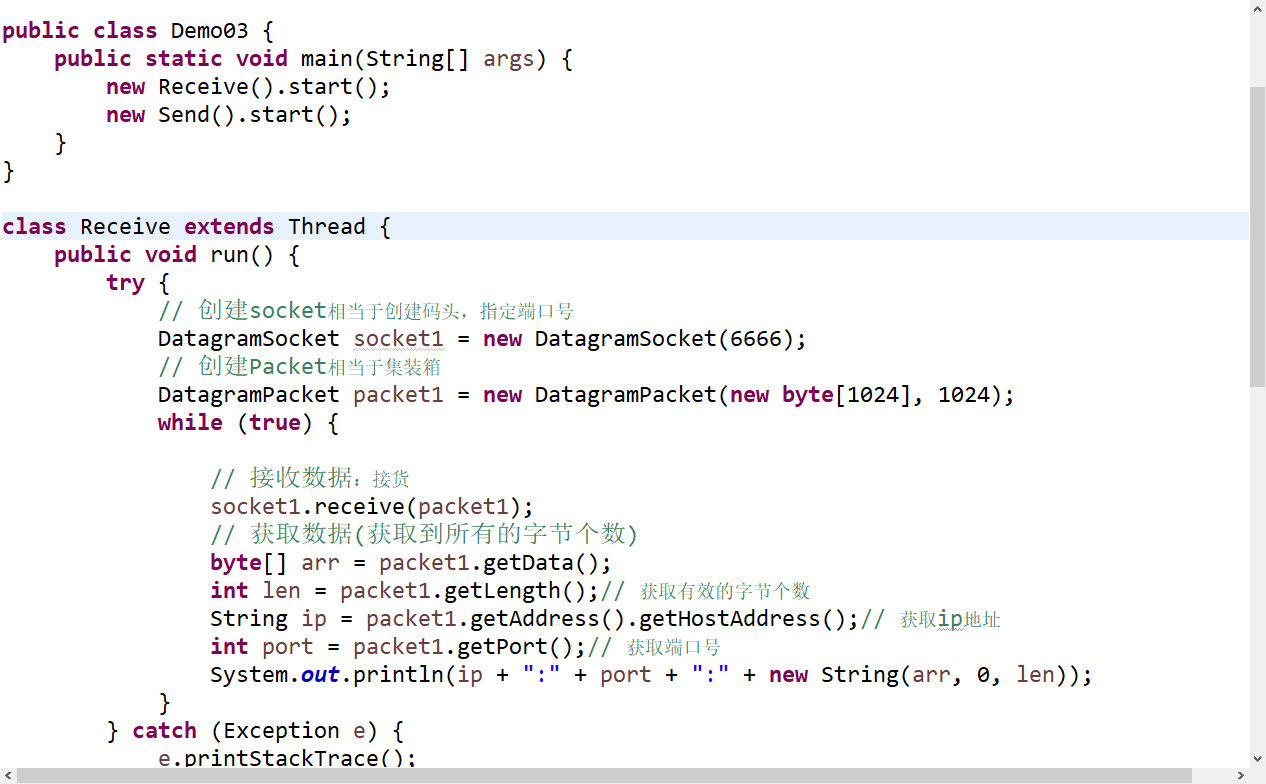
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Receive().start();
new Send().start();
}
}
class Receive extends Thread {
public void run() {
try {
// 创建socket相当于创建码头,指定端口号
DatagramSocket socket1 = new DatagramSocket(6666);
// 创建Packet相当于集装箱
DatagramPacket packet1 = new DatagramPacket(new byte[1024], 1024);
while (true) {
// 接收数据:接货
socket1.receive(packet1);
// 获取数据(获取到所有的字节个数)
byte[] arr = packet1.getData();
int len = packet1.getLength();// 获取有效的字节个数
String ip = packet1.getAddress().getHostAddress();// 获取ip地址
int port = packet1.getPort();// 获取端口号
System.out.println(ip + ":" + port + ":" + new String(arr, 0, len));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
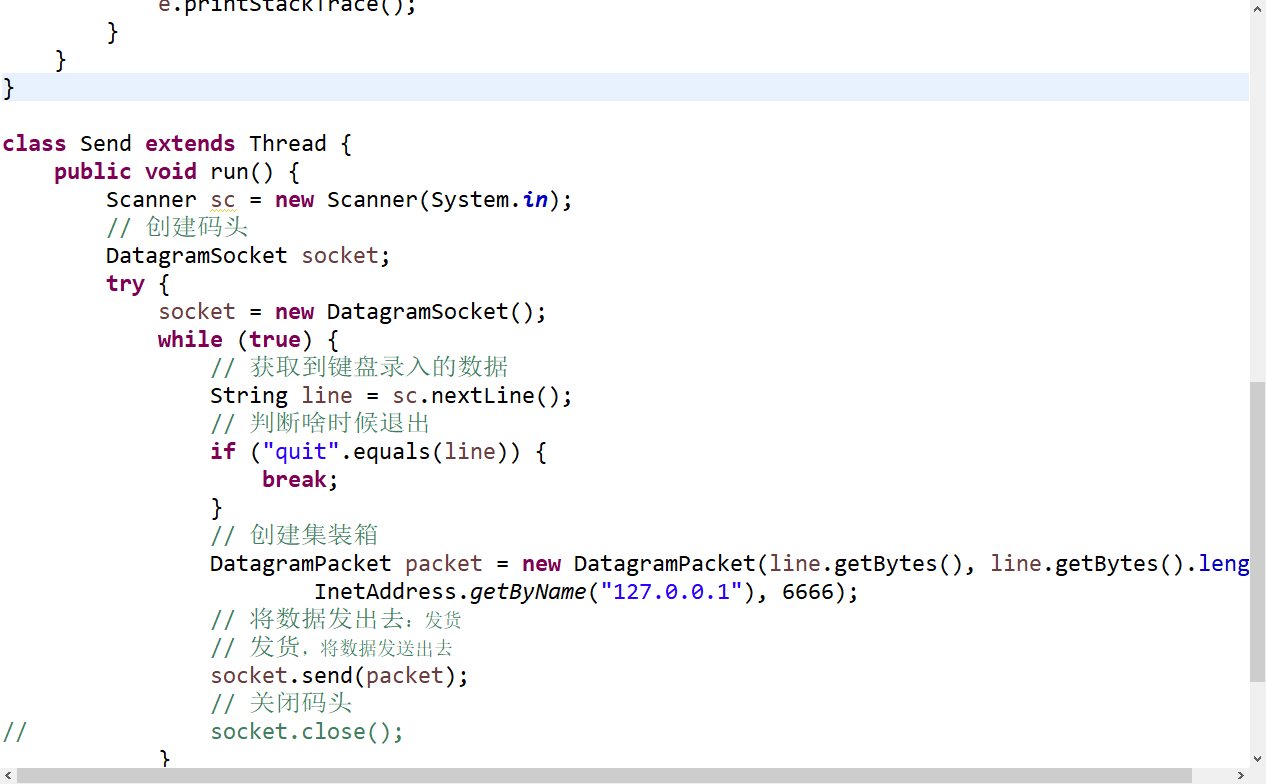
class Send extends Thread {
public void run() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 创建码头
DatagramSocket socket;
try {
socket = new DatagramSocket();
while (true) {
// 获取到键盘录入的数据
String line = sc.nextLine();
// 判断啥时候退出
if ("quit".equals(line)) {
break;
}
// 创建集装箱
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(line.getBytes(), line.getBytes().length,
InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 6666);
// 将数据发出去:发货
// 发货,将数据发送出去
socket.send(packet);
// 关闭码头
// socket.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}