1 正则表达式
在Python中正则表达式库需要导入re库
import re
正则表达式需要使用原生字符串来表达, 原生字符串(raw shtring)在普通的字符串前面加 r 表示
1.1 正则表达式的主要功能函数

search(pattern, string, flags=0)
search用于在字符串中搜索, 并且返回第一个位置的match对象
pattern: 正则表达式字符串
string: 待匹配的字符串
flags: 控制标记
re.I 忽略大小写
re.M ^能够将每行当做匹配的开始
re.S 能够匹配所有字符 (正常.只能匹配出换行以外的所有)
match(pattern, string, flahs=0)
从字符串开始匹配,是匹配, 如果不匹配的话就返回None, 匹配返回match对象
三个参数与search()相同
findall(pattern, string, flahs=0)
与search()不同, findall()会查找到所有满足匹配的, 且返回匹配的字符串形成的列表
三个参数与search()相同
split(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0)
是根据正则表达式来分割字符串, 形成一个列表返回
相同三个参数用法不变
maxsplit: 是最大分割数, 超过之后会吧剩余的作为一个元素输出
finditer(pattern, string, flahs=0)
功能与findall()一致, 只是返回迭代器内含match对象
三个参数与search()相同
sub(pattern, repl, string, count, flahs=0)
将匹配成功的字符串替换成repl
相同三个参数用法不变
repl: 替换成的字符串
count: 最大替换次数
subn(pattern, repl, string, count, flahs=0)
这个功能参数都和sub()相同, 只是结果是一个元组, 第一个元素是结果, 第二个元素是替换的次数
主要, re库的等价形式:
>>> rst = re.search(r'[1‐9]d{5}', 'BIT 100081')
等同于
>>> pat = re.compile(r'[1‐9]d{5}')
>>> rst = pat.search('BIT 100081')
如果利用compile()方法的话, 上述的方法就少写第一个参数
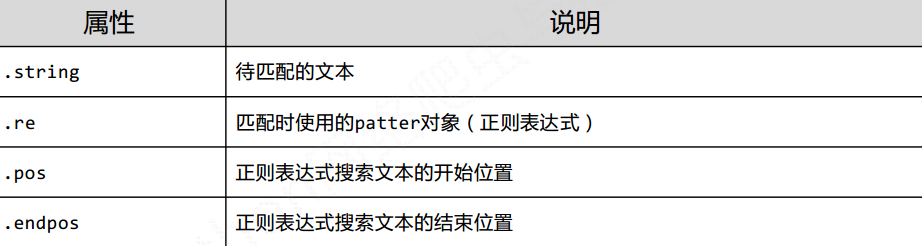
1.2 Match对象的介绍
Match有以下属性
Match对象的方法

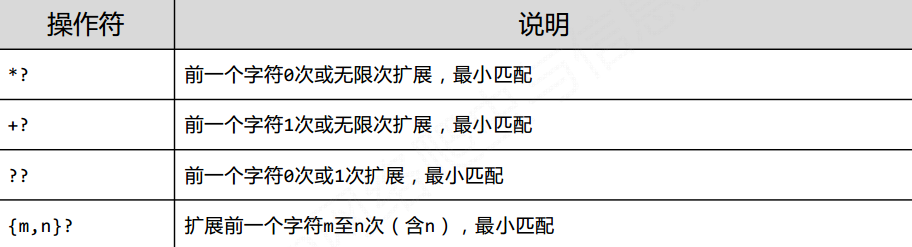
1.3 贪婪匹配
在默认的情况下, Python的正则匹配是贪婪匹配, 但是也有用的到最少匹配的情况, 此时需要使用?来标识
具体形式如下
2 淘宝商品价格的爬取
通过正则表达式匹配淘宝网页, 来获取商品价格和商品名称
观察淘宝页面发现https://s.taobao.com/search?q=后面紧跟搜索关键字
在url之后还有个&s表示翻页
观察具体页面

因而获得的商品名称和价格就可以通过正则表达式获取
具体代码如下
import requests
import re
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return ""
def parsePage(ilt, html):
try:
plt = re.findall(r'"view_price":"[d.]*"', html)
tlt = re.findall(r'"raw_title":".*?"', html)
for i in range(len(plt)):
price = eval(plt[i].split(':')[1])
title = eval(tlt[i].split(':')[1])
ilt.append([price, title])
except:
print("")
def printGoodsList(ilt):
tplt = "{:4} {:8} {:16}"
print(tplt.format("序号", "价格", "商品名称"))
count = 0
for g in ilt:
count = count + 1
print(tplt.format(count, g[0], g[1]))
def main():
goods = '书包'
depth = 3
start_url = 'https://s.taobao.com/search?q=' + goods
infoList = []
for i in range(depth):
try:
url = start_url + '&s=' + str(44 * i)
html = getHTMLText(url)
parsePage(infoList, html)
except:
continue
printGoodsList(infoList)
main()
实例二: 通过re库获得京东商品的价格, 通过BeautifulSoup来获取商品信息
京东的链接地址为: https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=
后面输入的关键字由于编码原因最好使用英文关键字如notebook等
经过分析页面处理, 有

具体源码为
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__author__ = 'weihuchao'
import re
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import bs4
def getUrl(url):
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
print("获取网页失败")
def getInfo(nList, pList, content):
soup = BeautifulSoup(content, "html.parser")
ptl = re.findall(r'data-price="[0-9.]*"', content)
for item in ptl:
price = eval( item.split('=')[1] )
pList.append(price)
for lis in soup.find('ul', attrs={'class':'gl-warp clearfix'}).children:
if isinstance(lis, bs4.element.Tag):
name = lis.find('a').attrs['title']
nList.append(name)
def printList(nList, pList):
tpl = "{0:<10} {1:<120} {2:<10}"
print(tpl.format("序号", "商品名称", "价格"))
allList = zip(nList, pList)
count = 0
for item in allList:
count += 1
print(tpl.format(count, item[0], item[1]))
def main():
nList, pList = [], []
keyword = "mac"
url = "https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=" + keyword
content = getUrl(url)
getInfo(nList, pList, content)
printList(nList, pList)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()