
测试工具使用递归的方式获取子进程的Msg消息,目前有2种常用的ExecutorService / ForkJoinPool
为了测试哪种效果较好,我们来写个测试Demo,循环5555555次+1(加锁),统计每种执行耗时
int nCpu = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
ExecutorService executorPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nCpu);
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(nCpu);
TestData:5555555 , RunTime:1543 ms :ExecutorService executorPool
TestData:5555555 , RunTime:746 ms :ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool
结果很明显,递归线程池使用ForkJoinPool更佳,2倍的执行效率
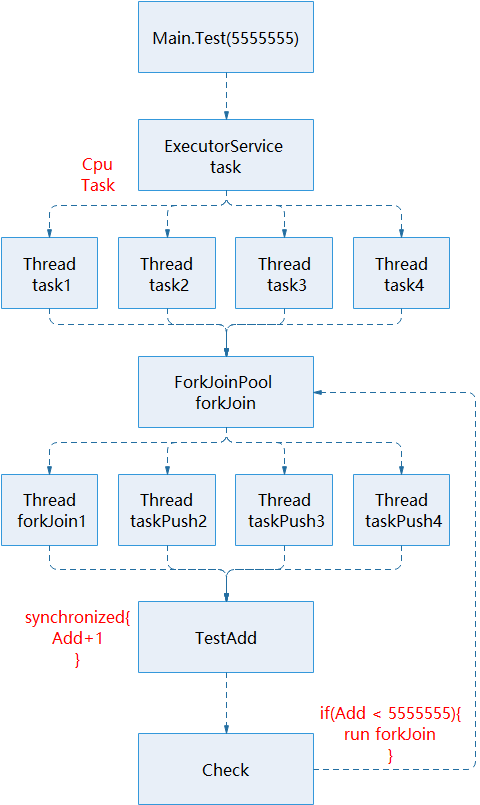
测试流程图
1 package test; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 5 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 6 import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; 7 8 /** 9 * 10 * @author weimjsam 11 */ 12 public class TestThrad { 13 14 public int addNum = 0; 15 16 //get cpu 17 int nCpu = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); 18 19 //Thread 20 ExecutorService taskPush = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nCpu); 21 ExecutorService executorPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nCpu); 22 ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(nCpu); 23 24 private void TaskPush(int iTestAdd) { 25 CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { 26 27 for (int i = 0; i < nCpu; i++) { 28 CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> TestRun(iTestAdd), forkJoinPool); 29 } 30 31 }, taskPush); 32 } 33 34 private void TestRun(int iTestAdd) { 35 CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> TestAdd(iTestAdd), forkJoinPool) 36 .thenRun(() -> CheckOver(iTestAdd)); 37 } 38 39 private void TestAdd(int iTestAdd) { 40 synchronized (this) { 41 if (addNum < iTestAdd) { 42 addNum = addNum + 1; 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 47 private void CheckOver(int iTestAdd) { 48 if (addNum < iTestAdd) { 49 TestRun(iTestAdd); 50 } 51 } 52 53 public void Test(int iTestMax) { 54 TaskPush(iTestMax); 55 } 56 57 }