今天继续研究管道,话不多说,言归正传:
对于管道,有一定的读写规则,所以这里主要是对它的规则进行探讨,具体规则如下:
规则一:

下面用程序来验证下,还是用上节学的子进程写数据,父进程读取数据的例子,只是基于这个程序进行修改来解释上面的理论,先看一下这个原程序:
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) do { perror(m); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while(0) int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int pipefd[2]; if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) ERR_EXIT("pipe error"); pid_t pid; pid = fork(); if (pid == -1) ERR_EXIT("fork error"); if (pid == 0) { close(pipefd[0]); write(pipefd[1], "hello", 5); close(pipefd[1]); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } close(pipefd[1]); char buf[10] = {0}; int ret = read(pipefd[0], buf, 10); if (ret == -1) ERR_EXIT("read error"); printf("buf=%s ", buf); return 0; }
编译运行:

先来验证第一条理论,"O_NONBLOCK disable:read调用阻塞,即进程暂停执行,一直等到有数据来到为止",为了看到效果,我们在子进程里写数据之前休眠3秒中,这样父进程在读取数据时就是一个没有数据状态,如下:

编译运行:

从运行效果来看,在没有发送数据之前的3秒,父进程读取状态是阻塞的,直到子进程写了数据,这是默认的行为。
下面,再来验证“O_NONBLOCK enable:read调用返回-1,errno值为EAGAIN”这条理论,所以我们将read的文件描述符设置为非阻塞模式(O_NONBLOCK),如下:

编译运行:

可见,在非阻塞模式下,read时会错误提示。
规则二:

具体代码如下:
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) do { perror(m); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while(0) int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int pipefd[2]; if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) ERR_EXIT("pipe error"); pid_t pid; pid = fork(); if (pid == -1) ERR_EXIT("fork error"); if (pid == 0) { close(pipefd[1]);//子进程关闭了管道对应的写端 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } close(pipefd[1]);//父进程关闭了管道对应的写端 sleep(1); char buf[10] = {0}; int ret = read(pipefd[0], buf, 10);//这时看一下读端返回值 printf("ret = %d ", ret); return 0; }
编译运行:

从结果中可以看出,确实是这样。
规则三:

具体代码如下:
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) do { perror(m); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while(0) int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int pipefd[2]; if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) ERR_EXIT("pipe error"); pid_t pid; pid = fork(); if (pid == -1) ERR_EXIT("fork error"); if (pid == 0) { close(pipefd[0]);//子进程关闭读端 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } close(pipefd[0]);//父进程也关闭读端 sleep(1);//休眠一秒也就是为了让子进程代码执行了close操作 int ret = write(pipefd[1], "hello", 5);//看下是否会产生SIGPIPE,而默认它的行为就是终止当前进程 if (ret == -1) printf("write error "); return 0; }
编译运行:

从运行结果来看,确实wirte error没有执行到,是因为write操作产生了SIGPIPE信号,从这个运行结果可能不是很确实就是产生了这个信号,那我们改变一下SIGPIPE的默认行为,就能知道了,修改代码如下:

编译运行:

规则四:

先来验证第一条理论,"O_NONBLOCK disable: write调用阻塞,直到有进程读走数据",实验原理很简单,就是不断往管道里面写东西,因为默认就是阻塞模式,所以看一下当管道满的时候,是否阻塞了,具体代码如下:
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) do { perror(m); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while(0) int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int pipefd[2]; if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) ERR_EXIT("pipe error"); int ret; int count = 0;//计划一下管道的大小,每写一个字符进行累加 while (1) {//不断往管道里面写东西 ret = write(pipefd[1], "A", 1); if (ret == -1) { printf("err=%s ", strerror(errno)); break; } count++; } printf("count=%d ", count); return 0; }
编译运行:

从运行结果来看,确实是阻塞了,我们打印管道大小的语句也没打印出来,论证了第一条观点,接下来来论证第二个观点:"O_NONBLOCK enable:调用返回-1,errno值为EAGAIN",实验原理就是将管道的写端描述符改成非阻塞模式,看下这次还会阻塞么?如果不阻塞了,那管道的最大容量是多少呢?具体代码如下:
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) do { perror(m); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while(0) int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int pipefd[2]; if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) ERR_EXIT("pipe error"); int ret; int count = 0;//计划一下管道的大小,每写一个字符进行累加 int flags = fcntl(pipefd[1], F_GETFL); fcntl(pipefd[1], F_SETFL, flags | O_NONBLOCK);//将写端改为非阻塞模式 while (1) {//不断往管道里面写东西 ret = write(pipefd[1], "A", 1); if (ret == -1) { printf("err=%s ", strerror(errno)); break; } count++; } printf("count=%d ", count); return 0; }
编译运行:

这次,可以清晰地看到,当管道写满时是不会阻塞的,且返回了错误码为EAGAIN,而且可以看到管道的最大容量为65536个字符,也就是64K的容量,实际上,关于这个,可以在man帮助中查找到:

最后一个规则:

【说明】:上图中提示的"写入原子性"是指:如果写入的数据量不大于PIPE_BUF,假如有两个进程同时往管道中写入数据,意味着第一个进程写入的数据是连续的,也就是中途不会插入第二个进程写入的数据,有点类似于线程的同步机制,同理不保证写入的原子性也就明白了。另外PIPE_BUF的大小是多少呢?咱们先来打印一下它的值:
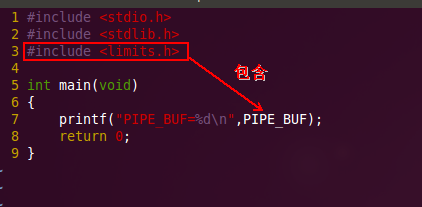
运行:

关于这个规则要难理解一些,没事,下面会用实例代码来一一验证上面的观点:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <errno.h> #include <fcntl.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) do { perror(m); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while(0) #define TEST_SIZE 68*1024//定义一个68K大小的缓冲区,以便撑爆管道的PIP_BUF大小的容量来看其是否保证原子性 int main(void) { char a[TEST_SIZE]; char b[TEST_SIZE];//定义了两个缓冲区,都是68K的大小 memset(a, 'A', sizeof(a));//将a缓冲区内容都初使化为A memset(b, 'B', sizeof(b));//将b缓冲区内容都初使化为A int pipefd[2]; int ret = pipe(pipefd);//创建一个管道 if (ret == -1) ERR_EXIT("pipe error"); pid_t pid; pid = fork(); if (pid == 0) {//第一个子进程 close(pipefd[0]); ret = write(pipefd[1], a, sizeof(a));//往管道中写入a缓冲区,看一下这个数据是连续的么?还是被下面第二个进程的数据给穿插了 printf("apid=%d write %d bytes to pipe ", getpid(), ret); exit(0); } pid = fork(); if (pid == 0) { //第二个子进程式,代码跟第一个子进程的类似 close(pipefd[0]); ret = write(pipefd[1], b, sizeof(b)); printf("bpid=%d write %d bytes to pipe ", getpid(), ret); exit(0); } close(pipefd[1]);//父进程,关闭写端 sleep(1);//休眠一秒的作用是为了让子进程都write数据至管道了 int fd = open("test.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);//将子进程写入管道的数据读到test.txt文件中进行查看 char buf[1024*4] = {0}; int n = 1; while (1) { ret = read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf));//每次从管道中读取4个字节,以便进行观察原子性 if (ret == 0) break; printf("n=%02d pid=%d read %d bytes from pipe buf[4095]=%c ", n++, getpid(), ret, buf[4095]); write(fd, buf, ret);//然后再写入到文件中 } return 0; }
编译运行:

再次运行:

关于小于PIPE_BUF这时就不演示了,这种情况肯定是能保证原子性的,关于这些规则,实际上在man帮助里面都可以看到:

【注意】:管道的容量之前我们已经验证过了是65536,而PIPE_BUF的大小为4096,也就是说这两者是不划等号的,需要注意。
好了,今天学到这,下回下见!!