1、Recursive Nerual Networks能够更好地体现每个词与词之间语法上的联系
这里我们选取的损失函数仍然是交叉熵函数
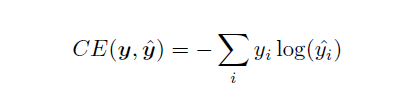
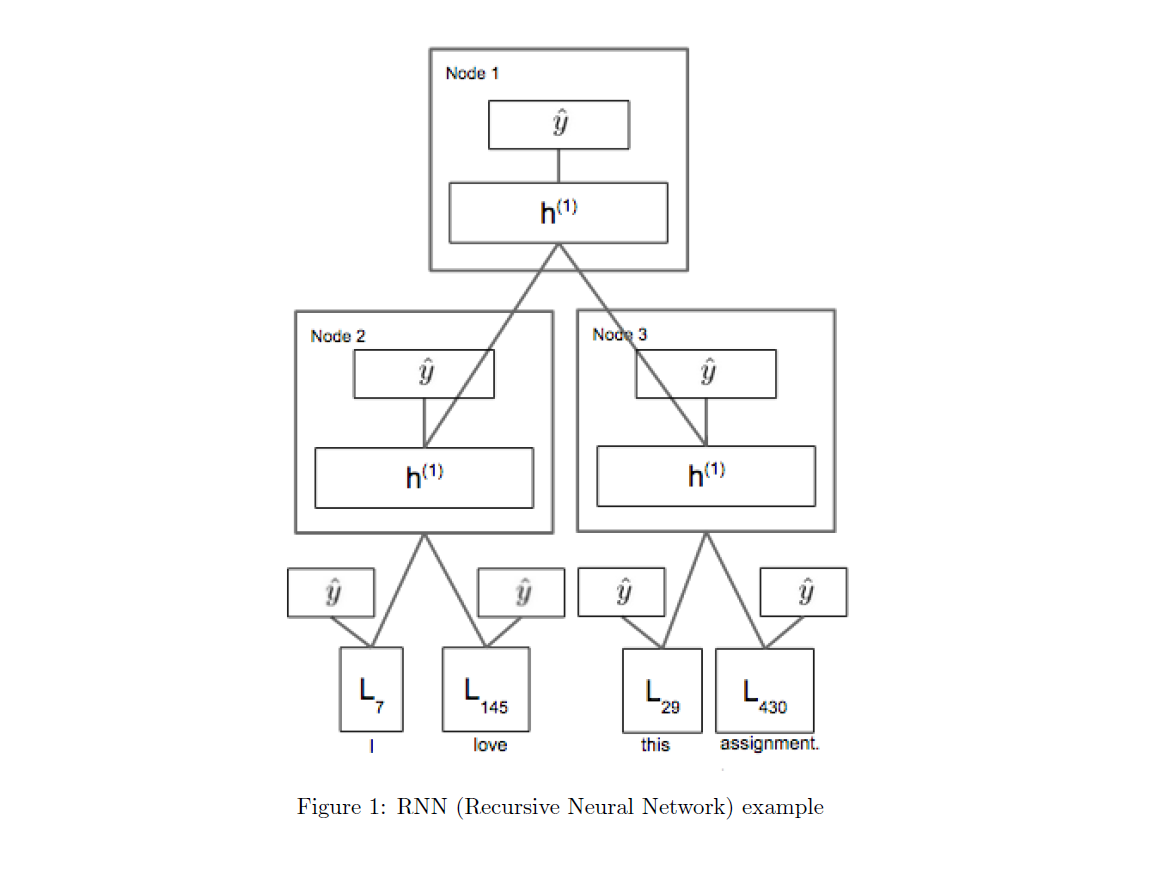
2、整个网络的结构如下图所示:
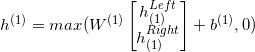

每个参数的更新时的梯队值如何计算,稍后再给大家计算相应的数学公式
这里先列出节点的合并规则
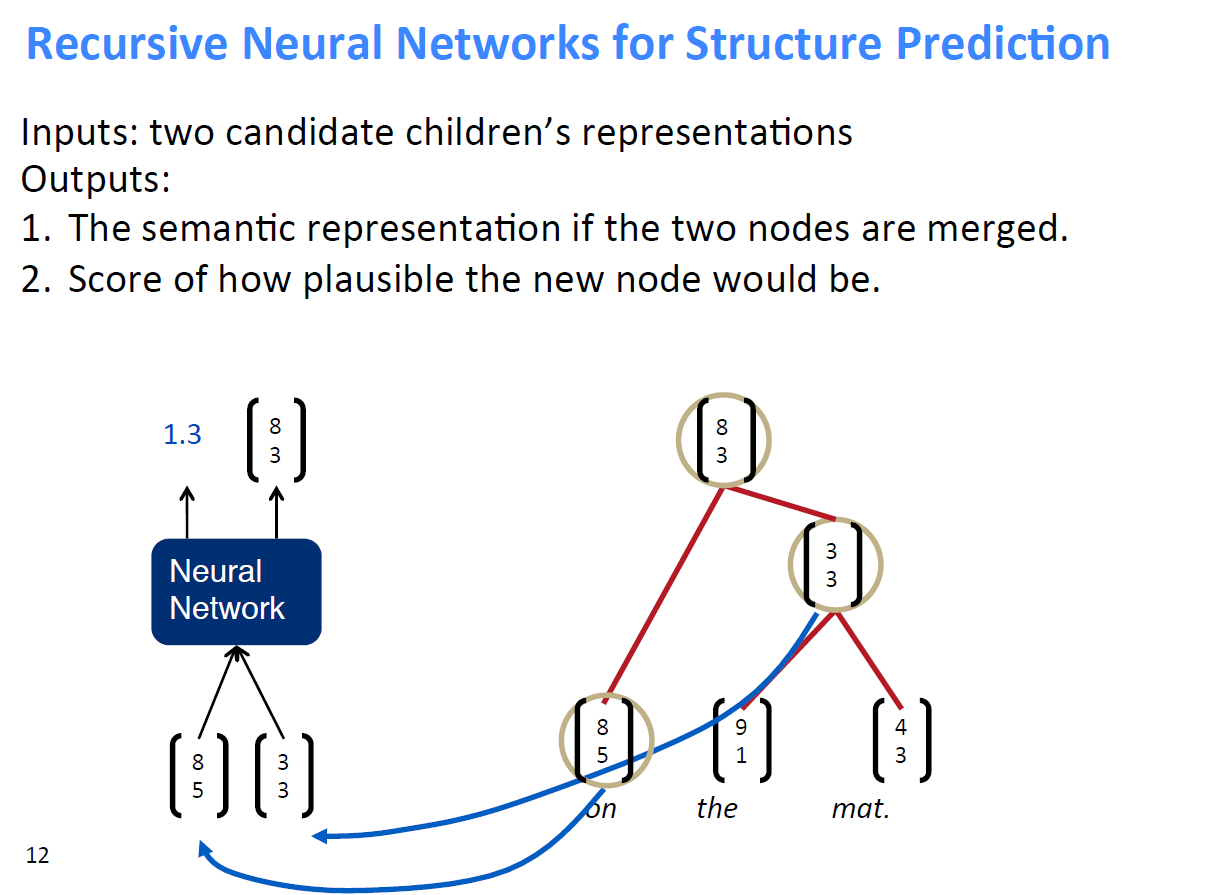

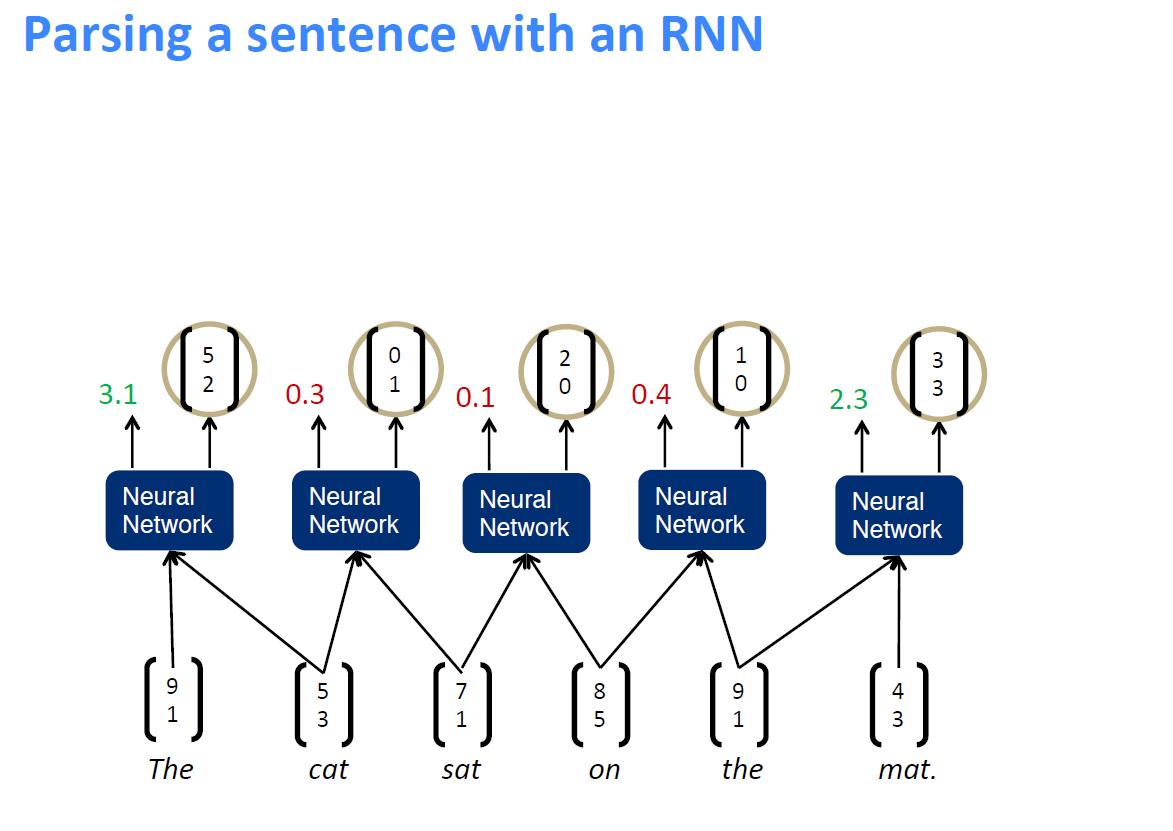
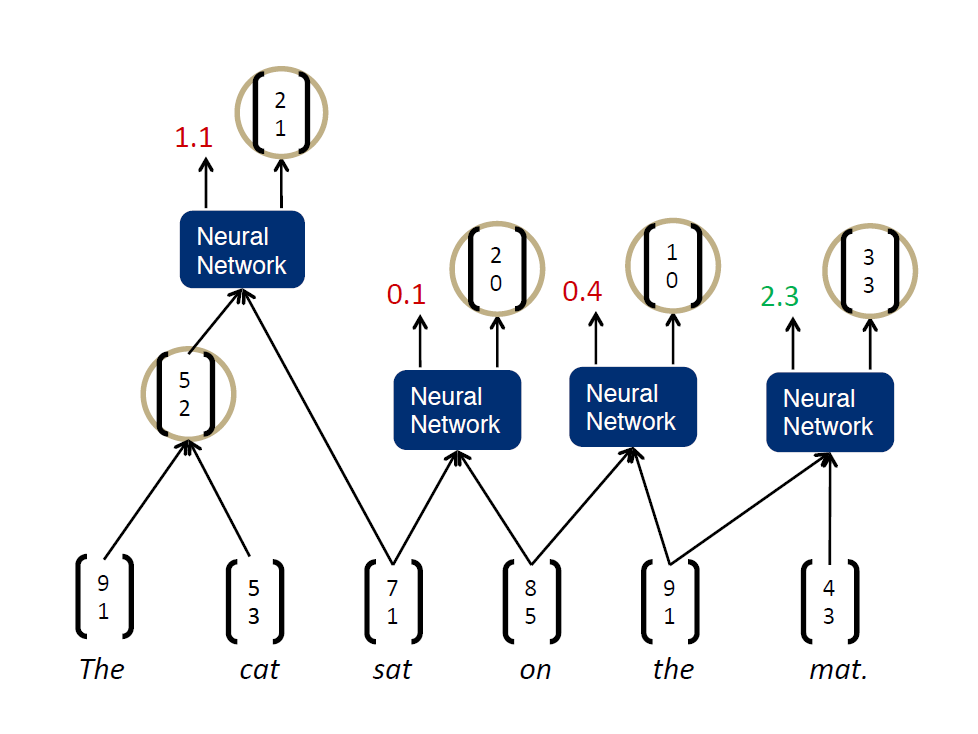
1、即假设将一句话中的词先两个合并,并通过神经网络计算出合并后的得分情况
2、然后找出合并后得分最高的两个词进行真正的合并,得到新的节点,其余节点不合并
3、将得到的新节点加入到下一轮两两合并的计算过程中,直至得到最终节点
下面是计算的代码:
''' Created on 2017年10月5日 @author: weizhen ''' # 一个简单的递归神经网络的实现,有着一个ReLU层和一个softmax层 # TODO : 必须要更新前向和后向传递函数 # 你可以通过执行 python rnn.py 方法来执行一个梯度检验 # 插入pdb.set_trace() 在你不确定将会发生什么的地方 import numpy as np import collections import pdb import tree as treeM import pickle class RNN: def __init__(self, wvecDim, outputDim, numWords, mbSize=30, rho=1e-4): self.wvecDim = wvecDim self.outputDim = outputDim self.numWords = numWords self.mbSize = mbSize self.defaultVec = lambda : np.zeros((wvecDim,)) self.rho = rho def initParams(self): np.random.seed(12341) # Word vectors self.L = 0.01 * np.random.randn(self.wvecDim, self.numWords) # Hidden layer parameters self.W = 0.01 * np.random.randn(self.wvecDim, 2 * self.wvecDim) self.b = np.zeros((self.wvecDim)) # Softmax weights # note this is " U "in the notes and the handout... # there is a reason for the change in notation self.Ws = 0.01 * np.random.randn(self.outputDim, self.wvecDim) self.bs = np.zeros((self.outputDim)) self.stack = [self.L, self.W, self.b, self.Ws, self.bs] # Gradients self.dW = np.empty(self.W.shape) self.db = np.empty((self.wvecDim)) self.dWs = np.empty(self.Ws.shape) self.dbs = np.empty((self.outputDim)) def costAndGrad(self, mbdata, test=False): """ 每一个datum在minibatch里边都是一个树 前向计算每一个树,反向传播到每一个树 返回值: cost: 梯度:w.r.t W,Ws,b,bs 以上变量的梯度都是在稀疏形式存储的 或者是以测试状态下的 Returns: cost,correctArray,guessArray,total """ cost = 0.0 correct = [] guess = [] total = 0.0 self.L, self.W, self.b, self.Ws, self.bs = self.stack # 初始化所有梯度都是0 self.dW[:] = 0 self.db[:] = 0 self.dWs[:] = 0 self.dbs[:] = 0 self.dL = collections.defaultdict(self.defaultVec) # 在每一个batch中前向计算每一个tree for tree in mbdata: c, tot = self.forwardProp(tree.root, correct, guess) cost += c total += tot if test: return (1. / len(mbdata)) * cost, correct, guess, total # 在每一个batch上进行反向传播 for tree in mbdata: self.backProp(tree.root) # 通过mb的大小来计算损失和梯度 scale = (1. / self.mbSize) for v in self.dL.values(): v *= scale # 添加L2正则化项 cost += (self.rho / 2) * np.sum(self.W ** 2) cost += (self.rho / 2) * np.sum(self.Ws ** 2) return scale * cost, [self.dL, scale * (self.dW + self.rho * self.W), scale * self.db, scale * (self.dWs + self.rho * self.Ws), scale * self.dbs] def forwardProp(self, node, correct=[], guess=[]): """损失应该是一个不断更新的变量,总损失是我们需要用在准确率报告里边的数据""" cost = total = 0.0 # 下面实现递归神经网络前向传播的函数 # 你应该更新 node.probs, node.hActsl,node.fprop,and cost # node :你当前节点是在语法树上的 # correct : 这是一个不断更新的标记真值的列表 # guess: 这是一个不断更新的猜测我们的模型会预测为哪一个结果的列表 # (我们会同时使用正确的和猜测的值来构造我们的混淆矩阵) L = self.L # 隐藏层的参数 W = self.W b = self.b # Softmax 权重 Ws = self.Ws bs = self.bs if node.isLeaf: node.hActsl = L[:, node.word] else: if not node.left.fprop: cost_left, total_left = self.forwardProp(node.left, correct, guess) cost += cost_left total += total_left if not node.right.fprop: cost_right, total_right = self.forwardProp(node.right, correct, guess) cost += cost_right total += total_right node.hActsl = W.dot(np.hstack((node.left.hActsl, node.right.hActsl))) + b node.hActsl[node.hActsl < 0] = 0 x = Ws.dot(node.hActsl) + bs x -= np.max(x) node.probs = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x)) correct += [node.label] guess += [np.argmax(node.probs)] cost -= np.log(node.probs[node.label]) node.fprop = True return cost, total + 1 def backProp(self, node, error=None): """ 实现递归神经网络的反向传播函数 应该更新 self.dWs, self.dbs, self.dW, self.db, and self.dL[node.word] 相关地 node:你在语法树种的当前节点 error:误差从之前一个迭代过程中传递进来的 """ # 清空节点 node.fprop = False L = self.L # 隐藏节点的参数 W = self.W b = self.b # Softmax层的权重 Ws = self.Ws bs = self.bs error_this = node.probs error_this[node.label] -= 1.0 delta = Ws.T.dot(error_this) self.dWs += np.outer(error_this, node.hActsl) self.dbs += error_this if error is not None: delta += error delta[node.hActsl == 0] = 0 if node.isLeaf: self.dL[node.word] += delta else: self.dW += np.outer(delta, np.hstack([node.left.hActsl, node.right.hActsl])) self.db += delta delta = np.dot(self.W.T, delta) self.backProp(node.left, delta[:self.wvecDim]) self.backProp(node.right, delta[self.wvecDim:]) def updateParams(self, scale, update, log=False): """ 如下这样更新参数 p:=p-scale*update 如果log是真的,输出根节点的均方误差,并且更新根节点的值 """ if log: for P, dP in zip(self.stack[1:], update[1:]): pRMS = np.sqrt(np.mean(P ** 2)) dpRMS = np.sqrt(np.mean((scale * dP) ** 2)) print("weight rms=%f -- update rms=%f" % (pRMS, dpRMS)) self.stack[1:] = [P + scale * dP for P, dP in zip(self.stack[1:], update[1:])] # 解决词典并且进行稀疏的更新 dL = update[0] for j in dL.iterkeys(): self.L[:, j] += scale.dL[j] def toFile(self, fid): pickle.dump(self.stack, fid) def fromFile(self, fid): self.stack = pickle.load(fid) def check_grad(self, data, epsilon=1e-6): cost, grad = self.costAndGrad(data) err1 = 0.0 count = 0.0 print("Checking dW...") for W, dW in zip(self.stack[1:], grad[1:]): W = W[..., None] dW = dW[..., None] for i in range(W.shape[0]): for j in range(W.shape[1]): W[i, j] += epsilon costP, _ = self.costAndGrad(data) W[i, j] -= epsilon numGrad = (costP - cost) / epsilon err = np.abs(dW[i, j] - numGrad) err1 += err count += 1 if 0.001 > err1 / count: print("Grad Check Passed for dW") else: print("Grad Check Failed for dW:Sum of Error=%.9f" % (err1 / count)) # check dL separately since dict dL = grad[0] L = self.stack[0] err2 = 0.0 count = 0.0 print("Checking dL...") for j in dL.keys(): for i in range(L.shape[0]): L[i, j] += epsilon costP, _ = self.costAndGrad(data) L[i, j] -= epsilon numGrad = (costP - cost) / epsilon err = np.abs(dL[j][i] - numGrad) err2 += err count += 1 if 0.001 > err2 / count: print("Grad Check Passed for dL") else: print("Grad Check Failed for dL: Sum of Error = %.9f" % (err2 / count)) if __name__ == '__main__': train = treeM.loadTrees() numW = len(treeM.loadWordMap()) wvecDim = 10 outputDim = 5 rnn = RNN(wvecDim, outputDim, numW, mbSize=4) rnn.initParams() mbData = train[:4] print("Numerical gradient check...") rnn.check_grad(mbData)
下面部分是构造节点的python文件tree.py
在进行计算时需要先运行tree.py文件进行tree结构的生成,然后进行合并计算
import collections import pickle UNK = 'UNK' # This file contains the dataset in a useful way. We populate a list of Trees to train/test our Neural Nets such that each Tree contains any number of Node objects. # The best way to get a feel for how these objects are used in the program is to drop pdb.set_trace() in a few places throughout the codebase # to see how the trees are used.. look where loadtrees() is called etc.. class Node: # a node in the tree def __init__(self,label,word=None): self.label = label self.word = word # NOT a word vector, but index into L.. i.e. wvec = L[:,node.word] self.parent = None # reference to parent self.left = None # reference to left child self.right = None # reference to right child self.isLeaf = False # true if I am a leaf (could have probably derived this from if I have a word) self.fprop = False # true if we have finished performing fowardprop on this node (note, there are many ways to implement the recursion.. some might not require this flag) self.hActs1 = None # h1 from the handout self.hActs2 = None # h2 from the handout (only used for RNN2) self.probs = None # yhat class Tree: def __init__(self,treeString,openChar='(',closeChar=')'): tokens = [] self.open = '(' self.close = ')' for toks in treeString.strip().split(): tokens += list(toks) self.root = self.parse(tokens) def parse(self, tokens, parent=None): assert tokens[0] == self.open, "Malformed tree" assert tokens[-1] == self.close, "Malformed tree" split = 2 # position after open and label countOpen = countClose = 0 if tokens[split] == self.open: countOpen += 1 split += 1 # Find where left child and right child split while countOpen != countClose: if tokens[split] == self.open: countOpen += 1 if tokens[split] == self.close: countClose += 1 split += 1 # New node node = Node(int(tokens[1])) # zero index labels node.parent = parent # leaf Node if countOpen == 0: node.word = ''.join(tokens[2:-1]).lower() # lower case? node.isLeaf = True return node node.left = self.parse(tokens[2:split],parent=node) node.right = self.parse(tokens[split:-1],parent=node) return node def leftTraverse(root,nodeFn=None,args=None): """ Recursive function traverses tree from left to right. Calls nodeFn at each node """ nodeFn(root,args) if root.left is not None: leftTraverse(root.left,nodeFn,args) if root.right is not None: leftTraverse(root.right,nodeFn,args) def countWords(node,words): if node.isLeaf: words[node.word] += 1 def clearFprop(node,words): node.fprop = False def mapWords(node,wordMap): if node.isLeaf: if node.word not in wordMap: node.word = wordMap[UNK] else: node.word = wordMap[node.word] def loadWordMap(): with open('wordMap.bin','rb') as fid: return pickle.load(fid) def buildWordMap(): """ Builds map of all words in training set to integer values. """ file = 'trees/train.txt' print("Reading trees to build word map..") with open(file,'r') as fid: trees = [Tree(l) for l in fid.readlines()] print("Counting words to give each word an index..") words = collections.defaultdict(int) for tree in trees: leftTraverse(tree.root,nodeFn=countWords,args=words) wordMap = dict(zip(words.keys(),range(len(words)))) wordMap[UNK] = len(words) # Add unknown as word print("Saving wordMap to wordMap.bin") with open('wordMap.bin','wb') as fid: pickle.dump(wordMap,fid) def loadTrees(dataSet='train'): """ Loads training trees. Maps leaf node words to word ids. """ wordMap = loadWordMap() file = 'trees/%s.txt'%dataSet print("Loading %sing trees.."%dataSet) with open(file,'r') as fid: trees = [Tree(l) for l in fid.readlines()] for tree in trees: leftTraverse(tree.root,nodeFn=mapWords,args=wordMap) return trees if __name__=='__main__': buildWordMap() train = loadTrees() print("Now you can do something with this list of trees!")
更详细的代码请参考github:
https://github.com/weizhenzhao/cs224d_problem_set3