Problem statement:
There is an m by n grid with a ball. Given the start coordinate (i,j) of the ball, you can move the ball to adjacent cell or cross the grid boundary in four directions (up, down, left, right). However, you can at most move N times. Find out the number of paths to move the ball out of grid boundary. The answer may be very large, return it after mod 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input:m = 2, n = 2, N = 2, i = 0, j = 0 Output: 6 Explanation:
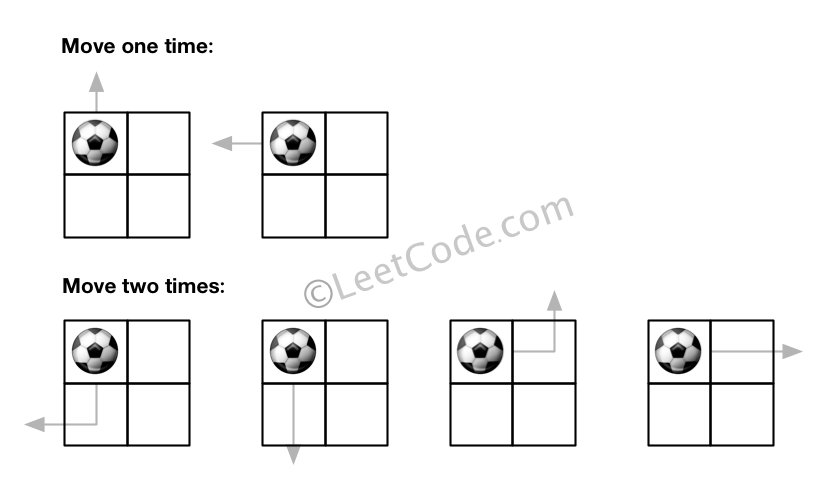
Example 2:
Input:m = 1, n = 3, N = 3, i = 0, j = 1 Output: 12 Explanation:
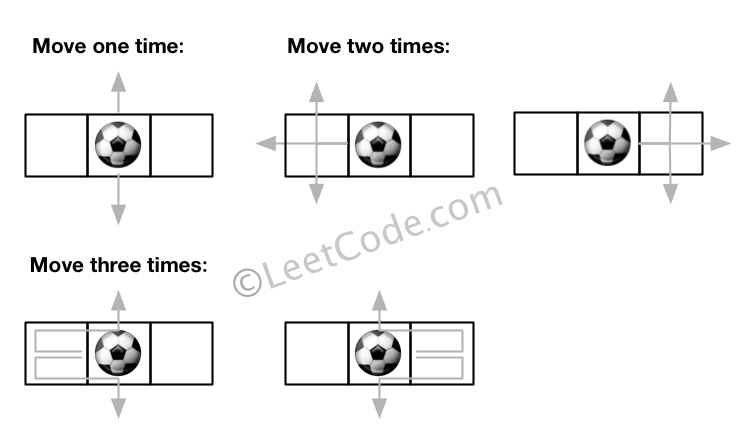
Note:
- Once you move the ball out of boundary, you cannot move it back.
- The length and height of the grid is in range [1,50].
- N is in range [0,50].
Analysis:
This question is the last one of leetcode weekly contest 31. Initially, it is tagged with medium, and then adjusted to hard today.
They mentioned a position in a two dimension board and at most N step to move and count the numbers to get out of boundary. Obviously, DP.
My first solution:
Start from (i, j), initialize all the element in the row i and col and j compared their value with N.
Do four direction dynamic programming, however, it ignored one fact that the value of one cell can come from all four directions except boundary.
The answer is wrong.
Solution:
This solution is quite simple, we have m * n board and N step to move, it is a 3 dimension DP.
The initialization status: dp[0][0 ... m -1][0 ... n - 1] is 0. means the step is 0, all value is 0.
Current value only comes from four directions of last move or 1 if it is boundary.
DP formula is:
dp[step][row][col] = dp[step - 1][row - 1][col] + dp[step - 1][row + 1][col] + dp[step - 1][row][col - 1] + dp[step - 1][row][col + 1]
we calculate the value of this three dimension matrix and return the value of dp[N][i][j].
The time complexity is O(N * m * n), space complexity is O((N + 1) * m * n)
class Solution { public: int findPaths(int m, int n, int N, int i, int j) { unsigned int dp[N + 1][m][n] = {}; for(int step = 1; step <= N; step++){ for(int row = 0; row < m; row++){ for(int col = 0; col < n; col++){ // the value come from four directoion // if one value comes from boundary: 1 // dp[step - 1][row - 1][col] // + dp[step - 1][row + 1][col] // + dp[step - 1][row][col - 1] // + dp[step - 1][row][col + 1] dp[step][row][col] = ((row == 0? 1 : dp[step - 1][row - 1][col]) + (row == m - 1? 1 : dp[step - 1][row + 1][col]) + (col == 0? 1 : dp[step - 1][row][col - 1]) + (col == n - 1? 1 : dp[step - 1][row][col + 1])) % 1000000007; } } } return dp[N][i][j]; } };