树型结构是一类非常重要的非线性结构。直观地,树型结构是以分支关系定义的层次结构。
树在计算机领域中也有着广泛的应用,例如在编译程序中,用树来表示源程序的语法结构;在数据库系统中,可用树来组织信息;在分析算法的行为时,可用树来描述其执行过程等等。
下面讲解的内容完整代码在这:https://github.com/LukeLin/data-structure-with-js/blob/master/Binary%20tree/BinaryTree.js
首先看看树的一些概念:
1.树(Tree)是n(n>=0)个结点的有限集。在任意一棵非空树中:
(1)有且仅有一个特定的称为根(Root)的结点;
(2)当n>1时,其余结点可分为m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集T1,T2,T3,...Tm,其中每一个集合本身又是一棵树,并且称为根的子树(Subtree)。
例如,(a)是只有一个根结点的树;(b)是有13个结点的树,其中A是根,其余结点分成3个互不相交的子集:T1={B,E,F,K,L},t2={D,H,I,J,M};T1,T2和T3都是根A的子树,且本身也是一棵树。
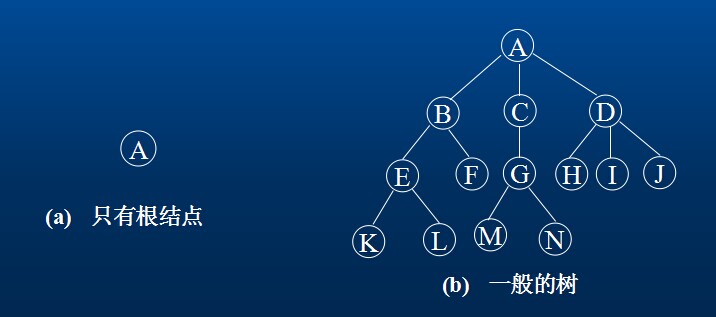
2.树的结点包含一个数据元素及若干指向其子树的分支。结点拥有的子树数称为结点的度(Degree)。例如,(b)中A的度为3,C的度为1,F的度为0.度为0的结点称为叶子(Leaf)或者终端结点。度不为0的结点称为非终端结点或分支结点。树的度是树内各结点的度的最大值。(b)的树的度为3.结点的子树的根称为该结点的孩子(Child)。相应的,该结点称为孩子的双亲(Parent)。同一个双亲的孩子之间互称兄弟(Sibling)。结点的祖先是从根到该结点所经分支上的所有结点。反之,以某结点为根的子树中的任一结点都称为该结点的子孙。
3.结点的层次(Level)从根开始定义起,根为第一层,跟的孩子为第二层。若某结点在第l层,则其子树的根就在第l+1层。其双亲在同一层的结点互为堂兄弟。例如,结点G与E,F,H,I,J互为堂兄弟。树中结点的最大层次称为树的深度(Depth)或高度。(b)的树的深度为4。
4.如果将树中结点的各子树看成从左至右是有次序的(即不能交换),则称该树为有序树,否则称为无序树。在有序树中最左边的子树的根称为第一个孩子,最右边的称为最后一个孩子。
5.森林(Forest)是m(m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合。对树中每个结点而言,其子树的集合即为森林。
接下来看看二叉树相关的概念:
二叉树(Binary Tree)是另一种树型结构,它的特点是每个结点至多只有两棵子树(即二叉树中不存在度大于2的结点),并且,二叉树的子树有左右之分(其次序不能任意颠倒。)
二叉树的性质:
1.在二叉树的第i层上至多有2的i-1次方个结点(i>=1)。
2.深度为k的二叉树至多有2的k次方-1个结点,(k>=1)。
3.对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0 = n2 + 1;
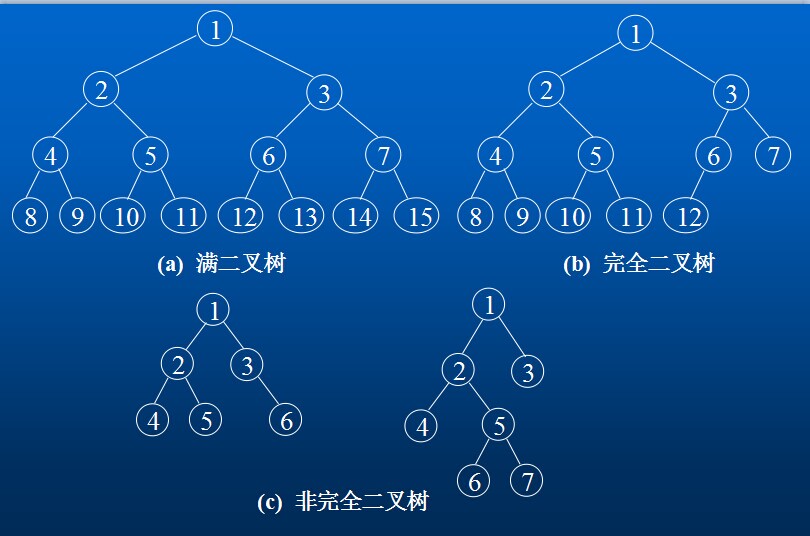
一棵深度为k且有2的k次方-1个结点的二叉树称为满二叉树。
深度为k的,有n个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为k的满二叉树中编号从1至n的结点一一对应时,称之为完全二叉树。
下面是完全二叉树的两个特性:
4.具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为Math.floor(log 2 n) + 1
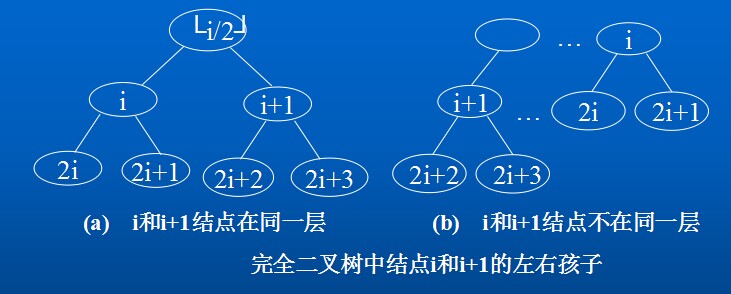
5.如果对一棵有n个结点的完全二叉树(其深度为Math.floor(log 2 n) + 1)的结点按层序编号(从第1层到第Math.floor(2 n) + 1,每层从左到右),则对任一结点(1<=i<=n)有:
(1)如果i=1,则结点i、是二叉树的根,无双亲;如果i>1,则其双亲parent(i)是结点Math.floor(i/2)。
(2)如果2i > n,则结点i无左孩子(结点i为叶子结点);否则其左孩子LChild(i)是结点2i.
(3)如果2i + 1 > n,则结点i无右孩子;否则其右孩子RChild(i)是结点2i + 1;
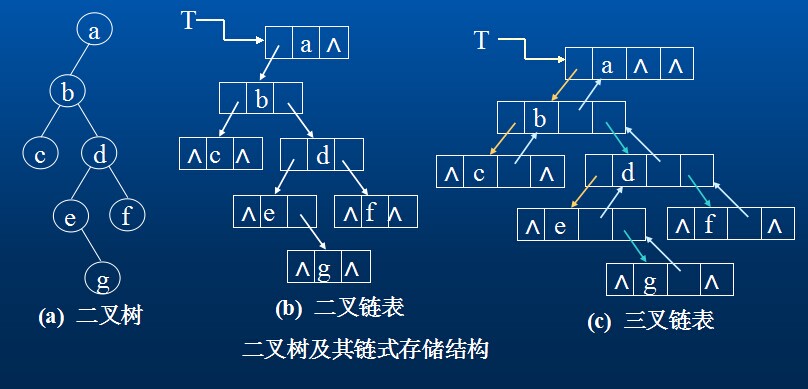
二叉树的存储结构
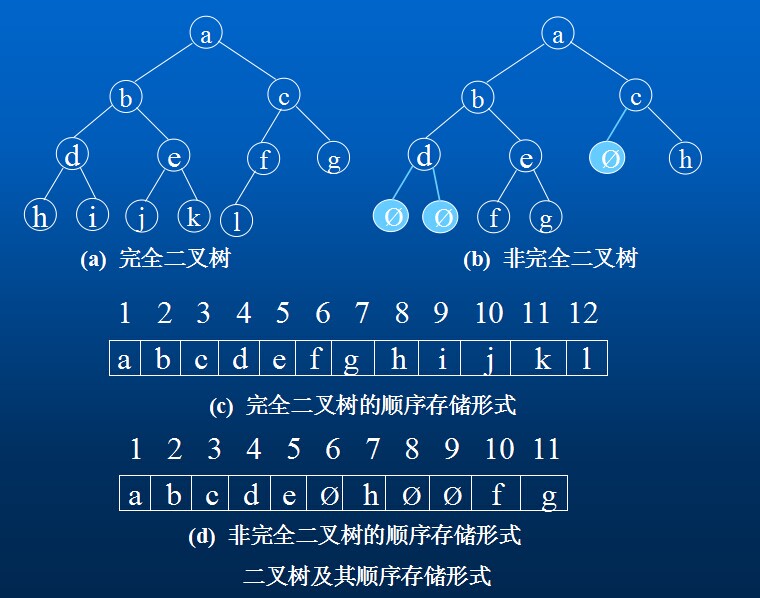
1.顺序存储结构
用一组连续的存储单元依次自上而下,自左至右存储完全二叉树上的结点元素,即将二叉树上编号为i的结点元素存储在加上定义的一维数组中下标为i-1的分量中。“0”表示不存在此结点。这种顺序存储结构仅适用于完全二叉树。
因为,在最坏情况下,一个深度为k且只有k个结点的单支树(树中不存在度为2的结点)却需要长度为2的n次方-1的一维数组。
2.链式存储结构
二叉树的结点由一个数据元素和分别指向其左右子树的两个分支构成,则表示二叉树的链表中的结点至少包含三个域:数据域和左右指针域。有时,为了便于找到结点的双亲,则还可在结点结构中增加一个指向其双亲结点的指针域。利用这两种结构所得的二叉树的存储结构分别称之为二叉链表和三叉链表。
在含有n个结点的二叉链表中有n+1个空链域,我们可以利用这些空链域存储其他有用信息,从而得到另一种链式存储结构---线索链表。
二叉树的遍历主要分三种:
先(根)序遍历:根左右
中(根)序遍历:左根右
后(根)序遍历:左右根
二叉树的顺序存储结构:
二叉树的链式存储形式:
// 顺序存储结构 var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; // 链式存储结构 function BinaryTree(data, leftChild, rightChild) { this.data = data || null; // 左右孩子结点 this.leftChild = leftChild || null; this.rightChild = rightChild || null; }
遍历二叉树(Traversing Binary Tree):是指按指定的规律对二叉树中的每个结点访问一次且仅访问一次。
1.先序遍历二叉树
1)算法的递归定义是:
若二叉树为空,则遍历结束;否则
⑴ 访问根结点;
⑵ 先序遍历左子树(递归调用本算法);
⑶ 先序遍历右子树(递归调用本算法)。
算法实现:
// 顺序存储结构的递归先序遍历 var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; console.log('preOrder:'); void function preOrderTraverse(x, visit) { visit(tree[x]); if (tree[2 * x + 1]) preOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit); if (tree[2 * x + 2]) preOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit); }(0, function (value) { console.log(value); }); // 链式存储结构的递归先序遍历 BinaryTree.prototype.preOrderTraverse = function preOrderTraverse(visit) { visit(this.data); if (this.leftChild) preOrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit); if (this.rightChild) preOrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit); };
2)非递归算法:
设T是指向二叉树根结点的变量,非递归算法是: 若二叉树为空,则返回;否则,令p=T;
(1) p为根结点;
(2) 若p不为空或者栈不为空;
(3) 若p不为空,访问p所指向的结点, p进栈, p = p.leftChild,访问左子树;
(4) 否则;退栈到p,然后p = p.rightChild, 访问右子树
(5) 转(2),直到栈空为止。
代码实现:
// 链式存储的非递归先序遍历 // 方法1 BinaryTree.prototype.preOrder_stack = function (visit) { var stack = new Stack(); stack.push(this); while (stack.top) { var p; // 向左走到尽头 while ((p = stack.peek())) { p.data && visit(p.data); stack.push(p.leftChild); } stack.pop(); if (stack.top) { p = stack.pop(); stack.push(p.rightChild); } } }; // 方法2 BinaryTree.prototype.preOrder_stack2 = function (visit) { var stack = new Stack(); var p = this; while (p || stack.top) { if (p) { stack.push(p); p.data && visit(p.data); p = p.leftChild; } else { p = stack.pop(); p = p.rightChild; } } };
2.中序遍历二叉树:
1)算法的递归定义是:
若二叉树为空,则遍历结束;否则
⑴ 中序遍历左子树(递归调用本算法);
⑵ 访问根结点;
⑶ 中序遍历右子树(递归调用本算法)。
// 顺序存储结构的递归中序遍历 var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; console.log('inOrder:'); void function inOrderTraverse(x, visit) { if (tree[2 * x + 1]) inOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit); visit(tree[x]); if (tree[2 * x + 2]) inOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit); }(0, function (value) { console.log(value); }); // 链式存储的递归中序遍历 BinaryTree.prototype.inPrderTraverse = function inPrderTraverse(visit) { if (this.leftChild) inPrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit); visit(this.data); if (this.rightChild) inPrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit); };
2) 非递归算法
T是指向二叉树根结点的变量,非递归算法是: 若二叉树为空,则返回;否则,令p=T
⑴ 若p不为空,p进栈, p=p.leftChild ;
⑵ 否则(即p为空),退栈到p,访问p所指向的结点,p=p.rightChild ;
⑶ 转(1);
直到栈空为止。
// 方法1 inOrder_stack1: function (visit) { var stack = new Stack(); stack.push(this); while (stack.top) { var p; // 向左走到尽头 while ((p = stack.peek())) { stack.push(p.leftChild); } stack.pop(); if (stack.top) { p = stack.pop(); p.data && visit(p.data); stack.push(p.rightChild); } } }, // 方法2 inOrder_stack2: function (visit) { var stack = new Stack(); var p = this; while (p || stack.top) { if (p) { stack.push(p); p = p.leftChild; } else { p = stack.pop(); p.data && visit(p.data); p = p.rightChild; } } },
3.后序遍历二叉树:
1)递归算法
若二叉树为空,则遍历结束;否则
⑴ 后序遍历左子树(递归调用本算法);
⑵ 后序遍历右子树(递归调用本算法) ;
⑶ 访问根结点 。
// 顺序存储结构的递归后序遍历 var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; console.log('postOrder:'); void function postOrderTraverse(x, visit) { if (tree[2 * x + 1]) postOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit); if (tree[2 * x + 2]) postOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit); visit(tree[x]); }(0, function (value) { console.log(value); }); // 链式存储的递归后序遍历 BinaryTree.prototype.postOrderTraverse = function postOrderTraverse(visit) { if (this.leftChild) postOrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit); if (this.rightChild) postOrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit); visit(this.data); };
2) 非递归算法
在后序遍历中,根结点是最后被访问的。因此,在遍历过程中,当搜索指针指向某一根结点时,不能立即访问,而要先遍历其左子树,此时根结点进栈。当其左子树遍历完后再搜索到该根结点时,还是不能访问,还需遍历其右子树。所以,此根结点还需再次进栈,当其右子树遍历完后再退栈到到该根结点时,才能被访问。 因此,设立一个状态标志变量mark:
mark=0表示刚刚访问此结点,mark=1表示左子树处理结束返回,
mark=2表示右子树处理结束返回。每次根据栈顶的mark域决定做何动作
算法实现思路:
(1) 根结点入栈,且mark = 0;
(2) 若栈不为空,出栈到node;
(3) 若node的mark = 0,修改当前node的mark为1,左子树入栈;
(4) 若node的mark = 1,修改当前node的mark为2,右子树入栈;
(5) 若node的mark = 2,访问当前node结点的值;
(6) 直到栈为空结束。
postOrder_stack: function (visit) { var stack = new Stack(); stack.push([this, 0]); while (stack.top) { var a = stack.pop(); var node = a[0]; switch (a[1]) { case 0: stack.push([node, 1]); // 修改mark域 if (node.leftChild) stack.push([node.leftChild, 0]); // 访问左子树 break; case 1: stack.push([node, 2]); if (node.rightChild) stack.push([node.rightChild, 0]); break; case 2: node.data && visit(node.data); break; default: break; } } }
下面是完整代码,其中包括二叉树的遍历和基本操作:

1 // 顺序存储结构 2 (function () { 3 // 顺序存储结构的遍历 4 var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; 5 6 console.log('preOrder:'); 7 void function preOrderTraverse(x, visit) { 8 visit(tree[x]); 9 if (tree[2 * x + 1]) preOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit); 10 if (tree[2 * x + 2]) preOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit); 11 }(0, function (value) { 12 console.log(value); 13 }); 14 15 console.log('inOrder:'); 16 void function inOrderTraverse(x, visit) { 17 if (tree[2 * x + 1]) inOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit); 18 visit(tree[x]); 19 if (tree[2 * x + 2]) inOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit); 20 }(0, function (value) { 21 console.log(value); 22 }); 23 24 console.log('postOrder:'); 25 void function postOrderTraverse(x, visit) { 26 if (tree[2 * x + 1]) postOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit); 27 if (tree[2 * x + 2]) postOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit); 28 visit(tree[x]); 29 }(0, function (value) { 30 console.log(value); 31 }); 32 }()); 33 34 var Stack = require('../Stack/stack'); 35 var Queue = require('../Queue/Queue').Queue; 36 37 // 链式存储结构 38 function BinaryTree(data, leftChild, rightChild) { 39 this.data = data || null; 40 // 左右孩子结点 41 this.leftChild = leftChild || null; 42 this.rightChild = rightChild || null; 43 } 44 exports.BinaryTree = BinaryTree; 45 BinaryTree.prototype = { 46 constructor: BinaryTree, 47 // 判断两棵树是否相似 48 isSimilar: function isSimilar(tree) { 49 return tree && 50 this.leftChild && isSimilar.call(this.leftChild, tree.leftChild) && 51 this.rightChild && isSimilar.call(this.rightChild, tree.rightChild); 52 }, 53 createBinaryTree: function (tree) { 54 void function preOrderTraverse(node, x, visit) { 55 visit(node, tree[x]); 56 57 if (tree[2 * x + 1]) preOrderTraverse(node.leftChild = new BinaryTree(), 2 * x + 1, visit); 58 if (tree[2 * x + 2]) preOrderTraverse(node.rightChild = new BinaryTree(), 2 * x + 2, visit); 59 }(this, 0, function (node, value) { 60 node.data = value; 61 }); 62 }, 63 64 // 先序遍历二叉树的非递归算法 65 preOrder_stack: function (visit) { 66 var stack = new Stack(); 67 stack.push(this); 68 69 while (stack.top) { 70 var p; 71 // 向左走到尽头 72 while ((p = stack.peek())) { 73 p.data && visit(p.data); 74 stack.push(p.leftChild); 75 } 76 77 stack.pop(); 78 79 if (stack.top) { 80 p = stack.pop(); 81 stack.push(p.rightChild); 82 } 83 } 84 }, 85 preOrder_stack2: function (visit) { 86 var stack = new Stack(); 87 var p = this; 88 89 while (p || stack.top) { 90 if (p) { 91 stack.push(p); 92 p.data && visit(p.data); 93 p = p.leftChild; 94 } else { 95 p = stack.pop(); 96 p = p.rightChild; 97 } 98 } 99 }, 100 inOrder_stack1: function (visit) { 101 var stack = new Stack(); 102 stack.push(this); 103 104 while (stack.top) { 105 var p; 106 // 向左走到尽头 107 while ((p = stack.peek())) { 108 stack.push(p.leftChild); 109 } 110 111 stack.pop(); 112 113 if (stack.top) { 114 p = stack.pop(); 115 p.data && visit(p.data); 116 stack.push(p.rightChild); 117 } 118 } 119 }, 120 inOrder_stack2: function (visit) { 121 var stack = new Stack(); 122 var p = this; 123 124 while (p || stack.top) { 125 if (p) { 126 stack.push(p); 127 p = p.leftChild; 128 } else { 129 p = stack.pop(); 130 p.data && visit(p.data); 131 p = p.rightChild; 132 } 133 } 134 }, 135 // 为了区分两次过栈的不同处理方式,在堆栈中增加一个mark域, 136 // mark=0表示刚刚访问此结点,mark=1表示左子树处理结束返回, 137 // mark=2表示右子树处理结束返回。每次根据栈顶的mark域决定做何动作 138 postOrder_stack: function (visit) { 139 var stack = new Stack(); 140 stack.push([this, 0]); 141 142 while (stack.top) { 143 var a = stack.pop(); 144 var node = a[0]; 145 146 switch (a[1]) { 147 case 0: 148 stack.push([node, 1]); // 修改mark域 149 if (node.leftChild) stack.push([node.leftChild, 0]); // 访问左子树 150 break; 151 case 1: 152 stack.push([node, 2]); 153 if (node.rightChild) stack.push([node.rightChild, 0]); 154 break; 155 case 2: 156 node.data && visit(node.data); 157 break; 158 default: 159 break; 160 } 161 } 162 }, 163 164 preOrderTraverse: function preOrderTraverse(visit) { 165 visit(this.data); 166 if (this.leftChild) preOrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit); 167 if (this.rightChild) preOrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit); 168 }, 169 inPrderTraverse: function inPrderTraverse(visit) { 170 if (this.leftChild) inPrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit); 171 visit(this.data); 172 if (this.rightChild) inPrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit); 173 }, 174 postOrderTraverse: function postOrderTraverse(visit) { 175 if (this.leftChild) postOrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit); 176 if (this.rightChild) postOrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit); 177 visit(this.data); 178 }, 179 180 levelOrderTraverse: function (visit) { 181 var queue = new Queue(); 182 queue.enQueue(this); 183 184 while (queue.rear) { 185 var p = queue.deQueue(); 186 p.data && visit(p.data); 187 p.leftChild && queue.enQueue(p.leftChild); 188 p.rightChild && queue.enQueue(p.rightChild); 189 } 190 }, 191 // 求先序序列为k的结点的值 192 getPreSequence: function (k) { 193 var count = 0; 194 195 void function recurse(node) { 196 if (node) { 197 if (++count === k) { 198 console.log('Value is: ' + node.data); 199 } else { 200 recurse(node.leftChild); 201 recurse(node.rightChild); 202 } 203 } 204 }(this); 205 }, 206 // 求二叉树中叶子结点的数目 207 countLeaves: function () { 208 return function recurse(node) { 209 if (!node) return 0; 210 else if (!node.leftChild && !node.rightChild) return 1; 211 else return recurse(node.leftChild) + recurse(node.rightChild); 212 }(this); 213 }, 214 // 交换所有结点的左右子树 215 revoluteBinaryTree: function revoluteBinaryTree() { 216 var temp = this.leftChild; 217 this.leftChild = this.rightChild; 218 this.rightChild = temp; 219 220 if (this.leftChild) revoluteBinaryTree.call(this.leftChild); 221 if (this.rightChild) revoluteBinaryTree.call(this.rightChild); 222 }, 223 // 求二叉树中以值为x的结点为根的子树深度 224 getSubDepth: function getSubDepth(x) { 225 if (this.data === x) { 226 console.log('subDepth: ' + this.getDepth()); 227 } else { 228 if (this.leftChild) getSubDepth.call(this.leftChild, x); 229 if (this.rightChild) getSubDepth.call(this.rightChild, x); 230 } 231 }, 232 getDepth: function getDepth() { 233 if (this === global) return 0; 234 else { 235 var m = getDepth.call(this.leftChild); 236 var n = getDepth.call(this.rightChild); 237 return (m > n ? m : n) + 1; 238 } 239 }, 240 // 删除所有以元素x为根的子树 241 delSubX: function delSubX(x) { 242 if (this.data === x) { 243 this.leftChild = null; 244 this.rightChild = null; 245 } else { 246 if (this.leftChild) delSubX.call(this.leftChild); 247 if (this.rightChild) delSubX.call(this.rightChild); 248 } 249 }, 250 // 非递归复制二叉树 251 copyBinaryTree_stack: function () { 252 // 用来存放本体结点的栈 253 var stack1 = new Stack(); 254 // 用来存放新二叉树结点的栈 255 var stack2 = new Stack(); 256 stack1.push(this); 257 var newTree = new BinaryTree(); 258 var q = newTree; 259 stack2.push(newTree); 260 var p; 261 262 while (stack1.top) { 263 // 向左走到尽头 264 while ((p = stack1.peek())) { 265 if (p.leftChild) q.leftChild = new BinaryTree(); 266 q = q.leftChild; 267 stack1.push(p.leftChild); 268 stack2.push(q); 269 } 270 271 p = stack1.pop(); 272 q = stack2.pop(); 273 274 if (stack1.top) { 275 p = stack1.pop(); 276 q = stack2.pop(); 277 if (p.rightChild) q.rightChild = new BinaryTree(); 278 q.data = p.data; 279 q = q.rightChild; 280 stack1.push(p.rightChild); // 向右一步 281 stack2.push(q); 282 } 283 } 284 285 return newTree; 286 }, 287 // 求二叉树中结点p和q的最近祖先 288 findNearAncient: function (pNode, qNode) { 289 var pathP = []; 290 var pathQ = []; 291 findPath(this, pNode, pathP, 0); 292 findPath(this, qNode, pathQ, 0); 293 294 for (var i = 0; pathP[i] == pathQ[i] && pathP[i]; i++); 295 return pathP[--i]; 296 }, 297 toString: function () { 298 }, 299 // 求一棵二叉树的繁茂度 300 lushDegree: function () { 301 var countArr = []; 302 var queue = new Queue(); 303 queue.enQueue({ 304 node: this, 305 layer: 0 306 }); 307 // 利用层序遍历来统计各层的结点数 308 var r; 309 while (queue.rear) { 310 r = queue.deQueue(); 311 countArr[r.layer] = (countArr[r.layer] || 0) + 1; 312 313 if (r.node.leftChild) 314 queue.enQueue({ 315 node: r.node.leftChild, 316 layer: r.layer + 1 317 }); 318 if (r.node.rightChild) 319 queue.enQueue({ 320 node: r.node.rightChild, 321 layer: r.layer + 1 322 }); 323 } 324 325 // 最后一个队列元素所在层就是树的高度 326 var height = r.layer; 327 for (var max = countArr[0], i = 1; countArr[i]; i++) 328 // 求层最大结点数 329 if (countArr[i] > max) max = countArr[i]; 330 331 return height * max; 332 }, 333 // 求深度等于书的高度减一的最靠左的结点 334 printPath_maxDepthS1: function () { 335 var maxh = this.getDepth(); 336 var path = []; 337 338 if (maxh < 2) return false; 339 find_h(this, 1); 340 341 function find_h(tree, h) { 342 path[h] = tree; 343 344 if (h == maxh - 1) { 345 var s = ' '; 346 for (var i = 1; path[i]; i++) s += path[i].data + (path[i + 1] ? ' -> ' : ''); 347 console.log(s); 348 return; 349 } else { 350 if (tree.leftChild) find_h(tree.leftChild, h + 1); 351 if (tree.rightChild) find_h(tree.rightChild, h + 1); 352 } 353 354 path[h] = null; 355 } 356 }, 357 // 求树结点的子孙总数填入descNum域中,并返回 358 descNum: function () { 359 return function recurse(node) { 360 var d; 361 if (!node) return -1; 362 else d = recurse(node.leftChild) + recurse(node.rightChild) + 2; 363 364 node.descNum = d; 365 366 return d; 367 }(this); 368 } 369 }; 370 371 // 判断二叉树是否完全二叉树 372 BinaryTree.isFullBinaryTree = function (tree) { 373 var queue = new Queue(); 374 var flag = 0; 375 queue.enQueue(tree); 376 377 while (queue.rear) { 378 var p = queue.deQueue(); 379 380 if (!p) flag = 1; 381 else if (flag) return false; 382 else { 383 queue.enQueue(p.leftChild); 384 queue.enQueue(p.rightChild); 385 } 386 } 387 388 return true; 389 }; 390 391 // 求从tree到node结点路径的递归算法 392 function findPath(tree, node, path, i) { 393 var found = false; 394 395 void function recurse(tree, i) { 396 if (tree == node) { 397 found = true; 398 return; 399 } 400 401 path[i] = tree; 402 if (tree.leftChild) recurse(tree.leftChild, i + 1); 403 if (tree.rightChild && !found) recurse(tree.rightChild, i + 1); 404 if (!found) path[i] = null; 405 }(tree, i); 406 } 407 408 var global = Function('return this;')(); 409 410 void function test() { 411 var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; 412 var test = new BinaryTree; 413 test.createBinaryTree(tree); 414 test.preOrderTraverse(function (value) { 415 console.log('preOrder: ' + value); 416 }); 417 test.inPrderTraverse(function (value) { 418 console.log('inOrder: ' + value); 419 }); 420 test.postOrderTraverse(function (value) { 421 console.log('postOrder: ' + value); 422 }); 423 test.preOrder_stack(function (data) { 424 console.log('preOrderNonRecusive: ' + data); 425 }); 426 test.preOrder_stack2(function (data) { 427 console.log('preOrder_stack2: ' + data); 428 }); 429 test.inOrder_stack1(function (value) { 430 console.log('inOrder_stack1: ' + value); 431 }); 432 test.inOrder_stack2(function (value) { 433 console.log('inOrder_stack2: ' + value); 434 }); 435 test.postOrder_stack(function (value) { 436 console.log('postOrder_stack: ' + value); 437 }); 438 test.getPreSequence(5); 439 console.log(test.countLeaves()); 440 test.getSubDepth(6); // 1 441 test.getSubDepth(2); // 3 442 test.levelOrderTraverse(function (value) { 443 console.log('levelOrderTraverse: ' + value); 444 }); 445 446 var newTree = test.copyBinaryTree_stack(); 447 448 var node1 = test.leftChild.leftChild; // 4 449 var node2 = test.leftChild.rightChild.leftChild; // 7 450 var ancient = test.findNearAncient(node1, node2); 451 console.log(ancient); 452 453 console.log('expect false: ' + BinaryTree.isFullBinaryTree(test)); 454 newTree.rightChild.leftChild = new BinaryTree(7); 455 newTree.leftChild.rightChild.leftChild = null; 456 console.log('expect true: ' + BinaryTree.isFullBinaryTree(newTree)); 457 console.log('lush degree: ' + test.lushDegree()); 458 459 test.printPath_maxDepthS1(); 460 console.log(test.descNum()); 461 }();
