如果想要python 文件展示两个窗口的方法

导入模块的顺序的讲解 建立一个a文件 输入print('哈哈哈哈') 在建立一个b文件 import a b文件会打印a文件的方法
输入import sdsdsadsa 这个就找不到为什么呢,这是因为impoer 导入的逻辑为
导入模块先从当前目录下找文件 ,找不到就去环境变量找 当前目录的截图为
import sys
print(sys.path) 查看python的环境变量
sys.path.append(r'G:untitled2cesces22.py') 加环境变量
import sys
sys.path.insert(0,r'G:untitled2cesces22.py') 在第一位看到 如果在pycharm 直接make操作就可以导入不标红
print(sys.path)
导入模块有两种方式 model是一个py文件 里面封装了方法
import my_model
print(my_model.name) 点的方式
my_model.my_func() 这也可以
也可另一种方式
from my_model import name as nhy_name, my_func as my_func2 as 就是起别名字
if __name__ == '__main__': 这行代码的作用
a = 1
def execute_sql(sql):
print('执行sql',sql)
print('__name__',__name__)
#__name__ 当前py文件的名字
if __name__ == '__main__':
execute_sql('select')
execute_sql('update')
execute_sql('insert')
execute_sql('sdfsd sdfsg')
a文件代码存数据库操作 b文件导入a文件的execute_sql('select')方法 如果不加if _name会执行下面的代码
如果加了就只执行你调用的代码
#如果这一个文件运行 一点用也没有,因为我自己用,什么时候有用,我自己用下面是我调试的调用代码方法
#什么时候有用比如你写一个数据库的操作 你自己写完要测试 ,你没问题要提交 ,这时候另一个人操作导入你的模块呢,因为导入模块
# 代码会执行一遍从头到尾,如果你不写if__name__就会被执行 ,
# 总结准确的描述
如果我在a.py文件下 想导入dd文件夹下的c.py的os函数 如何调用呢
import sys,json
# 导入模块很重要
# import my_model
# my_model.my_func()
#第一种方法将目录加入环境变量,加入环境变量两种方法,一种sys.append 一种是直接手动加目录,导入文件名字使用.方法调用函数 使用import 就可以.
#第二种方法from my_model impore name 这种方法不需要.直接拿过来用
from my_model import name,my_func
my_func()
# 两种方法的前提都需要加入环境变量
python 安装模块操作
c:/python/#安装目录
c:/python/Scripts #安装目录下的scripts
装完python 这两个目录要加入环境变量
就可以在cmd输入pip 安装模块 前提要先把修改pip 源文件
内置函数的操作
查看当前环境变量命令
import sys
print(sys.path)
如果导入文件 标红的话可以将这个文件目录加入环境变量,这时候就不会标红了

import random,string
print(random.randint(1,10))#1-10随机取一个数字
print(random.uniform(1,10))#随机小数
print(random.choice(string.digits))#随机选择一个 可能会有重复
print(random.sample(string.digits,10))#随机取多个转成集合 不会有重复
l=[1,2,3,45]
random.shuffle(l)#洗牌
print(l)
根据字典进行key和value排序
os模块的操作
# print(os.listdir('/Users/nhy/PycharmProjects/tmz-code') )#获取某个目录下的内容
# os.mkdir('python')
# os.mkdir('python/day2')
# os.mkdir('python/day3')
# os.makedirs('java/day1')
# os.makedirs('java/day2')
# os.makedirs('java/day3') #父目录不存在的时候,会创建父目录
# os.remove('python') #删除文件,不能删除文件夹
# os.rmdir('java')#删除空文件夹的
# os.rename('java','python') #重命名,文件和文件夹都可以
# print(os.getcwd())#获取当前所在的目录
# os.chdir('/Users/nhy/PycharmProjects/tmz-code')#进入到某个目录里面
# os.mkdir('java')
# print(os.getcwd())
# print(os.environ)#获取系统环境变量里面配置的内容
# result = os.system('sgw3dsgs') #执行操作系统命令的,它只能帮你执行,不能拿到命令的结果
#它返回的是命令执行是否成功,如果返回的是0,代表执行成功
# print('!!!!!!!!!',result)
# result = os.popen('ifconfig').read()
# print('result,,',result)
# os.path.join()
# os.path.abspath()
# os.path.split()
# os.path.dirname()
# os.walk()
# print(os.path.sep)#当前系统的路径分隔符
# print(os.path.isfile('a.py')) #是否为文件
# print(os.path.isdir('a.py')) #是否为文件夹
# print(os.path.exists('a.py')) #文件/文件夹是否存在
# print(os.path.getsize('a.py')) #获取大小
# print(os.path.getctime('a.py')) #创建时间
# print(os.path.getmtime('a.py')) #修改时间
# print(os.path.getatime('a.py')) #最后一个访问时间
# print(os.path.split('/Users/nhy/PycharmProjects/tmz-code/day5/a.py'))
#分隔路径和文件名的
# p = 'e:'+os.path.sep+'movies'+os.path.sep+'欧美大片'
# print(p)
# print(os.path.join('e:','movies','欧美大片','复仇者联盟.mp4'))
#拼接路径
# print(os.path.abspath(r'../day4/a.json')) #把相对路径,转换成绝对路径
#/Users/nhy/PycharmProjects/tmz-code/day4/a.json
#
# print(os.path.dirname(r'/Users/nhy/PycharmProjects/tmz-code/day4/a.json') )#取父目录
#e:xxxpythonsqls
for cur_path,dirs,files in os.walk(r'/Users/nhy/'):
print('当前在%s目录下查找'%cur_path)
for file in files:
if file.endswith('.mp4') or file.endswith('.avi'):
print('发现小电影在%s目录下'%cur_path)
break
查找文件的方法
import os
for cur_path,dirs,files in os.walk(r'C:UsersAdministratorPycharmProjectsuntitled6day5'):
# print(cur_path,dirs,files)
print('当前在%s目录下查找'%cur_path)
#会一次循环所有目录和文件名字和文件
for file in files:#查找文件的方法
if file.endswith('.mp4')or file.endswith('.avi'):
print('发现小电影的目录'%(cur_path))
break
时间的操作的处理方法
常用问题给你个时间,让你计算出28天后的时间的打印出来怎么办?时间戳就是写死的每过1s加1
我想机算十天后过了多少秒 一天24小时*60分钟*60s
原理
#算出八天后的格式化好的时间比如 2020-11-24
print(a+60*60*24*8)
#60*60*24*8 8天 一天24小时 一小时60分钟 一分钟60s
#时间戳转格式化好的时间
import time
print(time.time())#当前的时间戳
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))#当前时间
seven=int(time.time())+60*60*24*7 算出七天后的时间
str_time = '2020-08-29 17:31:02'
str_time2 = '2020-08-29'
time_stamp = 1599298262
时间元组
时间戳转格式化好的时间 传一个时间戳 1603123200
lt = time.localtime(time_stamp) #当前时区的时间
bt = time.gmtime(time_stamp) #标准时区的时间
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',lt))
格式化好的时间转时间戳 传一个时间 2020-10-20
time_tuple = time.strptime(str_time,'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
time_stamp_nwo = time.mktime(time_tuple)
print(time_stamp_nwo)
原理先转成时间元组,转成时间戳和时间
写成两个封装的函数 ,方便以后的调用
根据学习的写两个作业
1、写一个删除日志的脚本,把三天前的日志并且为空的日志删除
分析这个该如何写
# 1、写一个删除日志的脚本,把三天前的日志并且为空的日志删除
#思路 写一个将时间转成时间戳的函数 ,定义一个变量接收三天前的时间戳
#取到目录下的文件,然后分割取出时间
#拼接路径 判断下 如果文件小于三天前并且文件等于空的删除
import os,time
day=60*60*24*3 #定义三天前常量
def stram(data,frm='%Y-%m-%d'):#写一个时间格式转时间戳的函数
time_tuple = time.strptime(data,frm)
return int(time.mktime(time_tuple))
def clean_log(log):
if os.path.isdir(log):
for cur_path, dirs, files in os.walk(log):
for i in files:
file_time=i.split('.')[0].split('_')[1]#分割出来日期
file_time_sp=stram(file_time)#取当前目录下时间戳
cur_time=time.time()-day#三天前的时间戳
file_abs=os.path.join(cur_path,i)#拼接文件路径这里不会了
if file_time_sp<cur_time or os.path.getsize(file_abs)==0:#当前的时间小于三天前的文件会删除判断为文件目录大小为空的
os.remove(file_abs)
else:
print('路径错误')
clean_log(r'C:Usersv-dongchunguangPycharmProjectsuntitled复习day5练习logs')
写一个双色球的函数
思路
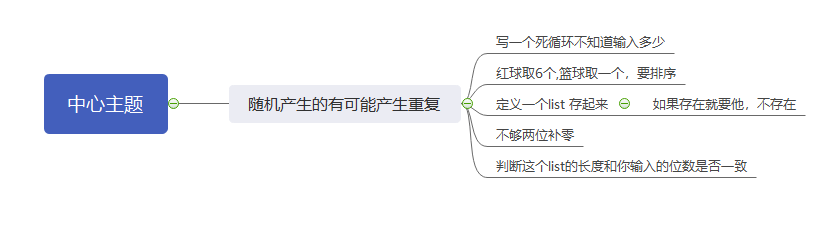
要求
import random,string
shuang=[]
name=input('输入产生位数').strip()
while True:#一直请求
a=random.sample(range(1,34),6)
a.sort()
b=random.sample(range(1,18),1)
c=a+b
result=[str(i).zfill(2) for i in c] #列表生成式把他加入一个list
sq=''.join(result)#将list转成字符串
if sq not in shuang:
shuang.append(sq)
print('产生的红球是%s,篮球是%s'%(result[:6],result[-1]))
if int(name)==len(shuang):#避免少位数
break
方法第二个
把商品管理写成数据库的形式
2、修改商品管理的作业,把数据改为从数据库中获取,
需要自己建表
import tools
def get_single_product(name): #判断输入的内容是否存在数据库的表里
sql = 'select * from tmz_ljj_commodity where trade_name = "%s";' % name
return tools.execute_sql(sql)
def is_digit(number):
s = str(number)
if s.isdigit():
if int(s) > 0:
return True
def is_price(price): #>0的整数和小数都可以 #1.7
s = str(price)
if is_digit(s):
return True
else:
if s.count('.') == 1: # 1.3
left, right = s.split('.')
if left.isdigit() and right.isdigit(): # 正小数 #0.0
if float(s)>0:
return True
def show_product():
product_name = input('请输入商品名称:').strip()
if product_name:
if product_name == 'all':
sql = 'select * from tmz_ljj_commodity;'
print(tools.execute_sql(sql))
else:
product = get_single_product(product_name)
if product:
print('商品信息:',product)
else:
print('你输入的商品不存在')
else:
print('不能为空')
def add_product():
product_name = input('请输入商品名称:').strip()
price = input('请输入商品价格:').strip()
count = input('请输入商品数量:').strip()
if product_name and price and count:
if is_price(price) and is_digit(count):
if get_single_product(product_name):
print('商品已经存在')
else:
insert_sql = 'insert into tmz_ljj_commodity (trade_name,count,price) '
'values ("%s",%s,%s);' % (product_name, count, price)
tools.execute_sql(insert_sql)
print('商品新增成功!')
else:
print('价格/数量不合法')
else:
print('不能为空')
def modify_product():
product_name = input('请输入商品名称:').strip()
price = input('请输入商品价格:').strip()
count = input('请输入商品数量:').strip()
if product_name and price and count:
if is_price(price) and is_digit(count):
if get_single_product(product_name):
sql = 'update tmz_ljj_commodity set price=%s,count=%s where trade_name="%s";' %(
price,count,product_name
)
tools.execute_sql(sql)
print('商品修改成功')
else:
print('商品不存在')
else:
print('价格/数量不合法')
else:
print('不能为空')
def delete_product():
product_name = input('请输入商品名称:').strip()
if product_name:
if get_single_product(product_name):
sql='delete from tmz_ljj_commodity where trade_name="%s"; ' % product_name
tools.execute_sql(sql)
print('商品已删除')
else:
print('商品不存在')
else:
print('不能为空')
choice = input('1、查看商品 2、新增 3、修改 4、删除: ')
func_map = {'1':show_product,'2':add_product,'3':modify_product,'4':delete_product}
if choice in func_map:
func_map[choice]()
else:
print('请输入正确的选项!')
# if choice == '1':
# show_product()
# elif choice == '2':
# add_product()