目前主流的框架都是SpringBoot,所以下来详细的阐述下RabbitMQ怎么和SpringBoot进行整合。
一、创建maven工程
首先创建maven的工程,然后创建两个springboot工程的module,具体结构如下:
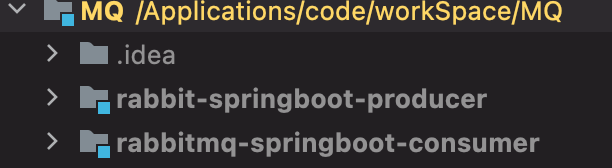
在如上的目录结构中,可以看到分别创建了生产者和消费者的工程。下面详细的阐述下针对生产者以及
消费者不同的配置以及具体代码的实现过程。
二、生产者工程
2.1、生产者配置
首先需要在配置文件中配置RabbitMQ服务的地址,账户以及密码,和针对生产者的配置代码,具体如下:
spring:
rabbitmq:
addresses: 101.***.***.84:5672
username: wuya
password: java
virtual-host: /
connection-timeout: 15000
publisher-confirms: true
publisher-returns: true
#可靠性投递的机制
template:
mandatory: true
server:
port: 80812.2、生产者配置代码
下来我们加载具体的配置信息,它的结构为:
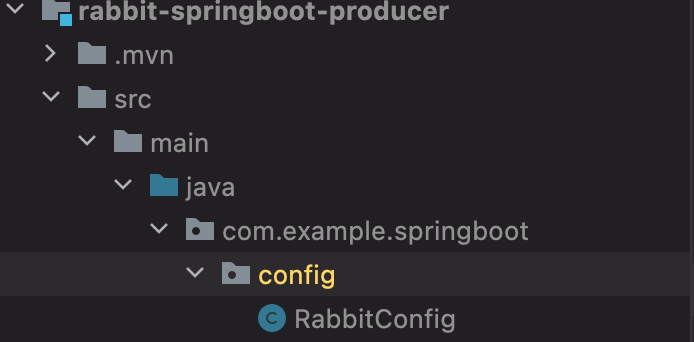
在RabbitConfig编写加载配置的代码,源码具体为:
package com.example.springboot.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.example.springboot.*"})
public class RabbitConfig
{
}2.3、生产者核心代码
下来在server的包下编写发送消息的核心代码。在这里我们主要发送实体的数据,所以需要在entity
包下创建新的实体信息,比如这里创建Person,它的字段主要是name,age,sex。同时需要在实体中继承序
列化的部分,因为最终发送的消息都是需要进行序列话的。Person.java的源码具体为:
package com.example.springboot.entity;
public class Person implements Serializable
{
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Person()
{
}
public Person(String name,int age,String sex)
{
super();
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.sex=sex;
}
}下来编写发送消息的具体代码,源码部分具体如下:
package com.example.springboot.service;
import com.example.springboot.entity.Order;
import com.example.springboot.entity.Person;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.messaging.MessageHeaders;
import org.springframework.messaging.support.MessageBuilder;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
@Component
public class RabbitSend
{
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
//实现生产端的确认应答机制
final RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback confirmCallback=new RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback()
{
//boolean ack:ack的结果信息
//String cause:异常的结果信息
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause)
{
//消息ID的唯一性,使用uuid来解决
System.err.println("correlationData:"+correlationData);
System.err.println("ack:"+ack);
if(!ack)
{
System.err.println("异常情况...需要补偿机制");
}
}
};
//消息投递确认机制
final RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback returnCallback=new RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback()
{
@Override
public void returnedMessage(org.springframework.amqp.core.Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey)
{
System.err.println("retutn replyCode"+replyCode+",return replyText"+replyText);
System.err.println("return exchange:"+exchange+",return routingKey:"+routingKey);
}
};
/*
* 发送Person的实体数据
* */
public void sendPersonMsg(Person person)throws Exception
{
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(confirmCallback);
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(returnCallback);
CorrelationData correlationData=new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("test_exchange_mq","test_mq",person,correlationData);
}
}
2.4、生产者测试代码
编写生产者后,下来编写生产者的测试代码,来验证消息是否发送出去,具体测试代码为:
package com.example.springboot;
import com.example.springboot.entity.Order;
import com.example.springboot.entity.Person;
import com.example.springboot.service.RabbitSend;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class ProducerApplicationTests
{
@Autowired
private RabbitSend rabbitSend;
@Test
public void test_person_sender() throws Exception
{
Person person=new Person("无涯",18,"男");
rabbitSend.sendPersonMsg(person);
}
}
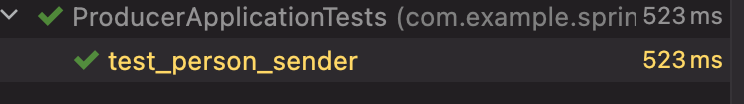
下来执行该测试方法,看是否能够把消息发送出去,执行该测试用例。执行后可以看到消息已发送
出去,见如下测试用例执行的结果信息:
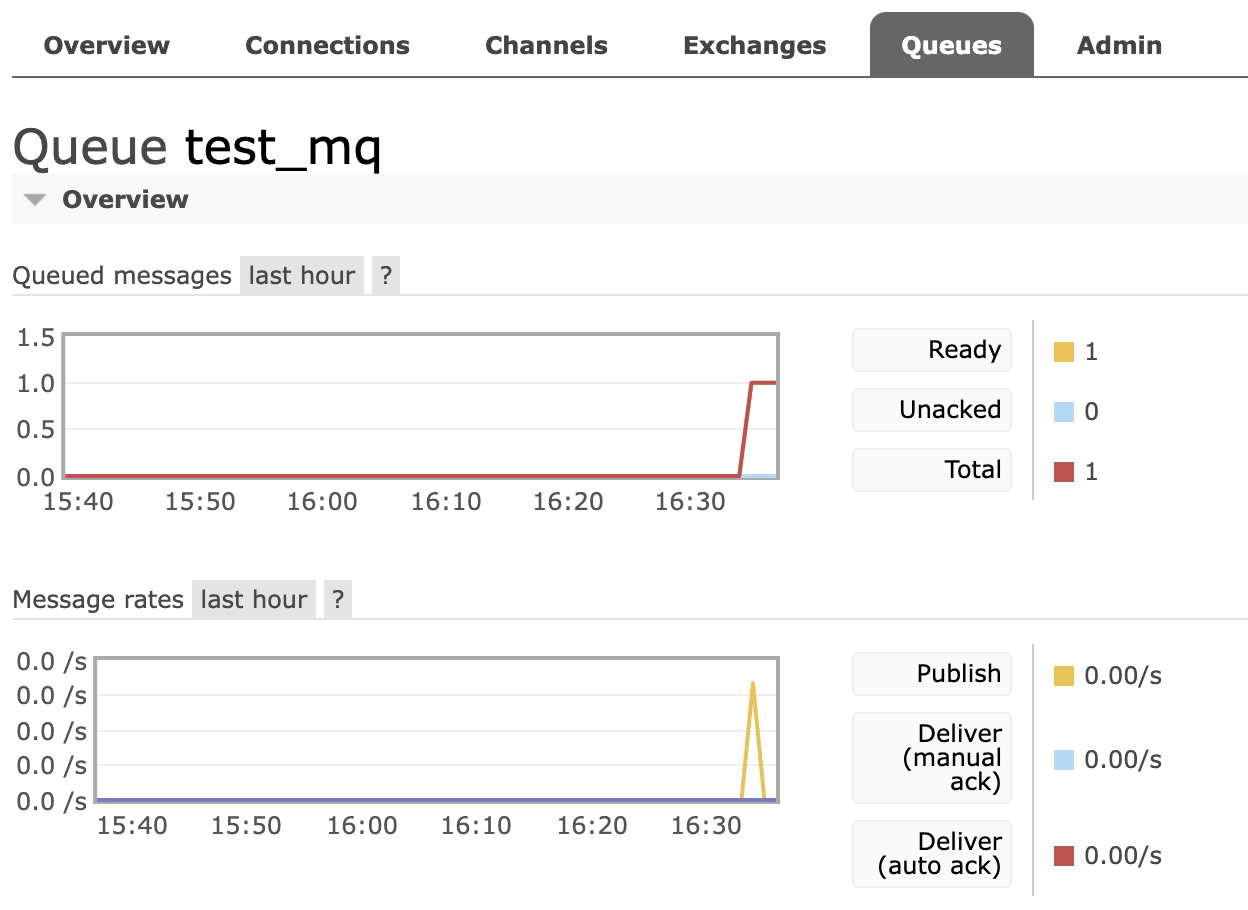
再次查看RabbitMQ的WEB控制台,看到生产者已把消息发送出去,等待消费者来进行消费,具体如下:
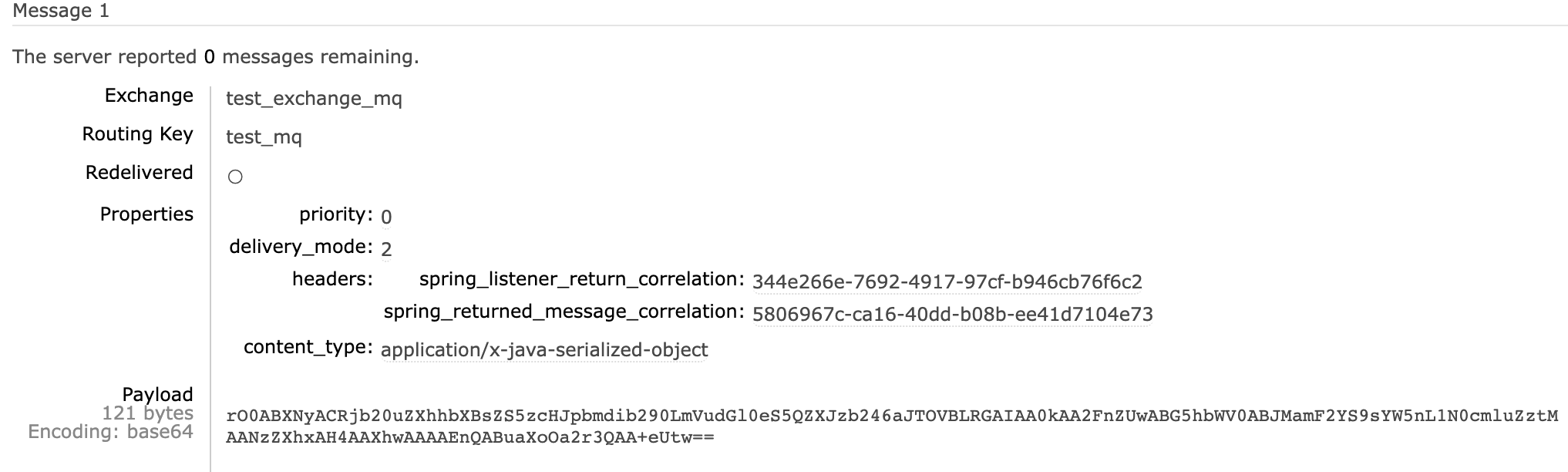
2.5、封装成REST API
下来封装成具体的REST的方式,这样可以通过PostMan的测试工具来进行发送,涉及到的源码为:
package com.example.springboot.controller;
import com.example.springboot.entity.Person;
import com.example.springboot.service.RabbitSend;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class SendMsg
{
@Autowired
RabbitSend rabbitSend;
@RequestMapping("/person")
public String sendPerson()throws Exception
{
Person person=new Person("无涯",18,"男");
rabbitSend.sendPersonMsg(person);
return "person message success!";
}
}
下来在PostMan中访问,可以看到接口请求成功,具体如下:
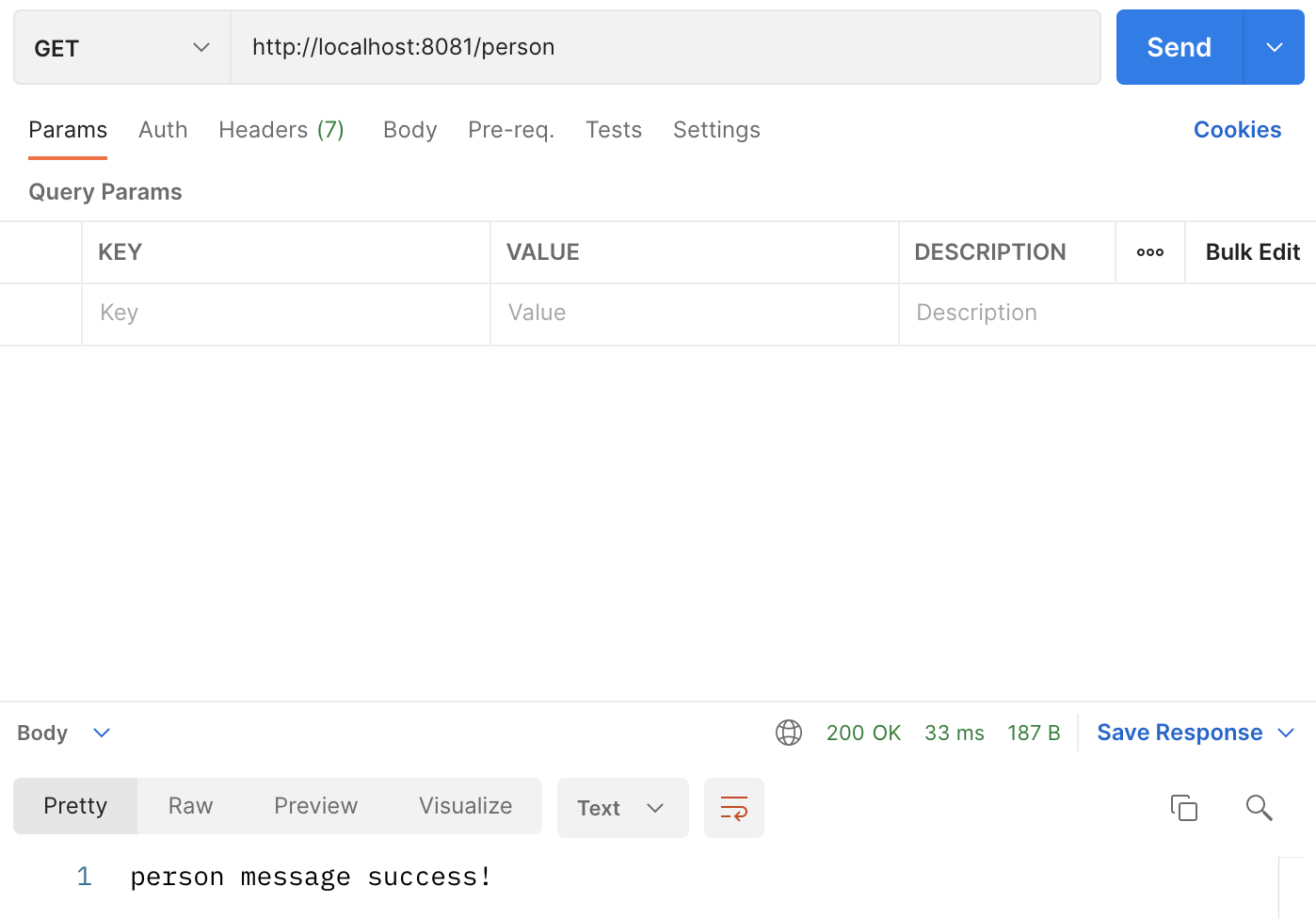
三、消费者工程
3.1、消费者配置
消费者依然是需要进行具体的配置,在配置文件需要配置具体的队列信息,RabbitMQ的地址账户以及
密码的信息。详细的配置如下:
spring:
rabbitmq:
addresses: 101.***.***.84:5672
username: wuya
password: java
connection-timeout: 15000
listener:
simple:
acknowledge-mode: MANUAL
concurrency: 1
max-concurrency: 5
order:
queue:
name: test_mq
durable: true
exchange:
name: test_exchange_mq
durable: true
type: topic
ignoreDeclarationExceptions: true
key: test_mq
3.2、消费者配置代码
下来创建新的config,编写加载RabbitMQ的代码,具体如下:
package com.example.springboot.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/*
* 主配置
* */
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.example.springboot.*"})
public class ConsumerConfig
{
}
3.3、消费者实体代码
在生产者编写了Person.java,那么在消费者里面也是需要该代码,同时需要与生产者的路径完全一致,
这点需要特别的注意。具体代码如下:
package com.example.springboot.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Person implements Serializable
{
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Person()
{
}
public Person(String name, int age, String sex)
{
super();
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.sex=sex;
}
}
3.4、消费者核心代码
下来编写消费者消费数据这部分的代码,具体如下:
package com.example.springboot.service;
/*
* 主要接收消息的类
* */
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.AmqpHeaders;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Headers;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Payload;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class RabbitReceiver
{
//监听消息
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(
value = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.queue.name}",
durable = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.queue.durable}"),
exchange = @Exchange(
value = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.exchange.name}",
durable = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.exchange.durable}",
type = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.exchange.type}",
ignoreDeclarationExceptions = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.exchange.ignoreDeclarationExceptions}"),
key = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.key}"
))
public void onMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws Exception
{
//接收生产端的消息
String msg= (String) message.getPayload();
String msgHeaders=(String)message.getHeaders().toString();
System.err.println("receiver msg:"+msg);
System.err.println("receiver headers:"+msgHeaders);
//手工签收的模式
Long deliveryTag=(Long) message.getHeaders().get(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG);
//接收消息的方式
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag,false);
}
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(
value = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.queue.name}",
durable = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.queue.durable}"),
exchange = @Exchange(
value = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.exchange.name}",
durable = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.exchange.durable}",
type = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.exchange.type}",
ignoreDeclarationExceptions = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.exchange.ignoreDeclarationExceptions}"),
key = "${spring.rabbitmq.listener.order.key}"
))
public void onPersonMessage(
@Payload com.example.springboot.entity.Person person,
Channel channel,
@Headers Map<String,Object> headers)throws Exception
{
System.err.println("===============================");
System.err.println("person name is:"+person.getName()+",and person age is:"+person.getAge()+",and person sex is:"+person.getSex());
Long deliveryTag=(Long) headers.get(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG);
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag,false);
}
}
3.5、测试验证
下来启动生产者和消费者的程序,然后生产者发送消息,消费者来接收消息,可以看到发送后能够
接收到消息,具体如下所示:
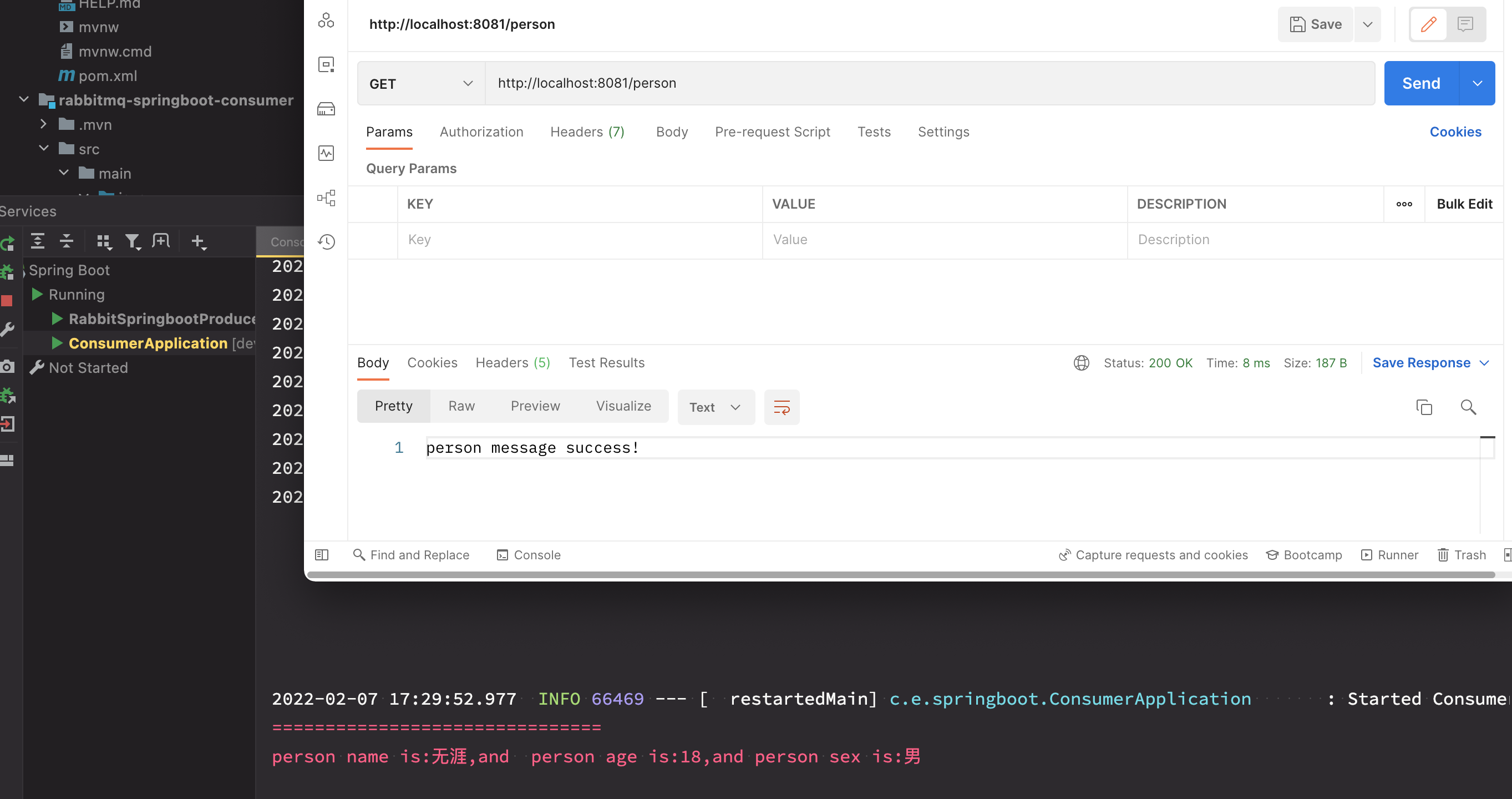
如上,可以看到生产的消息消费者就会接收到该消息。这样完整的实现了RabbitMQ与SpringBoot的整合。感谢
您的阅读,会持续进行更新。更多技术文章,关注个人公众号【Python自动化测试】。
