包装类是什么
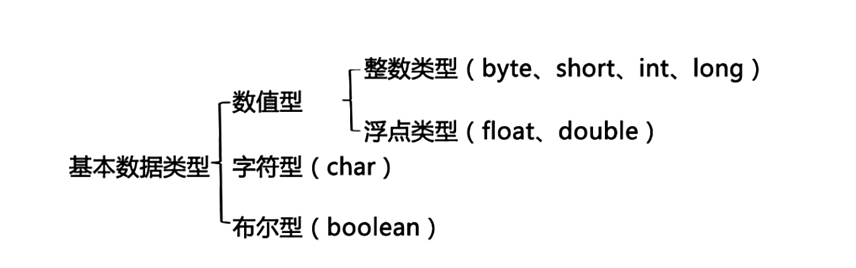
Java中的基本数据类型没有方法和属性,而包装类就是为了让这些拥有方法和属性,实现对象化交互。
数值型包装类都继承至Number,而字符型和布尔型继承至Object。
基本数据类型与包装类之间的转换
装箱:基本数据类型转换为包装类;
拆箱:包装类转换为基本数据类型。
基本数据类型和包装类的转换
通过包装类Integer.toString()将整型转换为字符串;
通过Integer.parseInt()将字符串转换为int类型;
通过valueOf()方法把字符串转换为包装类然后通过自动拆箱。
1 包装类
Java.lang包中的Integer,long类和short类,分别将基本类型Int,long,short封装成一个类
1. 构造方法
Integer(int number)
Integer number=new integer(7);
Integer number=new integer(“45”);//字符
2. 常用方法
-
byteValue();//以byte类型返回该integer类型
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer obj = new Integer(10);//integer类型
// returns the value of Integer as a byte
byte b = obj.byteValue();
System.out.println("Value of b = " + b);//输出Value of b = 10 -
CompareTo(Integer anotherInteger)
Integer int1 = new Integer(100); //定义一个Integer型变量
Integer int2 = new Integer(100); //定义一个Integer型变量
int value = int1.compareTo(int2);
System.out.println(value);
1.若两个值相等,则返回 0
2.若调用的对象的数值小于anotherInteger的数值则返回负值
3.若调用的对象的数值大于anotherInteger的数值返回正值
3. Equals(Object integerObj)
Integer b1=new Integer(1);
Integer b2=new Integer(1);
Integer i1 = 1;
Integer i2 = 1;
System.out.println(i1==i2); //这里i1和i2是同一个对象创建出来的
System.out.println(b1==b2);//false 这里要比较两个数的地址
System.out.println(b1.equals(b2)); //这里只比较数值大小
4. intValue()
Integer intNum = new Integer(10);
System.out.println(intNum.intValue());//以int类型返回
5. shortValue()
int i=10;
Integer shorts = new Integer(i);
short str = shorts.shortValue(); //把Integer类型转换成short型
System.out.println(str);
6.toString()//获取interger的字符串类型
Integer aa=new Integer(12);//使用包装类
String ii=aa.toString();//使用aa对象的toString()方法,将integer转换成String类
System.out.println(ii);//输出转换的结果
7. ValueOf(String str)
String str = "1";
Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf("1");//返回保存指定的String值的Interger对象
8. parseInt()//返回字符串等价int值
String[] a= {"89","12","10","18","35"};
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) {
int myint=Integer.parseInt(a[i]);
sum=sum+myint;
}
System.out.println(sum);//164
常量
- MAX_VALUE int类型的最大值
- MIN_VALUE int类型的最大值
- SIZE 以二进制补码形式表示int的位数
- TYPE 基本类型int的class实例
int max=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int min=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int size=Integer.SIZE; //int 32位 4字节
//1字节(Byte)= 8位(bit)
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println(min);
System.out.println(size);
8.2Boolean
构造方法
Boolean b=new Boolean(true)
Boolean bool=new Boolean(“ok”);
Boolean bool=new Boolean("true");
System.out.println(bool);//false
常用方法
-
Booleanvalue()//将Boolean对象的值以对应的Boolean值返回
-
Equals(object obj)//判断调用该方法的对象与obj是否相等。当且仅当参数不是null,而且与调用该方法的对象一样都表示同一个Boolean值的Boolean对象,才返回true
-
parseBoolean(string s)
String s="ok";
Boolean b=new Boolean(s);
System.out.println(b.parseBoolean(s)); -
Tostring()
Boolean b=new Boolean(true);
String s=b.toString();
System.out.println(s);
- valueOf(String s)
String str = "1";
Boolean i3 = Boolean.valueOf(str);
System.out.println(i3);
常量
- True
- False
- Type
Byte
- 构造方法
1.Byte(byte value)
Byte mybyte=45;
Byte b=new Byte(mybyte);
2.Byte(String str) 数值型String变量
常用方法
-
byteValue()
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Byte obj = new Byte(10);//integer类型
// returns the value of Integer as a byte
byte b = obj.byteValue();
System.out.println("Value of b = " + b);//输出Value of b = 10 -
compareTo(Byte anotherByte)
Byte int1 = new Byte( (byte) 100);//定义一个Integer型变量
Byte int2 = new Byte((byte) 100);//定义一个Integer型变量
int str = int1.compareTo(int2);
System.out.println(str);//0 相等返回0 大于返回1 小于返回-1 -
doubleValue()
Byte int1 = new Byte( (byte) 100);//定义一个Integer型变量
double str = int1.doubleValue();
System.out.println(str);//100.0 -
paseByte(String s)
String s="100";
Byte b=new Byte(s);
System.out.println(b.parseByte(s)); -
toString();
Byte b=new Byte((byte) 100);
String s=b.toString();
System.out.println(b.parseByte(s));//”100” -
valueOf(String str)
String s="100";
Byte b=Byte.valueOf(s);
System.out.println(b); -
Equals(object obj)
Byte b1=new Byte((byte) 1);
Byte b2=new Byte((byte) 1);
System.out.println(b1==b2); //比较内存
System.out.println(b1.equals(b2)); //这里只比较数值大小
常量有: -
MIN_VALUE
-
MAX_VALEU
-
TYPE SIZE
包装类
包装类对象的初始值为null(是一个对象);
Java中除了float和double的其他基本数据类型,都有常量池
(注:Python中int{-5~256,257 这个整数对象是区分作用域的,它只有在相同的作用域, 内存地址才会相同},str,byte也有)