Python的sys模块提供访问解释器使用或维护的变量,和与解释器进行交互的函数。通俗来讲,sys模块负责程序与python解释器的交互,提供了一系列的函数和变量,用于操控python运行时的环境。
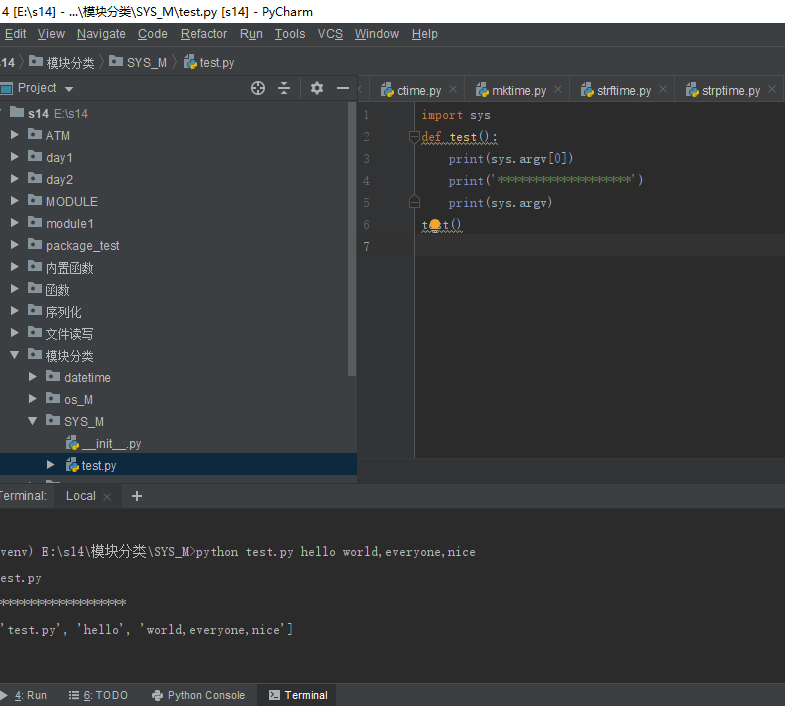
(1)sys.argv 获取当前正在执行的命令行参数的参数列表(list)
argv[0]表示代码本身的文件路径,最多只能传入两个命令行参数
(2) sys.modules.keys() 返回所有已经导入的模块列表
1 >>> import os,sys 2 >>> sys.modules.keys() 3 dict_keys(['sys', 'builtins', '_frozen_importlib', '_imp', '_thread', '_warnings', '_weakref', 'zipimport',
'_frozen_importlib_external', '_io', 'marshal', 'nt', 'winreg', 'encodings', 'codecs', '_codecs', 'encodings.aliases',
'encodings.utf_8', '_signal', '__main__', 'encodings.latin_1', 'io', 'abc', '_abc', 'site', 'os', 'stat', '_stat',
'ntpath', 'genericpath', 'os.path', '_collections_abc', '_sitebuiltins', 'atexit'])
(3)sys.platform 获取当前执行环境的平台
(4)sys.path path是一个目录列表,供Python从中查找第三方扩展模块。
(5) sys.exit(n) 调用sys.exit(n)可以中途退出程序,sys.exit(0)表示正常退出,n不为0时,会引发SystemExit异常,从而在主程序中可以捕获该异常。
1 import sys 2 print("running ...") 3 try: 4 sys.exit(1) 5 except SystemExit: 6 print("SystemExit exit 1") 7 print("exited")
输出结果:
1 E:s14+venvScriptspython.exe E:/s14/模块分类/SYS_M/test2.py 2 running ... 3 SystemExit exit 1 4 exited 5 6 Process finished with exit code 0
(6)sys.version 获取python解释程序的版本信息
(7) sys.stdin, sys.stdout, sys.stderr 标准输入,标准输出,错误输出
标准输入:一般为键盘输入,stdin对象为解释器提供输入字符流,一般使用raw_input()和input()函数
1 import sys 2 print("Please input you name:") 3 name = sys.stdin.readline() 4 print(name) 5 》》》》 6 Please input you name: 7 Xiao Ming #用户输入,然后Enter 8 Xiao Ming 9 10 11 Process finished with exit code 0
标准输出:一般为屏幕。stdout对象接收到print语句产生的输出
1 import sys 2 3 sys.stdout.write("123456 ") 4 sys.stdout.flush() 5 执行结果 6 123456 7 8 Process finished with exit code 0
错误输出:一般是错误信息,stderr对象接收出错的信息。
sys.stdout与print
当我们在 Python 中打印对象调用 print obj 时候,事实上是调用了 sys.stdout.write(obj+' ') ;print 将你需要的内容打印到了控制台,然后追加了一个换行符;print 会调用 sys.stdout 的 write 方法
以下两行在事实上等价:
1 sys.stdout.write('hello'+' ') 2 3 print 'hello'
sys.stdin与raw_input
当我们用 raw_input('Input promption: ') 时,事实上是先把提示信息输出,然后捕获输入
以下两组在事实上等价:
1 hi=raw_input('hello? ') 2 3 print 'hello? ', #comma to stay in the same line 4 hi=sys.stdin.readline()[:-1] # -1 to discard the ' ' in input stream
从控制台重定向到文件:
原始的sys.stdout指向控制台。如果把文件的对象引用赋给sys.stdout,那么print调用的就是文件对象的write方法
1 import sys 2 3 f_handler = open('out.log','w') 4 sys.stdout = f_handler 5 print("hello") 6 # this hello can't be viewed on console 7 # this hello is in file out.log
如果想要在控制台打印一些东西的话,最好先将原始的控制台对象引用保存下来,向文件中打印后再恢复sys.stdout:
1 __console__=sys.stdout 2 3 # redirection start # 4 5 ... 6 7 # redirection end 8 9 sys.stdout=__console__
q