1 理解CPU
CPU(Cental Processing Unit)是计算机系统的运算和控制核心,是信息处理、程序运行的最终执行单元,相当系统的“大脑”。
当 cpu 过于繁忙,就像“人脑”并发处理过多事情,会降低做事效率,严重时甚至会导致崩溃“宕机”。因此,理解 CPU 工作原理,合理控制资源,是保障系统稳定持续运行的重要手段。
1.1 多 cpu 和多核 cpu
多个物理CPU,CPU通过总线进行通信,效率比较低:
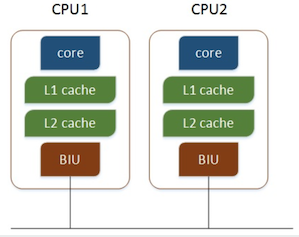
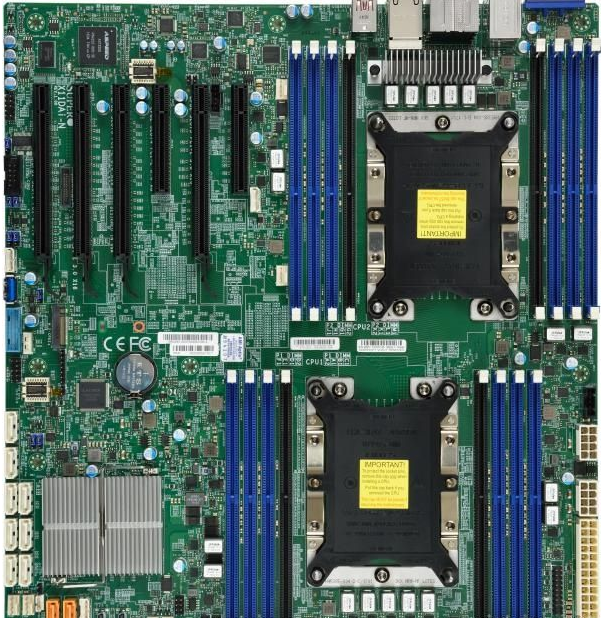
用于双路Xeon可扩展的主板:超微X11DAi-N
多核CPU,不同的核通过L2 cache进行通信,存储和外设通过总线与CPU通信:
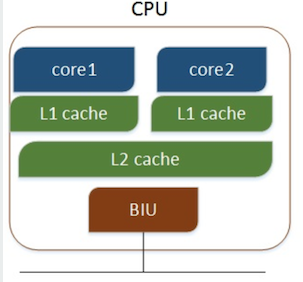
用于单路Xeon-W的主板:超微X11SRA
2 查询CPU信息
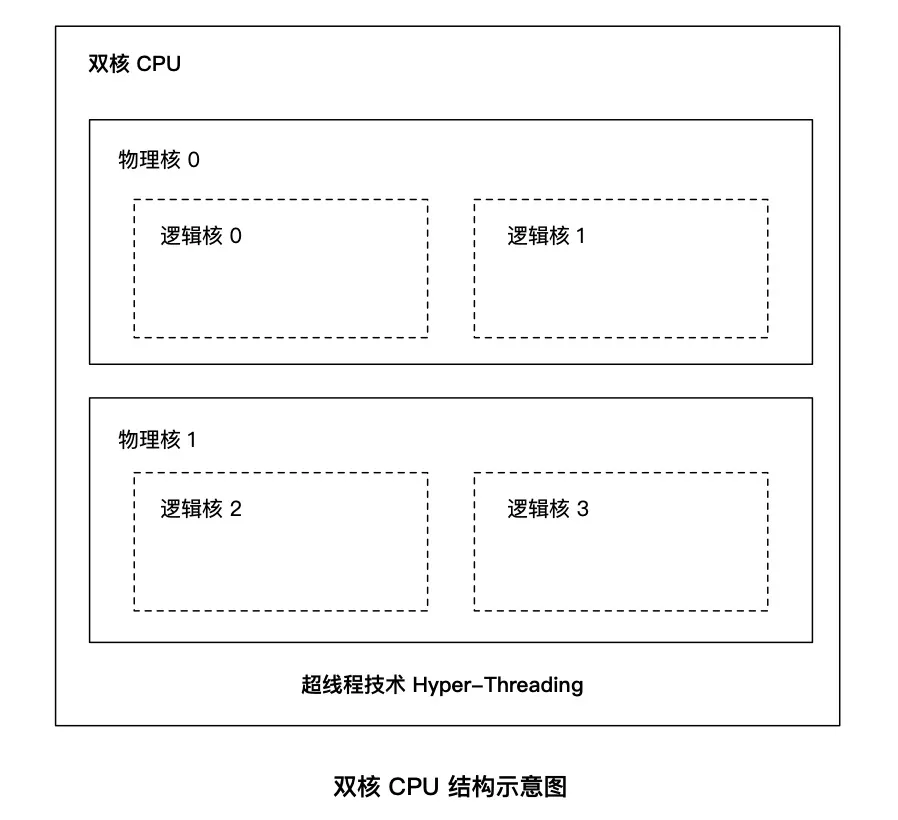
[root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'physical id' | sort | uniq | wc -l //查看 cpu 个数 2 [root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'cpu cores' | sort | uniq // 查看cpu物理核数 cpu cores : 3 [root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'siblings' | sort | uniq // 查看 cpu 逻辑核数 siblings : 3
3 平均负载含义
当系统变慢的时候,我们一般使用 top 或 uptime 命令来查看系统平均负载情况。
正确定义:单位时间内,系统中处于 可运行状态(R,Running/Runnable)和不可中断睡眠状态(D,Disk Sleep) 的平均进程数。
错误定义:单位时间内的 cpu 使用率。
可运行状态的进程:正在使用 cpu 或者正在等待 cpu 的进程,即 ps aux 命令下 STAT 处于 R 状态的进程
不可中断状态的进程:处于内核态关键流程中的进程,且不可被打断,如等待硬件设备IO响应,ps命令D状态的进程。
理想状态:每个 cpu 上都有一个活跃进程,即平均负载数等于 cpu 数。
过载经验值:平均负载高于 cpu 数量 70% 的时候。
假如在一个单 cpu 系统上看到 1.73 0.60 7.98,表示在过去一分钟内系统有73%的超载,而在15分钟内,有698%的超载。
注:可运行状态进程包括正在使用cpu或等待cpu的进程;不可中断状态进程是指处于内核关键流程中的进程,并且该流程不可被打断,比如当进程向磁盘写数据时,如果被打断,就可能出现磁盘数据与进程数据不一致。
不可中断进程状态,本质上是系统对进程和硬件设备的一种保护机制。
4 平均负载案例分析
系统环境和工具
系统环境和配置:CentOS 7 64bit 4G内存 2CPU
相关工具:stress、sysstat。
stress:一个Linux系统压力测试工具。
sysstat:监控和分析系统的性能工具,包括mpstat关于cpu详细信息(单独输出或分组输出)、pidstat(进程性能分析)命令、iostat等。
安装工具:yum install -y epel-release stress sysstat
同一个Linux系统开三个终端。
场景一:CPU密集型进程
第一个终端运行stress命令模拟一个cpu使用率100%
[root@localhost ~]# stress --cpu 1 --timeout 300 stress: info: [9716] dispatching hogs: 1 cpu, 0 io, 0 vm, 0 hdd
第二个终端运行uptime查看平均负载变化情况
#-d参数表示高亮显示变化的区域
[root@localhost ~]# watch -d uptime
第三个终端云溪mpstat查看cpu使用率变化情况
#-P ALL表示监控所有cpu,5表示间隔5秒输出一组数据
[root@localhost zhiwenwei]# mpstat -P ALL 5 Linux 3.10.0-957.10.1.el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月01日 _x86_64_ (2 CPU) 22时33分45秒 CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %gnice %idle 22时33分50秒 all 50.95 0.00 0.30 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 48.75 22时33分50秒 0 1.80 0.00 0.60 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 97.60 22时33分50秒 1 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
结论:从终端二看到1分钟的平均负载会慢慢增加到1.00;终端三正好有一个cpu使用率为100%,但它的iowait只有0,说明平均负载的升高正是由于cpu使用率的升高。
那么到底是哪个进程导致cpu使用率为100%,可以使用top命令来来查或使用pidstat命令。
[root@localhost zhiwenwei]# pidstat -u 5 1 Linux 3.10.0-957.10.1.el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月01日 _x86_64_ (2 CPU) 22时37分09秒 UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command 22时37分14秒 0 2334 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 0 xfsaild/dm-0 22时37分14秒 0 4805 1.20 0.20 0.00 0.00 1.40 0 mono 22时37分14秒 0 4808 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 0 rsyslogd 22时37分14秒 0 9783 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 0 watch 22时37分14秒 0 10078 100.20 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.20 1 stress 22时37分14秒 0 10087 0.20 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.40 0 pidstat 平均时间: UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command 平均时间: 0 2334 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 - xfsaild/dm-0 平均时间: 0 4805 1.20 0.20 0.00 0.00 1.40 - mono 平均时间: 0 4808 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 - rsyslogd 平均时间: 0 9783 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 - watch 平均时间: 0 10078 100.20 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.20 - stress 平均时间: 0 10087 0.20 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.40 - pidstat
场景二:I/O密集型进程
第一个终端运行stress命令模拟I/O压力
[root@localhost ~]# stress -i 1 --timeout 600
第二个终端运行uptime查看当前平均负载变化情况
[root@localhost ~]# watch -d uptime
第三个终端运行mpstat查看cpu使用率变化情况
[zhiwenwei@localhost tmp]$ mpstat -P ALL 5 1 Linux 3.10.0-957.10.1.el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月02日 _x86_64_ (2 CPU) 13时44分56秒 CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %gnice %idle 13时45分01秒 all 1.41 0.00 47.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 51.16 13时45分01秒 0 1.61 0.00 89.52 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 8.87 13时45分01秒 1 1.21 0.00 5.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 93.36 平均时间: CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %gnice %idle 平均时间: all 1.41 0.00 47.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 51.16 平均时间: 0 1.61 0.00 89.52 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 8.87 平均时间: 1 1.21 0.00 5.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 93.36
结论:1分钟的平均负载会慢慢增加到1,其中两个cpu平均使用率49.40,而idle平均达到50.40。说明平均负载的升高由于idle的升高。
查看导致idle升高的进程:
[zhiwenwei@localhost tmp]$ pidstat -u 5 1 Linux 3.10.0-957.10.1.el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月02日 _x86_64_ (2 CPU) 13时50分46秒 UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command 13时50分51秒 0 4273 0.00 8.58 0.00 1.60 8.58 0 kworker/u4:0 13时50分51秒 0 4805 1.40 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.40 1 mono 13时50分51秒 0 4815 1.00 62.08 0.00 3.59 63.07 0 stress 13时50分51秒 0 4816 0.00 14.77 0.00 1.60 14.77 1 kworker/u4:1 13时50分51秒 1007 4819 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 1 pidstat 平均时间: UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command 平均时间: 0 4273 0.00 8.58 0.00 1.60 8.58 - kworker/u4:0 平均时间: 0 4805 1.40 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.40 - mono 平均时间: 0 4815 1.00 62.08 0.00 3.59 63.07 - stress 平均时间: 0 4816 0.00 14.77 0.00 1.60 14.77 - kworker/u4:1 平均时间: 1007 4819 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 - pidstat
可以发现是stress进程导致的。
场景三:大量进程
第一个终端使用stress命令模拟10个进程
[root@localhost ~]# stress -c 10 --timeout 600
第二个终端用uptime查看平均负载变化情况
[root@localhost ~]# watch -d uptime
第三个终端pidstat查看进程情况
[root@localhost ~]# pidstat -u 5 1 Linux 3.10.0-957.10.1.el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月02日 _x86_64_ (2 CPU) 13时55分59秒 UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command 13时56分04秒 0 4805 1.38 0.20 0.00 0.00 1.58 0 mono 13时56分04秒 0 4828 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.49 19.53 0 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4829 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.49 19.72 0 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4830 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.68 19.72 1 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4831 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.68 19.72 0 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4832 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.09 19.53 0 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4833 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.29 19.72 1 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4834 19.53 0.00 0.00 78.90 19.53 1 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4835 19.72 0.00 0.00 80.08 19.72 1 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4836 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.09 19.53 0 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4837 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.29 19.72 1 stress 13时56分04秒 0 4848 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.39 0.20 0 pidstat 平均时间: UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command 平均时间: 0 4805 1.38 0.20 0.00 0.00 1.58 - mono 平均时间: 0 4828 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.49 19.53 - stress 平均时间: 0 4829 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.49 19.72 - stress 平均时间: 0 4830 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.68 19.72 - stress 平均时间: 0 4831 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.68 19.72 - stress 平均时间: 0 4832 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.09 19.53 - stress 平均时间: 0 4833 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.29 19.72 - stress 平均时间: 0 4834 19.53 0.00 0.00 78.90 19.53 - stress 平均时间: 0 4835 19.72 0.00 0.00 80.08 19.72 - stress 平均时间: 0 4836 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.09 19.53 - stress 平均时间: 0 4837 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.29 19.72 - stress 平均时间: 0 4848 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.39 0.20 - pidstat
总结:
平均负载高有可能是cpu密集型进程导致的;
平均负载高不一定是cpu使用率高,还有可能是I/O更繁忙
当发现负载高的时候,可以使用mpstat、pidstat等工具辅助分析负载高的根源。
参考文献