Given a string s and an integer array indices of the same length.
The string s will be shuffled such that the character at the ith position moves to indices[i] in the shuffled string.
Return the shuffled string.
Example 1:
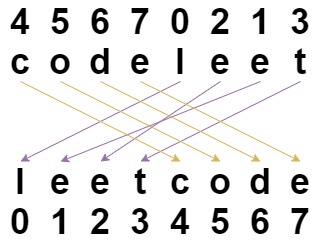
Input: s = "codeleet", indices = [4,5,6,7,0,2,1,3]
Output: "leetcode"
Explanation: As shown, "codeleet" becomes "leetcode" after shuffling.
Example 2:
Input: s = "abc", indices = [0,1,2]
Output: "abc"
Explanation: After shuffling, each character remains in its position.
Example 3:
Input: s = "aiohn", indices = [3,1,4,2,0]
Output: "nihao"
Example 4:
Input: s = "aaiougrt", indices = [4,0,2,6,7,3,1,5]
Output: "arigatou"
Example 5:
Input: s = "art", indices = [1,0,2]
Output: "rat"
Constraints:
s.length == indices.length == n1 <= n <= 100scontains only lower-case English letters.0 <= indices[i] < n- All values of
indicesare unique (i.e.indicesis a permutation of the integers from0ton - 1).
class Solution { public String restoreString(String s, int[] indices) { int n = s.length(); char[] arr = new char[n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ arr[indices[i]] = s.charAt(i); } return new String(arr); } }