1、存储引擎
数据创建,查询,更新和删除操作都是通过数据引擎来进行的。不同的存储引擎存储限制不同,支持不同的索引机制等。
查询数据库支持的存储引擎
MySQL 5.7.2支持的存储引擎有:InnoDB,MRG_MYISAM,MEMORY,BLACKHOLE,MyISAM,CSV,ARCHIVE,PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA,FEDERATED。默认的存储引擎是InnoDB。
SHOW ENGINES;
mysql> SHOW ENGINES;
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys | YES | YES | YES |
| MRG_MYISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
| BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | YES | MyISAM storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
| FEDERATED | NO | Federated MySQL storage engine | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
InnoDB的特点:存储限制64TB,支持事务,支持树索引和数据缓存,外键。
2、数据类型
MySQL常见的数据类型有整型,字符串类型,时间类型,二进制类型。
整型
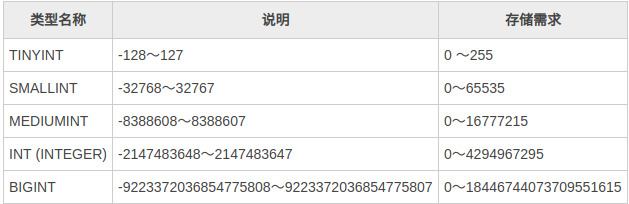
MySQL主要提供的整型有:TINYINT、SMALLINT、MEDIUMINT、INT、BIGINT。不同的整数类型支持的取值范围不同,需要的存储空间也不同。使用时根据需求选择合适的类型,节省存储空间提高查询的效率。
浮点数
MySQL的浮点数类型有单精度(FLOAT)和双精度(DOUBLE)以及定点类型(DECIMAL)。浮点类型和定点类型都可以用(M, D)来表示,其中M称为精度,表示总共的位数;D称为标度,表示小数的位数。
DECIMAL 的默认 D 值为 0、M 值为 10。
字符串
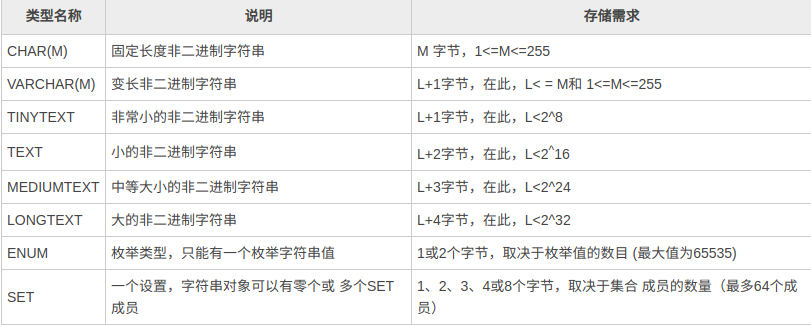
MySQL 中的字符串类型有 CHAR、VARCHAR、TINYTEXT、TEXT、MEDIUMTEXT、LONGTEXT、ENUM、SET 等。
二进制类型
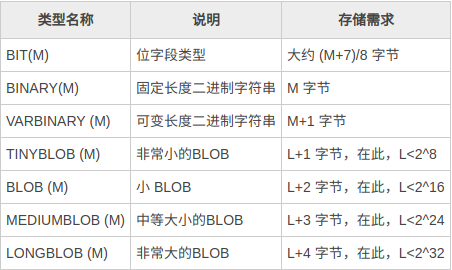
MySQL中的二进制字符串有: BIT、BINARY、VARBINARY、TINYBLOB、BLOB、MEDIUMBLOB 和 LONGBLOB。
时间或日期类型
MySQL中表示日期的数据类型有:YEAR、TIME、DATE、DTAETIME、TIMESTAMP。

3、主键与外键
主键
主键,英文名称:PRIMARY KEY,能够唯一表示每一行,由一列或者多列组成。
外键
MySQL 外键约束(FOREIGN KEY)用来在两个表的数据之间建立链接,它可以是一列或者多列。一个表可以有一个或多个外键。
外键对应的是参照完整性,一个表的外键可以为空值,若不为空值,则每一个外键的值必须等于另一个表中主键的某个值。
外键是表的一个字段,不是本表的主键,但对应另一个表的主键。定义外键后,不允许删除另一个表中具有关联关系的行。
示例
#创建表cluster 主键为id
create table cluster(
id Int(20) primary key,
name char(20) not null,
status char(10) not null,
userId Int(10) not null,
createAt datetime not null,
delAt datetime not null ,
updateAt datetime not null
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
#创建表instance主键为id,外键为fk_clusterId,和cluster表的id字段对应
create table instance(
id Int(20) primary key,
name char(20) not null,
clusterId Int(20) not null,
status char(10) not null,
isBilling tinyint not null,
delAt datetime not null,
CONSTRAINT fk_clusterId
foreign key (clusterId) REFERENCES cluster(id)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
4、内连接和外连接
连接是多表查询的基础。
#cluster表
mysql> select * from cluster;
+-------+-----------+--------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+
| id | name | status | userId | createAt | delAt | updateAt |
+-------+-----------+--------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+
| 18888 | qws-test | 200 | 18 | 2019-04-11 20:24:24 | NULL | 2019-04-11 20:24:24 |
| 18889 | qws-test1 | 300 | 18 | 2019-04-11 20:24:24 | 2019-04-11 20:30:30 | 2019-04-11 20:24:24 |
+-------+-----------+--------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#instance表
mysql> select * from instance;
+----+---------------+-----------+--------+-----------+---------------------+
| id | name | clusterId | status | isBilling | delAt |
+----+---------------+-----------+--------+-----------+---------------------+
| 1 | qws-test-1-1 | 18888 | 200 | 1 | NULL |
| 2 | qws-test-2-1 | 18888 | 200 | 1 | NULL |
| 3 | qws-test-3-1 | 18888 | 200 | 1 | NULL |
| 4 | qws-test1-1-1 | 18889 | 400 | 0 | 2019-04-11 20:30:30 |
| 5 | qws-test1-2-1 | 18889 | 400 | 0 | 2019-04-11 20:30:30 |
| 6 | qws-test1-3-1 | 18889 | 400 | 0 | 2019-04-11 20:30:30 |
+----+---------------+-----------+--------+-----------+---------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
内连接
返回满足的连接条件的所有行,类似于两个集合的交集。
#查询已删除的集群名称和实例名称
mysql> select c.name,d.name from cluster c inner join instance d on c.delAt = d.delAt;
+-----------+---------------+
| name | name |
+-----------+---------------+
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-1-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-2-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-3-1 |
+-----------+---------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
等价于:
mysql> select c.name,d.name from cluster c ,instance d where c.delAt = d.delAt;
+-----------+---------------+
| name | name |
+-----------+---------------+
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-1-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-2-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-3-1 |
+-----------+---------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
左外连接(left join)
返回左表中所有的记录以及符合连接条件的记录。把左表看成A集合,右表看出B集合。左连接的返回结果为:A并上AB的交集。
mysql> select c.name,c.status,d.name from cluster c left outer join instance d on c.delAt = d.delAt ;
+-----------+--------+---------------+
| name | status | name |
+-----------+--------+---------------+
| qws-test1 | 300 | qws-test1-1-1 |
| qws-test1 | 300 | qws-test1-2-1 |
| qws-test1 | 300 | qws-test1-3-1 |
| qws-test | 200 | NULL |
+-----------+--------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
等价于
<pre>mysql> select c.name,d.name from cluster c ,instance d where c.delAt = d.delAt;
+-----------+---------------+
| name | name |
+-----------+---------------+
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-1-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-2-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-3-1 |
+-----------+---------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec</pre>
右外连接(outer join)
返回右表中所有的记录和符合连接条件的记录。把左表看成A集合,右表看出B集合。左连接的返回结果为:B并上AB的交集。
mysql> select c.name,c.status,d.name from cluster c right outer join instance d on c.delAt = d.delAt ;
+-----------+--------+---------------+
| name | status | name |
+-----------+--------+---------------+
| qws-test1 | 300 | qws-test1-1-1 |
| qws-test1 | 300 | qws-test1-2-1 |
| qws-test1 | 300 | qws-test1-3-1 |
| NULL | NULL | qws-test-1-1 |
| NULL | NULL | qws-test-2-1 |
| NULL | NULL | qws-test-3-1 |
+-----------+--------+---------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
交叉连接
返回两个表的笛卡尔乘积,比如集合a={x,y} b={1,2}其迪卡尔乘积为(x,1)(x,2) (y,1) (y,2)。
mysql> select c.name,d.name from cluster c cross join instance d ;
+-----------+---------------+
| name | name |
+-----------+---------------+
| qws-test | qws-test-1-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test-1-1 |
| qws-test | qws-test-2-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test-2-1 |
| qws-test | qws-test-3-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test-3-1 |
| qws-test | qws-test1-1-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-1-1 |
| qws-test | qws-test1-2-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-2-1 |
| qws-test | qws-test1-3-1 |
| qws-test1 | qws-test1-3-1 |
+-----------+---------------+
12 rows in set (0.00 sec)
文中的部分概念来自:http://c.biancheng.net/mysql/