####Python的字符串###
1.字符串的特性
(1)索引:0,1,2,3,4 索引值是从0开始的
类似于,找出字符串里的某一个字符
示例:
s = 'hello'
print s[0] ##执行以后输出的结果是 h
print s[1] ##执行以后输出的结果是 e
(2)切片
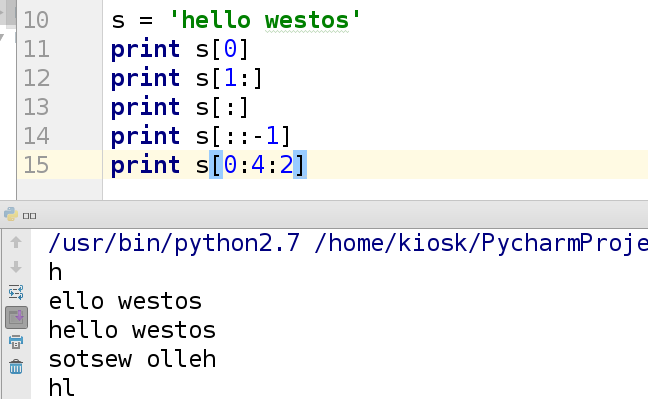
规则:s[start:stop] 从start开始到end-1结束
示例:
s = 'hello'
print s[0:3] ##执行以后输出的结果是 hel
print s[0:4:2] ##输出结果是 hl
print s[:] ##输出字符串的所有字符
print s[:3] ##输出字符串的前三个字符
print s[::-1] ##对字符串倒叙输出
print s[1:] ##输出字符串除了第一个字符以外的所有字符

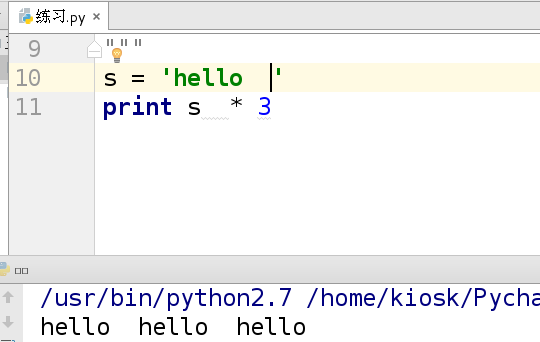
(3)重复
示例:
s = 'hello'
print s*10 ##输出10遍hello
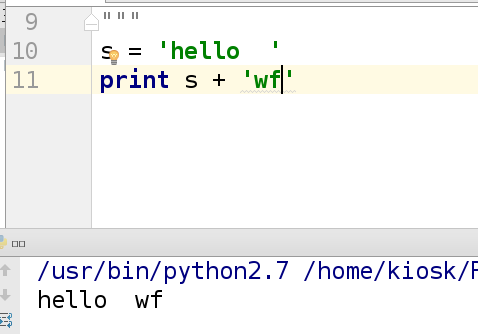
(4)连接
示例:
s = 'hello'
print 'hello' + 'westos' ##在hello的后面加一个westos
输出: hello westos
(5)成员操作符
示例:
s = 'hello'
print 'h' in s ##判断 s 字符串中是否含有 h
##有h,输出True;没有就输出False
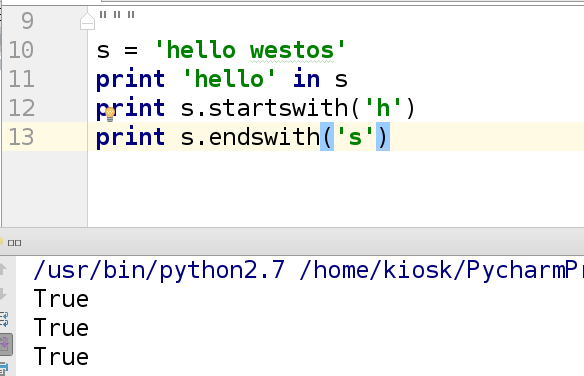
2.字符串开头和结尾的匹配
示例:
s = 'hello.jpg'
print s.endswith('.png') ##输出为False
print s.endswith('.jpg') ##输出为True
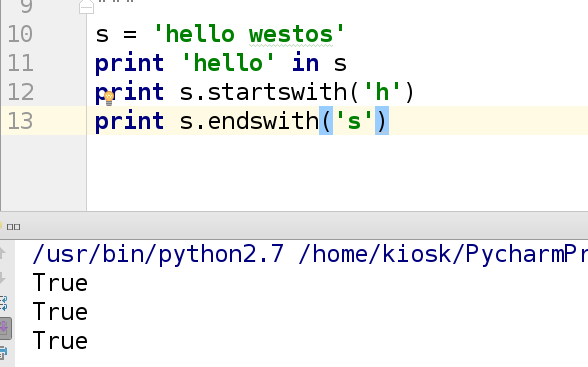
url1='http://172.25.254.110'
url1='file:///mnt'
print url1.startswith('http://') ##输出为True
3.字符串判断是否大小写或数字
(1)判断字符串里面的每个元素是什么类型,只要有一个元素不满足,就返回False
示例:
print '123'.isdigit() ##True
print '123abd'.isdigit() ##False
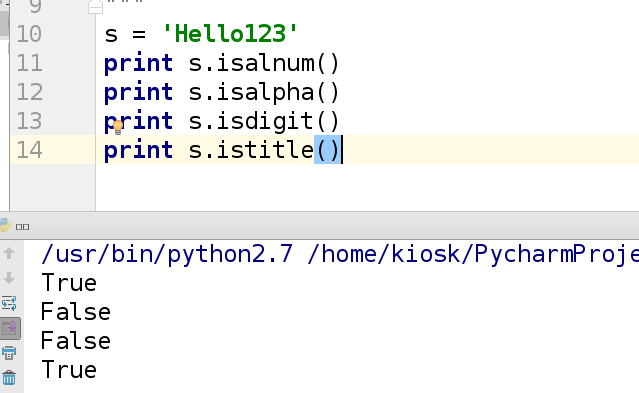
(2)title标题
判断某个字符串是否为标题(首字母大写,其余的小写)
print 'Hello'.istitle() ##True
print 'hEllo'.istitle() ##False
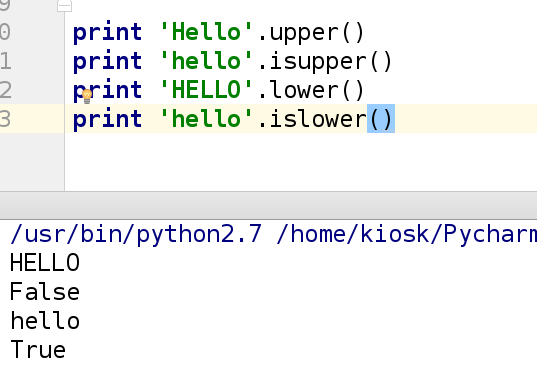
(3)判断字符串
示例:
print 'hello'.upper() ##HELLO 将字符串全部大写输出
print 'hello'.isupper() ##False 判断字符串是否为大写
print 'HELLO'.lower() ##hello 将字符串全部小写输出
print 'hello'.islower() ##True 判断字符串是否为小写
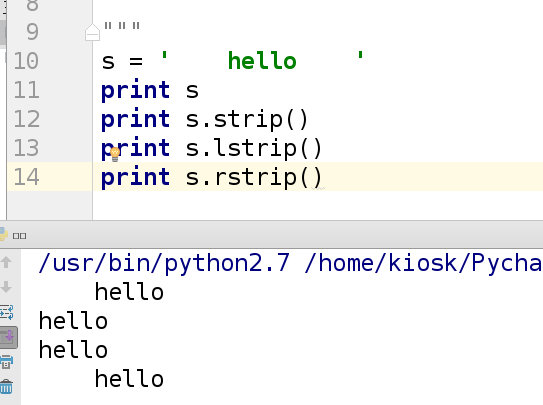
4.删除字符串的空格(广义的空格 包括' ',' ',' ')
示例:
s = " hello "
s.strip() ##删除全部的空格,字符前后的所有空格都删
'hello'
s.lstrip() ##删除字符左边的所有空格
'hello '
s.rstrip() ##删除字符右边的所有空格
' hello'
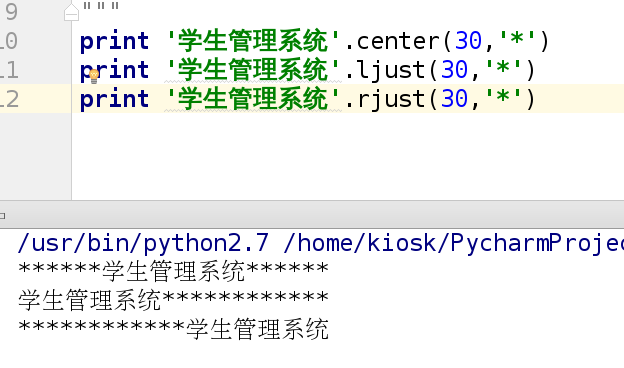
5.居中 center
print '学生管理系统'.center(50,'*')
**************学生管理系统**************
print '学生管理系统'.ljust(50,'*')
学生管理系统**************
print '学生管理系统'.rjust(50,'*')
**************学生管理系统
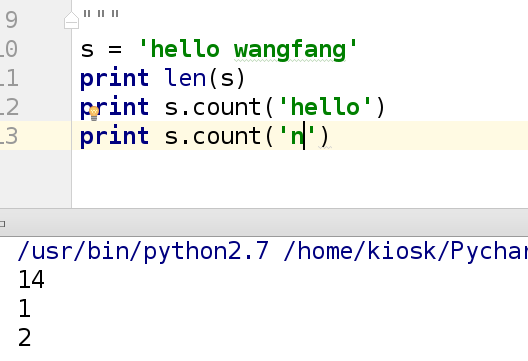
6.计算字符串长度
s = 'hello world'
print len(s) ##输出结果为 11
7.查找(替换)字符串内的字符
注意:这里查找到想要查找的单词以后会返回最小的索引值。
s = 'hello world'
print s.find('hello')
print s.find('world')
输出结果: 0 6
print s.replace('hello','westos')
输出结果:westos world
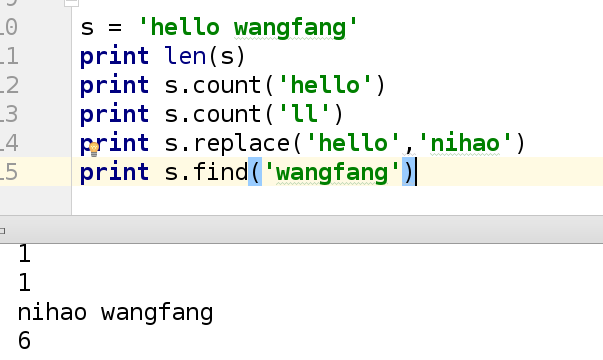
8.计算字符串中的某一字符的个数
示例:
print 'hello'.count('ll')
输出结果: 1
print 'hello'.count('l')
输出结果: 2

9.字符串的分离和连接
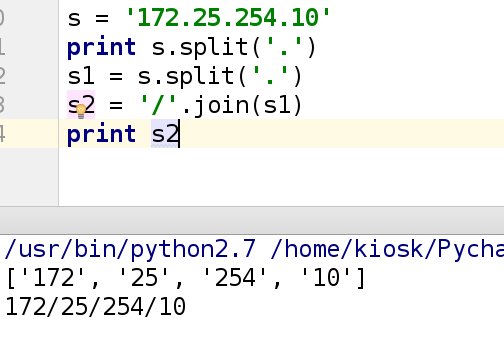
split 是对于字符串进行分离,默认分割符为 空格 ‘ ’
示例:
s = '172.25.254.210'
s1 = s.split('.')
print s1
输出结果: ['172','25','254','210']
print '-'.join(s1)
输出结果: 17225254210
print '-'join('hello')
输出结果: h-e-l-l-o