以下内容主要注重应用,对源码不做分析,对源码有兴趣的可参考官方具体文档,相关链接:https://doc.micrium.com/display/ucos/
开发环境:TrueSTUDIO
单片机:STM32F103VET6(HAL库)
一、创建一个任务,OSTaskCreate()或OSTaskCreateExt()
创建任务的函数有两种,后者相较与前者会占用更多的资源,在确保使用的硬件资源足够充分的情况下,使用后者会更加方便开发者观察系统中资源的使用情况。函数原型分别为:
1、INT8U OSTaskCreate (void (*task)(void *pd), void *pdata, OS_STK *ptos, INT8U prio);
- task是指向任务代码的指针(即所创建的任务函数名);
- pdata是一个指针,指向一个参数,该参数在任务开始执行时传递给它(在创建任务的时候通常传递一个0值);
- ptos是一个指向分配给任务的堆栈顶部的指针(注意:由于其支持具有从高内存到低内存或从低内存到高内存Stack增长的处理器,所以在调用OSTaskCreate()时,你必须知道Stack是如何增长的,因为你需要将任务的Stack顶传递给这些函数,默认是从高到低增长);
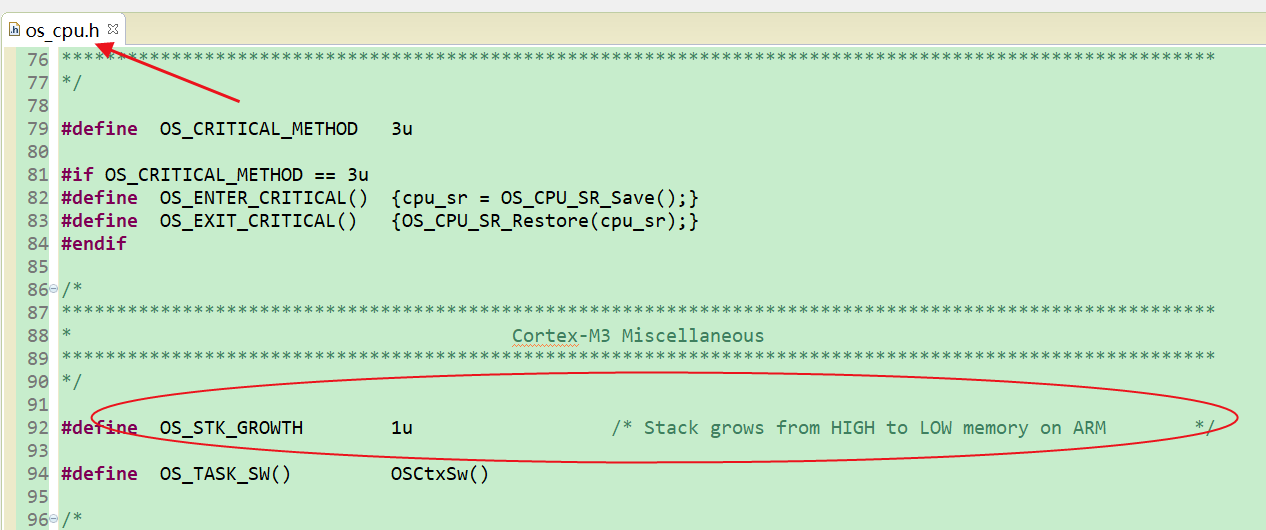
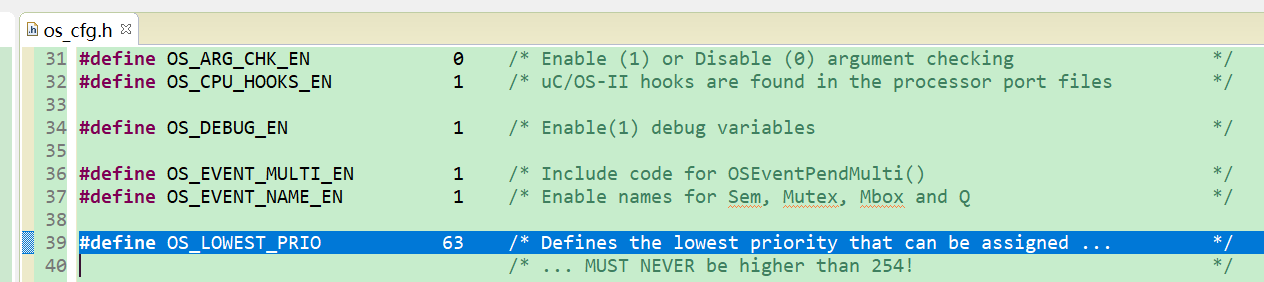
- prio是需要的任务优先级(要注意最低优先级)。
2、INT8U OSTaskCreateExt (void (*task)(void *pd),void *pdata, OS_STK *ptos, INT8U prio, INT16U id, OS_STK *pbos, INT32U stk_size, void *pext, INT16U opt)。
这里只介绍与OSTaskCreate ()不同的地方,因为用的不多,这里我直接摘录了官方的原话,有兴趣的可以自行了解。
|
id |
establishes a unique identifier for the task being created. This argument has been added for future expansion and is otherwise unused by µC/OS-II. This identifier will allow me to extend µC/OS-II beyond its limit of 64 tasks. For now, simply set the task’s ID to the same value as the task’s priority. |
|
pbos |
is a pointer to the task’s bottom-of-stack and this argument is used to perform stack checking. |
|
stk_size |
specifies the size of the stack in number of elements. This means that if a stack entry is four bytes wide, then a stk_size of 1000 means that the stack will have 4,000 bytes. Again, this argument is used for stack checking. |
|
pext |
is a pointer to a user-supplied data area that can be used to extend the |
|
opt |
specifies options to |
二、挂起一个任务,OSTaskSuspend()
任务如果挂起将不会再执行,直到任务恢复,恢复任务只可以可以使用OSTaskResume()恢复;一个任务可以挂起自己或者其他任务。函数的原型为:
1、INT8U OSTaskSuspend (INT8U prio)。
- prio是要挂起任务的优先级(如果指定OS_PRIO_SELF,则调用任务将挂起自己,并将发生重新调度)。
三、恢复一个挂起的任务,OSTaskResume()
恢复用于挂起的任务,函数原型为:
1、INT8U OSTaskResume (INT8U prio)。
- prio是要恢复被挂起的任务的优先级。
四、删除一个任务,OSTaskDel()
删除任务意味着该任务将返回到休眠状态,任务代码不再被调用,而不是该任务的代码将被删除。函数原型为:
1、INT8U OSTaskDel (INT8U prio)。
- prio要被删除任务的优先级。
五、请求删除一个任务, OSTaskDelReq()
有时,任务拥有内存缓冲区或信号量等资源。如果另一个任务试图删除此任务,则资源不会被释放,因此会丢失。这将导致内存泄漏,这对于任何嵌入式系统都是不可接受的。在这种情况下,你需要以某种方式告诉拥有这些资源的任务在使用这些资源后删除自己。请求者和要删除的任务都需要调用OSTaskDelReq()。函数原型为:
1、INT8U OSTaskDelReq (INT8U prio)。
- prio请求要被删除任务的优先级。
2、请求者伪代码如下所示:
void RequestorTask (void *pdata) { INT8U err; pdata = pdata; for (;;) { /* Application code */ if ('TaskToBeDeleted()' needs to be deleted) { (1) while (OSTaskDelReq(TASK_TO_DEL_PRIO) != OS_TASK_NOT_EXIST) { (2) OSTimeDly(1); (3) } } /* Application code */ (4) } }
(1)发出请求的任务需要确定什么条件会导致删除该任务的请求。换句话说,您的应用程序决定了什么条件导致这个决定。
(2)如果需要删除任务,通过传递要删除任务的优先级调用OSTaskDelReq()。如果要删除的任务不存在,OSTaskDelReq()返回OS_TASK_NOT_EXIST。如果要删除的任务已被删除或尚未创建,则将获得此值。如果返回值是OS_NO_ERR,则请求已被接受,但任务尚未被删除。您可能想要等待,直到要删除的任务实际上删除了自己。
(3)您可以通过延迟请求者一段时间来做到这一点。
(4)当被请求的任务最终删除自己时,返回值为OS_TASK_NOT_EXIST,循环退出。
3、需要删除本身的任务的伪代码如下所示:
void TaskToBeDeleted (void *pdata) { INT8U err; pdata = pdata; for (;;) { /* Application code */ if (OSTaskDelReq(OS_PRIO_SELF) == OS_TASK_DEL_REQ) { (1) Release any owned resources; (2) De-allocate any dynamic memory; OSTaskDel(OS_PRIO_SELF); (3) } else { /* Application code */ } } }
(1)当OSTaskDelReq()返回OS_TASK_DEL_REQ给它的调用者时,它表明另一个任务请求删除这个任务。
(2)和(3)在这种情况下,要删除的任务释放所有的资源,并调用OSTaskDel(OS_PRIO_SELF)来删除自己。如前所述,该任务的代码实际上并未删除。只是不调度任务的执行,任务代码将不再运行。但是,您可以通过调用OSTaskCreate()或OSTaskCreateExt()重新创建该任务。
六、示例代码
1、主函数中创建一个起始任务:
/** * @brief 主函数 * @param None * @retval None */ int main (void) { /* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */ HAL_Init(); bsp_clk_init(); CPU_IntDis(); /* Disable all interrupts until we are ready to accept them */ OSInit(); /* Initialize "uC/OS-II, The Real-Time Kernel" */ OSTaskCreate (AppTaskStart, 0, &AppTaskStartStk[APP_TASK_START_STK_SIZE - 1], APP_TASK_START_PRIO); OSStart(); /* Start multitasking (i.e. give control to uC/OS-II) */ }
2、起始任务中创建两个任务,同时在该任务中通过获取按键值实现任务挂起、恢复和删除、创建:
/** * @brief 起始任务 * @param None * @retval None */ static void AppTaskStart (void *p_arg) { INT8U err1, err2; INT8U status1 = 1, status2 = 1; CPU_INT32U hclk_freq; CPU_INT32U cnts; (void)p_arg; BSP_Init(); /* Init BSP fncts. */ CPU_Init(); /* Init CPU name & int. dis. time measuring fncts. */ hclk_freq = BSP_CPU_ClkFreq(); /* Determine SysTick reference freq. */ cnts = hclk_freq / (CPU_INT32U)OS_TICKS_PER_SEC; /* Determine nbr SysTick increments in OS_TICKS_PER_SEC. */ OS_CPU_SysTickInit(cnts); /* Init uC/OS periodic time src (SysTick). */ Mem_Init(); /* Init Memory Management Module. */ err1 = OSTaskCreate (AppTaskLed1, 0, &AppTaskLed1Stk[APP_TASK_START_STK_SIZE-1], APP_TASK_LED1_PRIO); if(err1 == OS_ERR_NONE) { status1 = 0; } err2 = OSTaskCreate (AppTaskLed2, 0, &AppTaskLed2Stk[APP_TASK_START_STK_SIZE-1], APP_TASK_LED2_PRIO); if(err2 == OS_ERR_NONE) { status2 = 0; } while(1) { if(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_0) == GPIO_PIN_SET) { if(status1 == 0) { /* 挂起AppTaskLed1任务 */ err1 = OSTaskSuspend(APP_TASK_LED1_PRIO); if(err1 == OS_ERR_NONE) { status1 = 1; } } if(status2 == 1) { /* 创建删除的AppTaskLed2任务 */ err2 = OSTaskCreate (AppTaskLed2, 0, &AppTaskLed2Stk[APP_TASK_START_STK_SIZE-1], APP_TASK_LED2_PRIO); if(err2 == OS_ERR_NONE) { status2 = 0; } } } else if(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOC, GPIO_PIN_13) == GPIO_PIN_SET) { if(status1 == 1) { /* 把挂起的AppTaskLed1任务恢复 */ err1 = OSTaskResume(APP_TASK_LED1_PRIO); if(err1 == OS_ERR_NONE) { status1 = 0; } } if(status2 == 0) { /* 删除AppTaskLed2任务 */ err2 = OSTaskDel(APP_TASK_LED2_PRIO); if(err2 == OS_ERR_NONE) { status2 = 1; } } } OSTimeDlyHMSM(0, 0, 0, 100); } }
3、起始任务创建的两个任务,这两个任务是控制led灯闪烁,通过观察灯闪烁的状态判断对应的任务是否被执行挂起、恢复和删除、创建:
/** * @brief led1任务 * @param None * @retval None */ static void AppTaskLed1(void *p_arg) { (void)p_arg; while(1) { HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1); OSTimeDlyHMSM(0, 0, 0, 100); } } /** * @brief led2任务 * @param None * @retval None */ static void AppTaskLed2(void *p_arg) { (void)p_arg; while(1) { HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0); OSTimeDlyHMSM(0, 0, 0, 200); } }
#endif