摘要
- 目前形势:一些现存得方法使用边修复(
edge inpainting)来帮助图像修复任务,这种方法是通过图像梯度(image gradient)来生成二值边图(binary edge map)。存在得缺点:仅使用二值边图,会丢失梯度信息,产生一些问题(例如颜色差异)。 - 本文研究方法:
- 提出
Gradient Augmented Inpainting Network (GAIN),该网络利用梯度信息(而不边信息)来促进图像修复。 - 提出得网络是一个多任务得学习框架,可以同时进行图像修复和梯度修复。
- 提出了一个
GAI-Block,目的是为了融合image feature map和gradient feature map,实现两者信息的共享。 - 同时,梯度特征图(
gradient feature map)决定填充的优先级,减轻空洞卷积层的影响,能够指导网络重构更加真实语义结构。
- 提出
- 数据集:
CelebA-HQ、Places2
INTRODUCTION
-
缺失的区域(
missing area)称为masked area,非缺失区域(background area)称为unmask area。 -
图像修复应用方向有:
image or video completion, recovery, distracting objects removing and replacing. -
图像修复存在研究难点:重构的缺失区域(
filling area)很难和非缺失区域(background area)在语义上一致。因为缺失部分复杂的结构和不同可能的样式(layout)。 -
研究方法总结
传统方法 深度学习方法 diffusion-basediffusion-base with deep learningreconstruct the current patch with the features around the patch. 由于感受野的大小有限,这些方法将会产生带有伪影或者不规则结构的缺失区域。 通过增加下采样层和使用空洞卷积层来获得更大的感受野,但是这不利于生成高清的图片。 examplar-baseused edge inpainting to guide image inpaintingsearch exemplar patches and paste them to fill the mask. They can produce vivid images but suffer from high time cost for searching exemplar patches. The edge map, which is obtained from image gradient and translated into a binary map, can define shapes and spaces in the image and help the model hallucinate(幻想) the structure inside the holes. But the binary edge map discards the fruitful information in the image gradient, leaving some critical issues like color discrepancy unaddressed, leading to the inconsistency between the holes and the background regions. 两者的比较 与 examplar-base相比,diffusion-base方法生成图像的速度快,但是生成的部分过于平滑的,并且存在伪影。存在的问题:由于缺失部分大小的限制,这些方法不能获得高级的信息( hight-level information)来产生与背景区域一致的令人信服的语义结构。 -
与基于梯度生成
edge map的方法相比,使用图像梯度的方法生成的图片是自然的,并且不需要后处理。(图像的梯度广泛用于处理图像编辑和融合(blending)的颜色差异问题,这也是这篇文章的灵感。) -
本文的贡献
贡献 提出了一个带有梯度信息修复的一阶段(one-stage network)网络结构。 提出了一个卷积块(convolution block)即为GAI Block,促进了图像特征图和梯度特征图之间的信息融合。 根据梯度信息设计了一个基于优先级的 mask收缩策略,来实现更好的语义结构和避免空洞卷积层产生的伪影。在 CelebA-HQ和Places2数据集上定性和定量上,展示了我们方法的优越性。
RELATEDWORKS
Traditional image inpainting
- diffusion-based methods: Diffusion-based methods propagate neighboring information from available background regions into the missing holes.
- exemplar-based methods: Exemplar-based methods fill in holes by copying information from similar exemplar patches in the background regions or a collection of other candidate images.
- 存在的缺点:Compared with diffusion-based methods, these methods can provide images with a plausible structure. Unfortunately, these methods are computationally expensive when computing similarity scores between the holes and candidate regions.
Deep image inpainting
最初。most deep image inpainting methods train their models by deep feature learning and adversarial learning with a Context Encoder, an auto-encoder liked structure.之后一些损失函数被添加到网络中,用于提升修复图片的质量。Some other auxiliary losses like perceptual loss and Total Variation (TV) loss are introduced to further improve the quality of the synthesized images.为了获取更大感受野,空洞卷积被引用。Dilated convolution layers was applied to increase the receptive field of the feature map .attention和swapping 层被引入。Similar to exemplar-based methods, many deep learning methods designedattentionorswappinglayers that can search the exemplar patches in the background feature map for the missing regions in an end-to-end manner.与传统方法相比较。In the adversarial training is extended with both global and local discriminators. Compared with traditional methods, deep learning methods can generate almost realistic images in promising speed.
Deep image inpainting with irregular holes
Partial Convolution:convolution weights are normalized by the mask area of the window to
eliminate the effects caused by the irregular missing regions.Gated Convolution:introduced to split each of the convolution layers into the product of feature filters and gating filters. Gating filters learn attentions on the whole feature map to reduce the effects of irregular holes in an end-to-end manner.- 但是这两种方法都不是为不规则缺失特别设计的。
Image inpainting with image gradient
- 图像梯度:图像梯度是根据图像方向的变换计算的,被广泛的用于边界检测
edge detection,图像编辑image editing和图像融合image blending。 - 在图像修复的
传统任务中,图像梯度用于指导填充mask区域的方向或者优先级或者是计算Patch的相似性。此文是第一篇用图像梯度进行深度学习来研究图像修复。
Deep image inpainting with edge map
-
一些方法不是使用图像梯度,而是采用边信息(edge information)。
-
采用边信息修复图像的论文 [43]Holistically-nested Edge Detection (HED) edge detector 被用于指导生成缺失区域(masked area)。 [29]两阶段模型,通过Canny edge detector在第一阶段生成边图(edge map)。在第二阶段,利用生成的边图指导masked region的修复。 [39]将整个过程分为三个阶段,contour inpainting, edge inpainting,and image inpainting, 目的是为了生成结构更好的图像。 上面方法存在的问题:上面的方法都是在边缘检测器上做选择,与梯度图像相比,二进制边缘图不适合于对抗性的学习,并且在图像修复问题上留下一些关键的问题,比如图像色差问题。而我们的方法,使用图像的梯度信息与图像特征信息融合再加填优先级的填充顺序,实现了为不规则缺失生成合理的语义结构。
METHODS
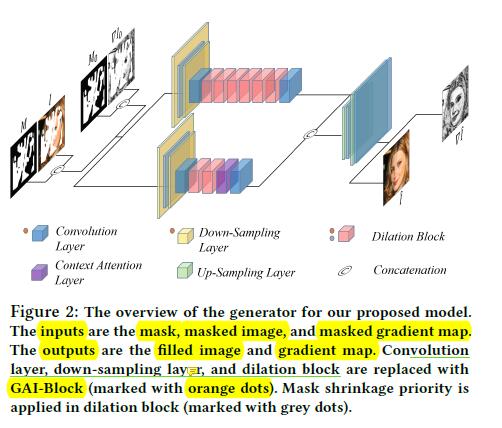
作者采用对抗模型(adversarial model)遵循的encoder-decoder framework来实现对图像的修复。
令G是encoder-decoder network,D为discriminator network,G的总体结构如下:
- 生成模型
G包括两个分支,第一个分支注重的是重构待修复图像的结构,第二个分支注重的是重构待修复图像的内容。 - 网络的输入和输出图像大小都是
256×256. - 网络的输入为: the mask, masked image, and masked gradient map。网络的输出为 :the reconstructed images and gradient map.
- 第一个分支注重图像结构的修复,网络的设置为downsamples the input image twice using two convolution layers with stride 2 followed by six dilation blocks. Each dilation block contains four convolution layers with dilation factors of (2, 4, 8, 16), which means that for a feature map with a size of 64 × 64, two dilation blocks will make sure that each position of the feature map has a receptive field as large as the whole feature map.
- 第二个分支注重图像内容的修复,网络的设置为downsamples the input image twice using two convolution layers with stride 2 followed by two dilation blocks and a
context attention block. The context attention block matches the generated feature in the holes with the features of the known regions, and then selectively assigns the features from the known regions to the holes according to the matching scores. The context attention block will improve the quality of the synthetic images, and its details can be found in
[44]. The output feature maps of two branches areconcatenatedand then upsampled twice using bilinear upsampling layers. - GAI-Block:用于取代原始的卷积层,包括下采样层和空洞块(dilation blocks)。GAI-Block的目的是为了利用梯度特征图(gradient feature map)去重构图像。GAI-Block有助于网络收集梯度特征并将其与图像特征融合以生成具有引人注目的结构的图像。
- mask shrinkage priority:在网络的前向传播阶段,
Priority mask shrinkage将会减轻生成图像存在的误导操作。 - 注意:GAI-block is applied to convolution layers, downsampling layers, and dilation blocks, while mask shrinkage priority is applied to the first four dilation blocks in the first branch to help the network generate plausible images with better structure.
Definitions
令I表示groundtruth image,M表示Mask(the available pixels are marked as 1 (i.e., unmasked area) while the missing pixels in the holes are 0 (i.e., masked area).)令∇I表示图像I的梯度图(image gradient map)。
-
在计算图像梯度的时候,作者先将图像转换为灰度图(grayscale)。
-
图像梯度有较强的健壮性。图像梯度最常见的用途适用于边缘检测,具有较大梯度值的像素很可能是变元像素。
-
图像的梯度公式:(水平方向和竖直方向)
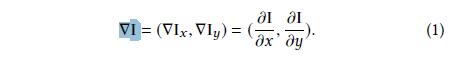
其中
∂I/∂x和∂I/∂y分别表示水平和竖直方向。我们使用有限的差分(finite differences )近似的上面的导数,可以表示为3×3的卷积形式: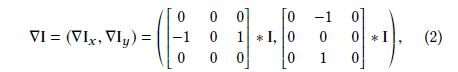
其中
*表示卷积操作,定义 ρ = arctan(∇Iy/∇Ix) 为图像的梯度方向,(({∇I_x^2}+{∇I_y^2})^{(1/2)})为图像梯度的大小。
-
在作者提出的网络中,待修复的图像和梯度图(gradient map)同时被修复。
-
生成网络
G可以用一下公式总结:-
按照编码器-解码器结构构建了生成网络
G,G分别N个块(即多个层或者多个层的组合) -
定义:(I_1 = I⊙M),(M_1 = M),其中⊙表示逐像素乘机的含义,生成网络
G的初始梯度输入为(∇I_1)((∇I_1)的计算过程为:1.用值1扩张M,记为(M_0),则(∇I_0=∇I⊙M_0),这样做目的是为了避免不合理使用Mask区域内的信息。2.使用(∇I_1=Pconv(∇I_0,M_0))来更新梯度信息,同时缩小mask为(M_1)) -
对于每种类型的块,我们引入函数G,该函数定义块如何将输入更改为输出。 对于网络中的第k个块,我们有
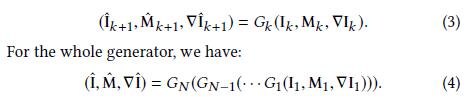
其中(I^*)和({∇I_1}^*)分别代表重构的图像和梯度图(
gradient map),这两者应该相似于(I)和(∇I_1),最终(M)应该全为(1)((M)仅为(0)或(1)),这也就意味着全部像素都已经重构完成。
-
Objective Functions
- 目标函数仅有两个组成:
l1-loss和GAN loss。
-
l1-losscalculates the distance between the predict image (resp(或者)., gradient map) and the groundtruth image (resp(或者)., gradient map).The l1-loss for image can be defined as: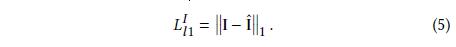
同样,可以得到l1-loss (L_{∇I}^{l1}) for the gradient。
-
l1-losscan help the generator to synthesize images which are close but coarse compared with the groundtruth image.
-
作者训练了两个判别器网络(
discriminator network),(D^I)和(D^S)分别为图像和梯度图(gradient map)的判别器。 -
我们采用
WGAN的hinge loss和GAN loss做为待修复图像的损失函数: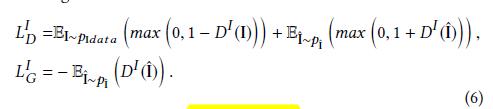
其中,(D(x))表示(D)网络的输出,(P_x)表示(x)的分布。同理,可以得到梯度图的损失函数,记为(L^{∇I}_{D})和(L^{∇I}_{G})
-
为什么梯度图(
gradient map)更加适合GAN网络,而不是二值边图(binary edge map)?
- 总结,作者提出生成器
G的整体损失函数为: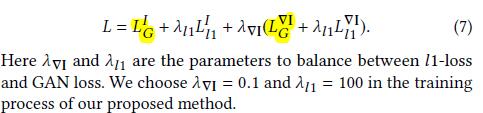
GAI-Block
-
作者将所有的
vanilla convolution layer都替换成他自己设计的块,命名为GAI-Block。该块的作用是从当前特征图(feature map)收集梯度信息,并将此信息传播到mask区域。 -
GAI-Block包括两个流(flows):image feature flowandgradient feature flow. -
在每个块(
Block)中,部分卷积(partial convolution)和梯度卷积核(gradient filter)被应用到每个流中传播信息并在两个流之间进行共享信息.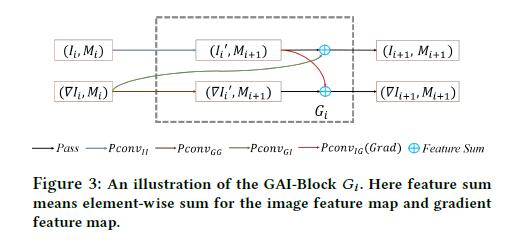
Partial Convolution And Gradient filter

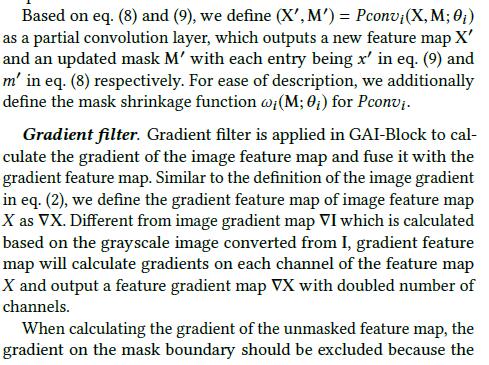

- 在
GAI-Block应用梯度过滤器/梯度卷积核(Gradient filter),以计算图像特征图的梯度将其与梯度特征图融合。 - 定义:将图像特征图
X的梯度特征图定义为∇X,不同于图像的梯度图∇I,它的是来自从I转换的灰度图,图像的梯度特征图将计算特征图X的每个通道上的梯度,并输出通道数量加倍的特征梯度图∇X。 - 在计算未掩盖的特征图(
unmasked feature map)的梯度时,应排除掩膜边界上(mask boundary)的梯度,因为被掩盖的特征图是未知的。 因此,梯度特征图的可用区域(未掩码区域)应为掩模M的1扩展(mask M dilated by 1)。可以通过与内核大小3(kernel),步幅1(stride)和膨胀率1(dilation rate)的卷积来实现掩模扩展1的逆过程,即掩模侵蚀1(mask erosion by 1)的逆过程。 - 记(wg(·))表示为
mask erosion,(w^{-1}g(·))表示为mask dilation。 - 然后,在应用梯度卷积之后,梯度特征图的可用区域将为(w^{-1}g(M)),我们使用(Grad(X,M)=(∇X,w^{-1}g(M)))来表示计算具有扩展掩码(w^{-1}g(M))的梯度特征图∇X的过程
GAI-Block

-
GAI-Block的整体结构如上图。作者计算图像特征图(image feature map)和梯度特征图(gradient feature map)相互共享信息。 -
对于
Block(G_i),记它的输入为((I_i,∇I_i,M_i))。我们将它分为带有mask图像特征图,即((I_i,M_i)),和带有mask的梯度特征图,即((∇I_i,M_i))。 -
GAI-Block执行的过程:- 首先为((I_i,M_i))和((∇I_i,M_i))应用两个部分卷积,产生两个间接的结果分别为:带有
mask图像特征图的间接结果((I′_ i ,ω_i (M_i )))和带有mask梯度特征图的间接结果((∇I′_i ,ω_i (M_i ))),公式表示如下:(记(M_{i+1}=ω_i(M_i )))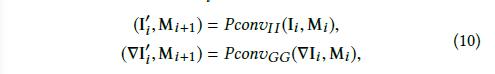
- 然后再产生两个间接的结果分别为:带有
mask图像特征图的间接结果(Pconv_{GI} ((∇I_i ,M_i )))和带有mask梯度特征图的间接结果(Pconv_{IG}(Grad(I′_i ,M_{i+1}))). - 保持
mask不变,分别求两个中间图像特征图和两个中间梯度特征图的和: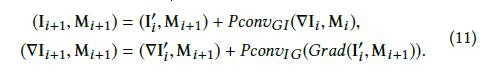
GAI-Block的设计可以确保用于求和的两个输入的mask相同的。- 注意:在每个块(G_i)中的(Pconv_{GG}), (Pconv_{II}) 和(Pconv_{GI})有相同的超参数(即卷积核大小,步长,
dilaton rate),但是卷积核权重不同。(Pconv_{IG})的卷积大小固定为3,步长为1,dilation rate 为1。所以卷积内核权重在不同块之间均不同。
- 首先为((I_i,M_i))和((∇I_i,M_i))应用两个部分卷积,产生两个间接的结果分别为:带有
-
GAI-Block,当网络与Gradient inpainting结合时候,将帮助网络在缺失区域和背景区域之间获得更好的颜色一致性。借助GAI-Block,可以将梯度信息缝合到图像特征信息中,这可以帮助模型从未掩盖的区域中学习稳定的特征并将梯度信息传播到整个图像。
Mask Shrinkage Priority
-
部分卷积提供了一种将
unmasked regions的特征与masked regions隔离的好主意。- 一方面,卷积核不能太大,否则会导致
Mask收缩的太快。部分卷积将不会太有效,当核大小太大时,Mask边界上的patch缺少可用的上下文信息。 - 另一方面,卷积层的内核尺寸不能太小,因为小的内核尺寸导致每个像素的
receptive field较小,这将阻碍更好结构的重建。
- 一方面,卷积核不能太大,否则会导致
-
以前论文种增大
receptive field的方法:- 增加下采样层(
downsampleing layer),将会导致生成的图片存在伪影。 - 使用
dilation convolution,这种方法类似增大卷积核,但是减少了计算消耗。 - 因此,我们的方法也采用
dilation blocks。 但是,dilation convolution对于部分卷积也将是有害的,因为遮罩收缩得太快,这将为缺失区域生成伪像。
- 增加下采样层(
-
为了保持较大的
receptive field和避免Mask Shrinkage太快,受之前examplar-baseed methods的启发,为像素分配优先级,并根据分配的优先级依次填充像素。作者也根据梯度信息设计了一个优先级策略,为每个像素设置优先级,只允许优先级高的相似先进行Mask Shrinkage。-
定义每个像素
x的优先级为: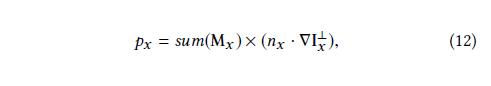
其中(P_x)为像素
x的优先级,(sum(·))和(M_ x)的定义与等式9一致。(n_x)
is the normal vector of the mask borderand (∇I^⊥_x) is the normal vector of gradient.Specifically, (∇I^⊥_x)is calculated by the normal vector for the channel-wise mean of the gradient feature map (∇I) in GAI-Block. (n_x) is the normal vector for the mask border, which is calculated by the gradient of the mask. Note that the mask only contains binary values; if we directly calculate the normal vector, there will be only9possible normal vectors. Hence, we first calculate the3 × 3windowed average of the mask centered atxthen calculate the nx based on this smoothed mask. -
优先级公式分为两个部分:
- 第一部分是(sum(M_x)),用作
calculates the number of pixels that are available for the current pixel。首先用更多的上下文知识填充像素是很合理的,因为具有较高(sum(M_x))的像素应该具有较高的优先级。 - 第二部分是(n_x · ∇I^⊥_x),用作`calculate the overlapping ratio of the normal vector of gradient and the mask border. (n_x · ∇I^⊥_x) 的值较高的像素更有可能来自信息区域,例如Mask的边框上的边缘。
- 第一部分是(sum(M_x)),用作
-
使用(P_i^{max})表示由块(G_i)生成的特征图的最高优先级,我们讲只允许优先级高于(δ·P_i^{max})的像素来控制
mask shrinkage的速度,其中δ为超参数,我们设置他为0.4。类似等式8,有: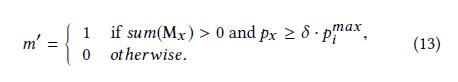
在这里,我们仅更新
mask shrinkage过程,即等式中的特征传播过程。 (9)将保持不变。 实际上,当δ= 0时,(9)是(13)的特例。 -
注意:Note that px = 0 for these pixels are not on the mask border, which means x is in Mx or sum(Mx ) = 0。
-
-
 将会把有较高结构知识(例如,小房子的边框或线条,树叶的质地)和内容知识(
将会把有较高结构知识(例如,小房子的边框或线条,树叶的质地)和内容知识(mask边界)masked的区域优先填充。在此优先考虑下,我们提出的模型以完美的结构和合理的上下文填补了缺失部分。
Implement Details
- Tensorflow
- image size:256×256
- bitchSize:8
- optimizer:Adam optimizer
- Leraning rate:(10^{-4})
- iteration:(10^6)
- 对于判别器,为了GAN训练稳定、快:Gradient penalty 、spectral normalization layer 被使用。
- The number of channels for the output of the first convolution block is
64forIand128for∇I. - The number of channels will be
doubledafter eachdownsampling
layer and reduced byhalfafter eachupsamplinglayer.
EXPERIMENTS
Datasets, Masks and Evaluation Metrics
- 数据集:
CelebA-HQ、Places2. - 评估标准:
relative l1、Structural Similarity(SSIM)、Peak Signal-to-NoiseRatio(PSNR)、Frechet Inception Distance(FID)- The first three metrics assume pixel-wise independence, which may assign favorable scores to perceptually inaccurate results.
- While FID measures theWasserstein-2 distance between the feature representations of real and inpainted images using a pre-trained Inception-V3 model, which is a popular perceptual metric to evaluate the quality of synthesized images.
Quantitative Results
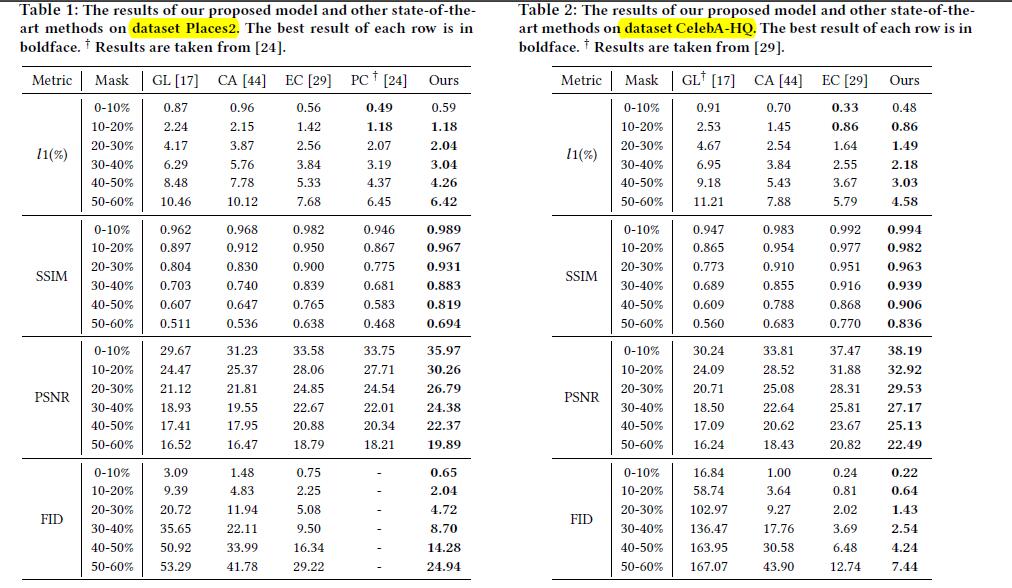
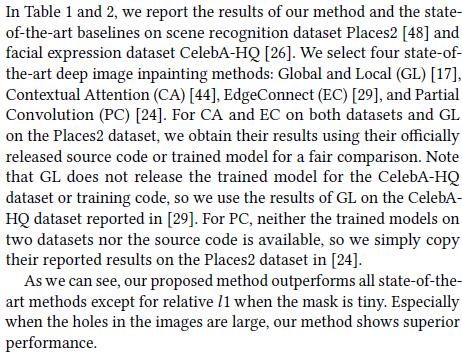
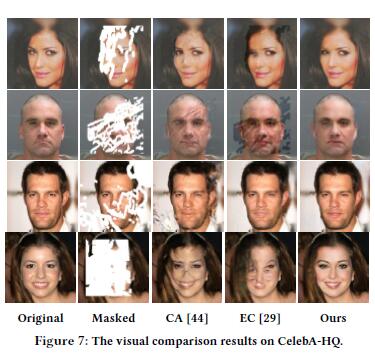
Qualitative Results



Ablation Studies
CONCLUSION