A harmonic sound is said to have a missing fundamental, suppressed fundamental, orphantom fundamental when its overtones suggest a fundamental frequency but the sound lacks a component at the fundamental frequency itself. The brain perceives the pitch of a tone not only by its fundamental frequency, but also by the periodicity implied by the relationship between the higher harmonics; we may perceive the same pitch (perhaps with a differenttimbre) even if the fundamental frequency is missing from a tone.
For example, when a note (that is not a pure tone) has a pitch of 100 Hz, it will consist of frequency components that are integer multiples of that value (e.g. 100, 200, 300, 400, 500.... Hz). However, smaller loudspeakers may not produce low frequencies, and so in our example, the 100 Hz component may be missing. Nevertheless, a pitch corresponding to the fundamental may still be heard.
1.衰减高频部分,有利于突出低音部分。
2.衰减弱分量,有利于增加对比度。
2.根据人理听觉心理学感知,即便基音丢失,增强频谱的主要谐波,达到低音增强的目的。
试听:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1ntNz5wd
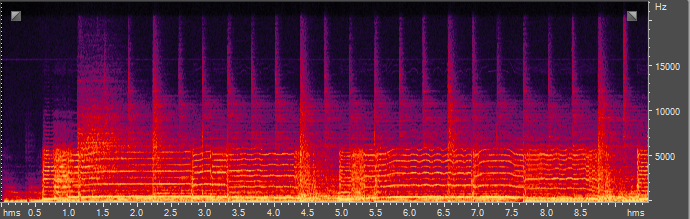
原始音频
处理后的音频
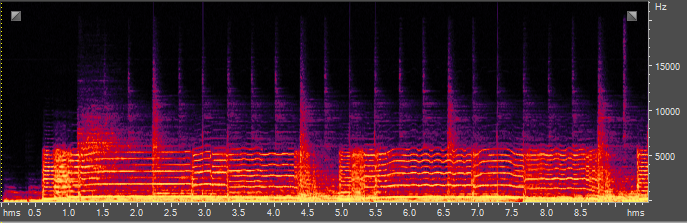
处理的手法:找出基频,然后对相关谐波进行增强。
最简单的方法:相位不变,改变幅度谱,例如峰值匹配;更简单的用非线性处理实现。
另外也可以合成新的谐波分量进行叠加,但是心的谐波分量的相位与现有的对应分量的相位可能产生对消或者说是一致性,垂直方向上很难保证相位之间的关系。