Given a m x n grid. Each cell of the grid has a sign pointing to the next cell you should visit if you are currently in this cell. The sign of grid[i][j] can be:
- 1 which means go to the cell to the right. (i.e go from
grid[i][j]togrid[i][j + 1]) - 2 which means go to the cell to the left. (i.e go from
grid[i][j]togrid[i][j - 1]) - 3 which means go to the lower cell. (i.e go from
grid[i][j]togrid[i + 1][j]) - 4 which means go to the upper cell. (i.e go from
grid[i][j]togrid[i - 1][j])
Notice that there could be some invalid signs on the cells of the grid which points outside the grid.
You will initially start at the upper left cell (0,0). A valid path in the grid is a path which starts from the upper left cell (0,0) and ends at the bottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1) following the signs on the grid. The valid path doesn't have to be the shortest.
You can modify the sign on a cell with cost = 1. You can modify the sign on a cell one time only.
Return the minimum cost to make the grid have at least one valid path.
Example 1:
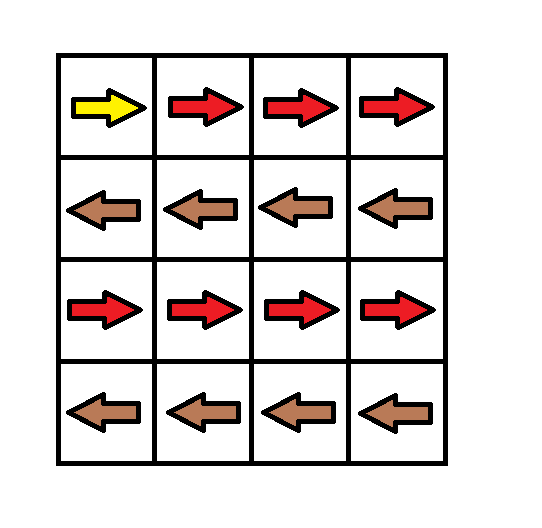
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]] Output: 3 Explanation: You will start at point (0, 0). The path to (3, 3) is as follows. (0, 0) --> (0, 1) --> (0, 2) --> (0, 3) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (1, 3) --> (1, 2) --> (1, 1) --> (1, 0) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (2, 0) --> (2, 1) --> (2, 2) --> (2, 3) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (3, 3) The total cost = 3.
Example 2:
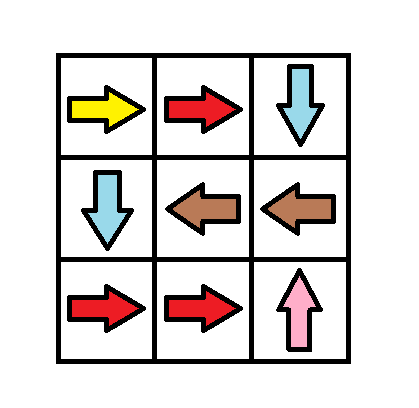
Input: grid = [[1,1,3],[3,2,2],[1,1,4]] Output: 0 Explanation: You can follow the path from (0, 0) to (2, 2).
Example 3:
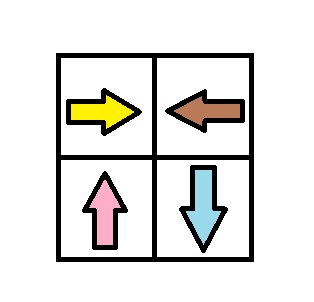
Input: grid = [[1,2],[4,3]] Output: 1
Example 4:
Input: grid = [[2,2,2],[2,2,2]] Output: 3
Example 5:
Input: grid = [[4]] Output: 0
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100
class Solution { int[][] DIR = new int[][]{{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}; public int minCost(int[][] grid) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length, cost = 0; int[][] dp = new int[m][n]; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) Arrays.fill(dp[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE); Queue<int[]> bfs = new LinkedList<>(); dfs(grid, 0, 0, dp, cost, bfs); while (!bfs.isEmpty()) { cost++; for (int size = bfs.size(); size > 0; size--) { int[] top = bfs.poll(); int r = top[0], c = top[1]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) dfs(grid, r + DIR[i][0], c + DIR[i][1], dp, cost, bfs); } } return dp[m - 1][n - 1]; } void dfs(int[][] grid, int r, int c, int[][] dp, int cost, Queue<int[]> bfs) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || dp[r][c] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) return; dp[r][c] = cost; bfs.offer(new int[]{r, c}); // add to try to change direction later int nextDir = grid[r][c] - 1; dfs(grid, r + DIR[nextDir][0], c + DIR[nextDir][1], dp, cost, bfs); } }