python风控建模实战lendingClub(博主录制,catboost,lightgbm建模,2K超清分辨率)
https://study.163.com/course/courseMain.htm?courseId=1005988013&share=2&shareId=400000000398149
机器学习,统计项目联系:QQ:231469242
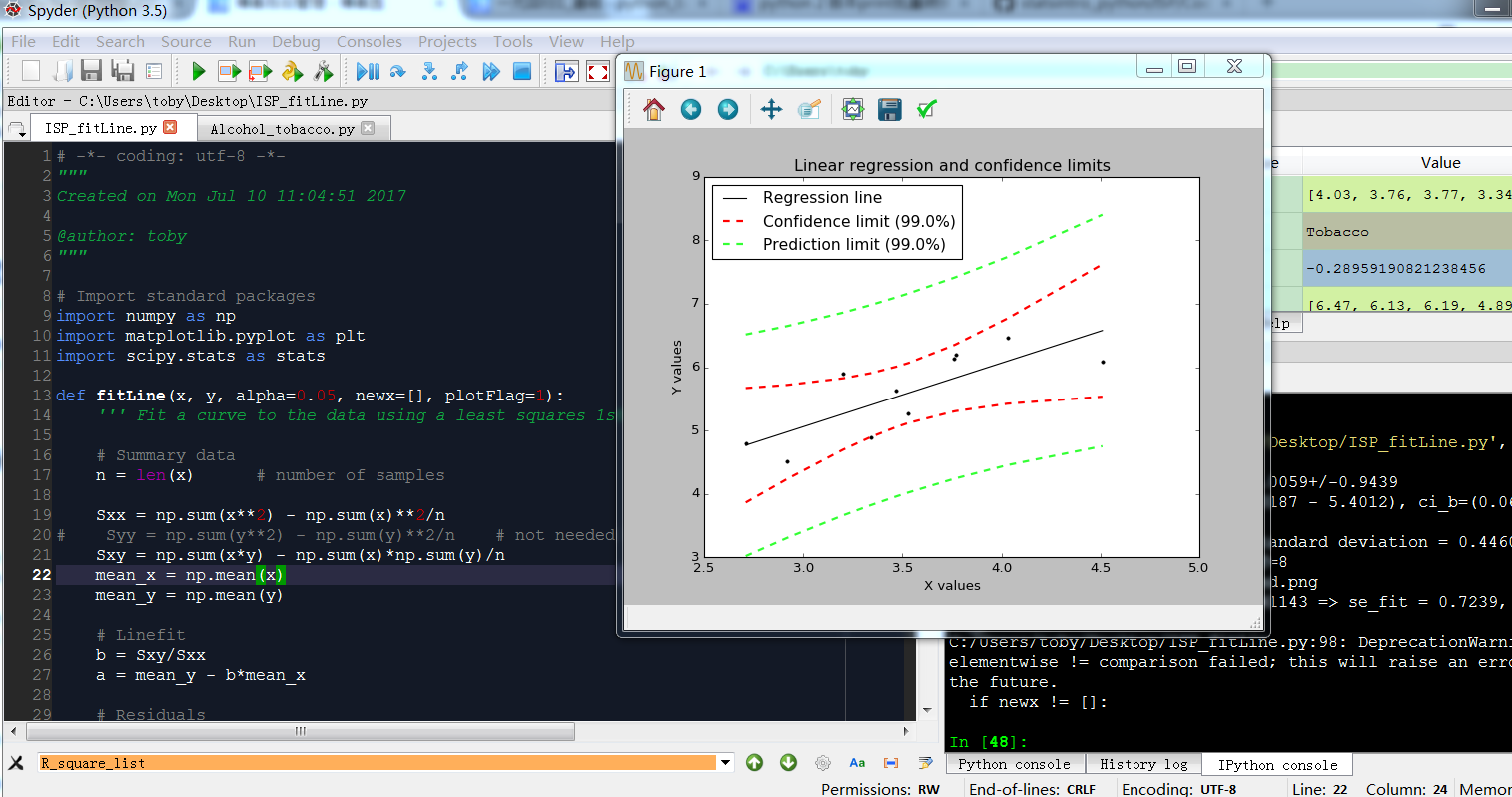
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Jul 10 11:04:51 2017
@author: toby
"""
# Import standard packages
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.stats as stats
def fitLine(x, y, alpha=0.05, newx=[], plotFlag=1):
''' Fit a curve to the data using a least squares 1st order polynomial fit '''
# Summary data
n = len(x) # number of samples
Sxx = np.sum(x**2) - np.sum(x)**2/n
# Syy = np.sum(y**2) - np.sum(y)**2/n # not needed here
Sxy = np.sum(x*y) - np.sum(x)*np.sum(y)/n
mean_x = np.mean(x)
mean_y = np.mean(y)
# Linefit
b = Sxy/Sxx
a = mean_y - b*mean_x
# Residuals
fit = lambda xx: a + b*xx
residuals = y - fit(x)
var_res = np.sum(residuals**2)/(n-2)
sd_res = np.sqrt(var_res)
# Confidence intervals
se_b = sd_res/np.sqrt(Sxx)
se_a = sd_res*np.sqrt(np.sum(x**2)/(n*Sxx))
df = n-2 # degrees of freedom
tval = stats.t.isf(alpha/2., df) # appropriate t value
ci_a = a + tval*se_a*np.array([-1,1])
ci_b = b + tval*se_b*np.array([-1,1])
# create series of new test x-values to predict for
npts = 100
px = np.linspace(np.min(x),np.max(x),num=npts)
se_fit = lambda x: sd_res * np.sqrt( 1./n + (x-mean_x)**2/Sxx)
se_predict = lambda x: sd_res * np.sqrt(1+1./n + (x-mean_x)**2/Sxx)
print(('Summary: a={0:5.4f}+/-{1:5.4f}, b={2:5.4f}+/-{3:5.4f}'.format(a,tval*se_a,b,tval*se_b)))
print(('Confidence intervals: ci_a=({0:5.4f} - {1:5.4f}), ci_b=({2:5.4f} - {3:5.4f})'.format(ci_a[0], ci_a[1], ci_b[0], ci_b[1])))
print(('Residuals: variance = {0:5.4f}, standard deviation = {1:5.4f}'.format(var_res, sd_res)))
print(('alpha = {0:.3f}, tval = {1:5.4f}, df={2:d}'.format(alpha, tval, df)))
# Return info
ri = {'residuals': residuals,
'var_res': var_res,
'sd_res': sd_res,
'alpha': alpha,
'tval': tval,
'df': df}
if plotFlag == 1:
# Plot the data
plt.figure()
plt.plot(px, fit(px),'k', label='Regression line')
#plt.plot(x,y,'k.', label='Sample observations', ms=10)
plt.plot(x,y,'k.')
x.sort()
limit = (1-alpha)*100
plt.plot(x, fit(x)+tval*se_fit(x), 'r--', lw=2, label='Confidence limit ({0:.1f}%)'.format(limit))
plt.plot(x, fit(x)-tval*se_fit(x), 'r--', lw=2 )
plt.plot(x, fit(x)+tval*se_predict(x), '--', lw=2, color=(0.2,1,0.2), label='Prediction limit ({0:.1f}%)'.format(limit))
plt.plot(x, fit(x)-tval*se_predict(x), '--', lw=2, color=(0.2,1,0.2))
plt.xlabel('X values')
plt.ylabel('Y values')
plt.title('Linear regression and confidence limits')
# configure legend
plt.legend(loc=0)
leg = plt.gca().get_legend()
ltext = leg.get_texts()
plt.setp(ltext, fontsize=14)
# show the plot
outFile = 'regression_wLegend.png'
plt.savefig(outFile, dpi=200)
print('Image saved to {0}'.format(outFile))
plt.show()
if newx != []:
try:
newx.size
except AttributeError:
newx = np.array([newx])
print(('Example: x = {0}+/-{1} => se_fit = {2:5.4f}, se_predict = {3:6.5f}'
.format(newx[0], tval*se_predict(newx[0]), se_fit(newx[0]), se_predict(newx[0]))))
newy = (fit(newx), fit(newx)-se_predict(newx), fit(newx)+se_predict(newx))
return (a,b,(ci_a, ci_b), ri, newy)
else:
return (a,b,(ci_a, ci_b), ri)
def Draw_confidenceInterval(x,y):
x=np.array(x)
y=np.array(y)
goodIndex = np.invert(np.logical_or(np.isnan(x), np.isnan(y)))
(a,b,(ci_a, ci_b), ri,newy) = fitLine(x[goodIndex],y[goodIndex], alpha=0.01,newx=np.array([1,4.5]))
y=[6.47,6.13,6.19,4.89,5.63,4.52,5.89,4.79,5.27,6.08]
x=[4.03,3.76,3.77,3.34,3.47,2.92,3.20,2.71,3.53,4.51]
Draw_confidenceInterval(x,y)
https://study.163.com/provider/400000000398149/index.htm?share=2&shareId=400000000398149( 欢迎关注博主主页,学习python视频资源,还有大量免费python经典文章)