| 一、简介 |
django rest framework 给我们带来了很多组件,除了认证、权限、序列化...其中一个重要组件就是视图,一般视图是和路由配合使用,这种方式给我们提供了更灵活的使用方法,对于使用者而言不同的视图具有不同的功能,这样我们可以根据需求定制自己视图。以下是官网传送门:http://www.django-rest-framework.org/api-guide/views/
在之前的文章中,由于参杂了权限、认证等(如果不了解请看博客的以前的文章),但在本章中基本可以不使用,所进使用以下简单模型进行说明:
settings中注册django rest framework
INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'app01.apps.App01Config', 'rest_framework', ]
models.py
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class UserInfo(models.Model): username = models.CharField(max_length=32,unique=True) password = models.CharField(max_length=64)
urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^api/v1/users', views.UerView.as_view()), ]
| 二、各类视图使用 |
1.APIView
该视图是最基本的视图,之前的章节中已经介绍如何使用,参考:Django Rest Framework源码剖析(一)-----认证
2.GenericAPIView
该视图为我们封装一些静态字段,用于调用其他组件,示例(解释请看注解):
from django.shortcuts import render # Create your views here. from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView from rest_framework import serializers from rest_framework import pagination from app01 import models class Userserializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): #序列化类定义,前面章节已经介绍 class Meta: model = models.UserInfo fields = '__all__' #序列化字段 class Mypagination(pagination.PageNumberPagination): # 分页类定义,前面章节也已经介绍 """自定义分页""" page_size=2 #默认每页显示个数配置 page_query_param = 'p' # 页面传参的key,默认是page page_size_query_param='size' # 指定每页显示个数参数 max_page_size=4 # 每页最多显示个数配置,使用以上配置,可以支持每页可显示2~4条数据 class UerView(GenericAPIView): #视图 queryset = models.UserInfo.objects.all() #数据的queryset serializer_class = Userserializer # 序列化类使用 permission_classes = [] # 权限认证,这里不做认证,前面章节也有介绍权限 pagination_class = Mypagination #分页类,前面章节也已经介绍 def get(self,*args,**kwargs): roles=self.get_queryset() # 获取queryset,实际取queryset,也就是models.UserInfo.objects.all() page_res=self.paginate_queryset(queryset=roles) #分页结果 res=self.get_serializer(instance=page_res,many=True) #序列化 return Response(res.data) #返回结果
访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/users,查看结果如下:

3.GenericViewSet
该视图类需要和路由配合使用,修改后的urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), # url(r'^api/v1/users', views.UserView.as_view()), url(r'^api/v2/users', views.UserView.as_view({'get':'show','post':'create'})), #重写as_view方法,并对请求方法进行映射 ]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render # Create your views here. from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView from rest_framework import serializers from rest_framework import pagination from rest_framework.viewsets import GenericViewSet from app01 import models class Userserializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): #序列化类定义,前面章节已经介绍 class Meta: model = models.UserInfo fields = '__all__' #序列化字段 class Mypagination(pagination.PageNumberPagination): # 分页类定义,前面章节也已经介绍 """自定义分页""" page_size=2 #默认每页显示个数配置 page_query_param = 'p' # 页面传参的key,默认是page page_size_query_param='size' # 指定每页显示个数参数 max_page_size=4 # 每页最多显示个数配置,使用以上配置,可以支持每页可显示2~4条数据 class UserView(GenericViewSet): #视图 queryset = models.UserInfo.objects.all() #数据的queryset serializer_class = Userserializer # 序列化类使用 permission_classes = [] # 权限认证,这里不做认证,前面章节也有介绍权限 pagination_class = Mypagination #分页类,前面章节也已经介绍 def show(self,*args,**kwargs): #与url中映射的方法名称相同 roles=self.get_queryset() # 获取queryset,实际取queryset,也就是models.UserInfo.objects.all() page_res=self.paginate_queryset(queryset=roles) #分页结果 res=self.get_serializer(instance=page_res,many=True) #序列化 return Response(res.data) #返回结果 def create(self,*args,**kwargs): pass
访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v2/users,结果和上面结果一样如图:
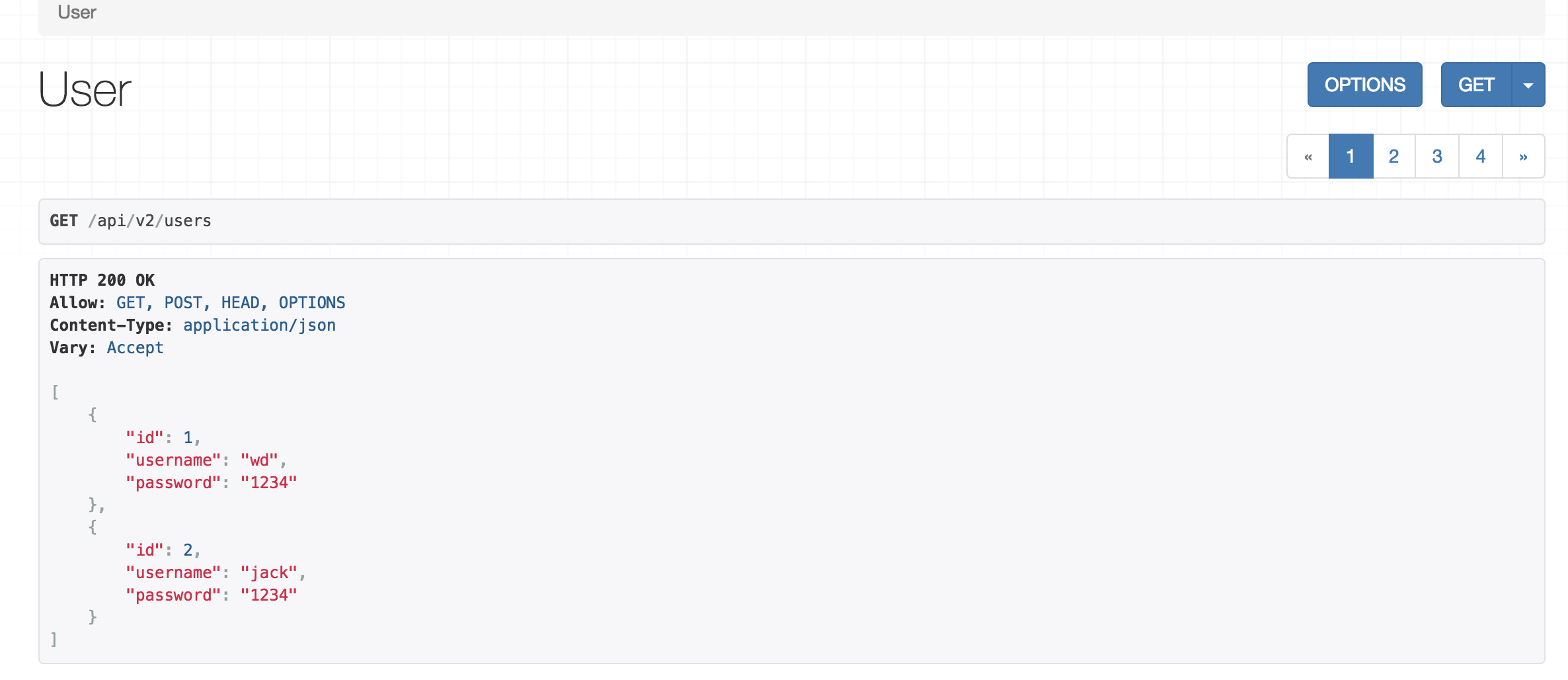
4.ModelViewSet
modelViewSet继承了mixins.CreateModelMixin、mixins.RetrieveModelMixin、mixins.UpdateModelMixin、mixins.DestroyModelMixin、mixins.ListModelMixin、GenericViewSet所以它有很父类的所有功能,而这些父类分别提供创建、获取、更新、删除等方法,所以我们不需要写增删该查,视图已经帮我实现了,示例:
此时路由urls.py
"""resetful URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.conf.urls import url, include 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^api/v1/users$', views.UserView.as_view({'get':'list','post':'create'})), #路由,retrieve、delete、create、update、partial_update,在UserView的父类全部实现,其中pk参数必须携带,想当于key,类可操作 url(r'^api/v1/users/(?P<pk>d+)$', views.UserView.as_view({'get':'retrieve','delete':'destroy','post':'create','put':'update','patch':'partial_update'})), ]
视图views.py
from django.shortcuts import render # Create your views here. from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView from rest_framework import serializers from rest_framework import pagination from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet from app01 import models class Userserializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): #序列化类定义,前面章节已经介绍 class Meta: model = models.UserInfo fields = '__all__' #序列化字段 class Mypagination(pagination.PageNumberPagination): # 分页类定义,前面章节也已经介绍 """自定义分页""" page_size=2 #默认每页显示个数配置 page_query_param = 'p' # 页面传参的key,默认是page page_size_query_param='size' # 指定每页显示个数参数 max_page_size=4 # 每页最多显示个数配置,使用以上配置,可以支持每页可显示2~4条数据 class UserView(ModelViewSet): #视图 queryset = models.UserInfo.objects.all() #数据的queryset serializer_class = Userserializer # 序列化类使用 permission_classes = [] # 权限认证,这里不做认证,前面章节也有介绍权限 pagination_class = Mypagination #分页类,前面章节也已经介绍
访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/users/1,查看多增删改。
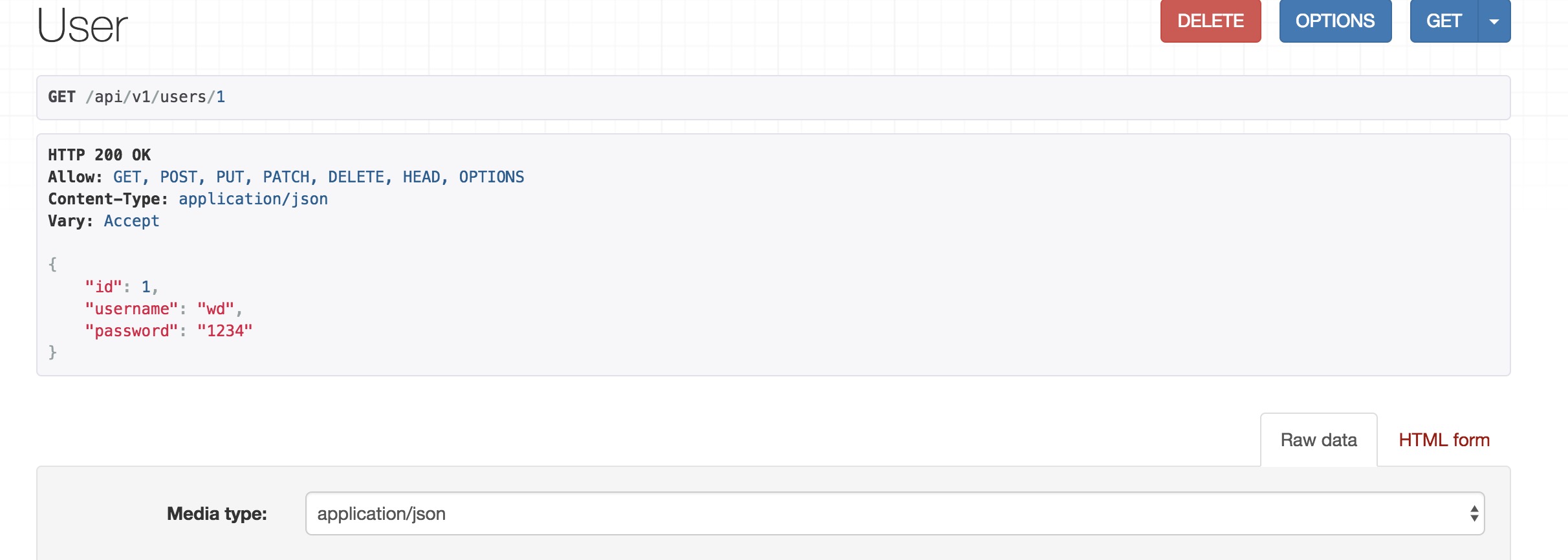
| 三、路由 |
前面的示例中已经用到类路由的功能,在这里介绍下router使用方法,一般情况,我们写路由时候对于增删该查可能写多个路由,其实我们可以借助DRF的router自动帮我们生成路由,示例:
"""resetful URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.conf.urls import url, include 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.conf.urls import url,include from django.contrib import admin from app01 import views from rest_framework import routers router=routers.DefaultRouter() #是列化router类 router.register(r'userinfo$',views.UserView) #注册一个url,后续会生成我们想要的个url ##生成的url urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^api/v1/users$', views.UserView.as_view({'get':'list','post':'create'})), #路由,retrieve、delete、create、update、partial_update,在UserView的父类全部实现 url(r'^api/v1/users/(?P<pk>d+)$', views.UserView.as_view({'get':'retrieve','delete':'destroy','post':'create','put':'update','patch':'partial_update'})), url(r'^api/v1',include(router.urls)),#将生成的url加入到路由中 ]
此时我们找一个不存在的页面查看路由:
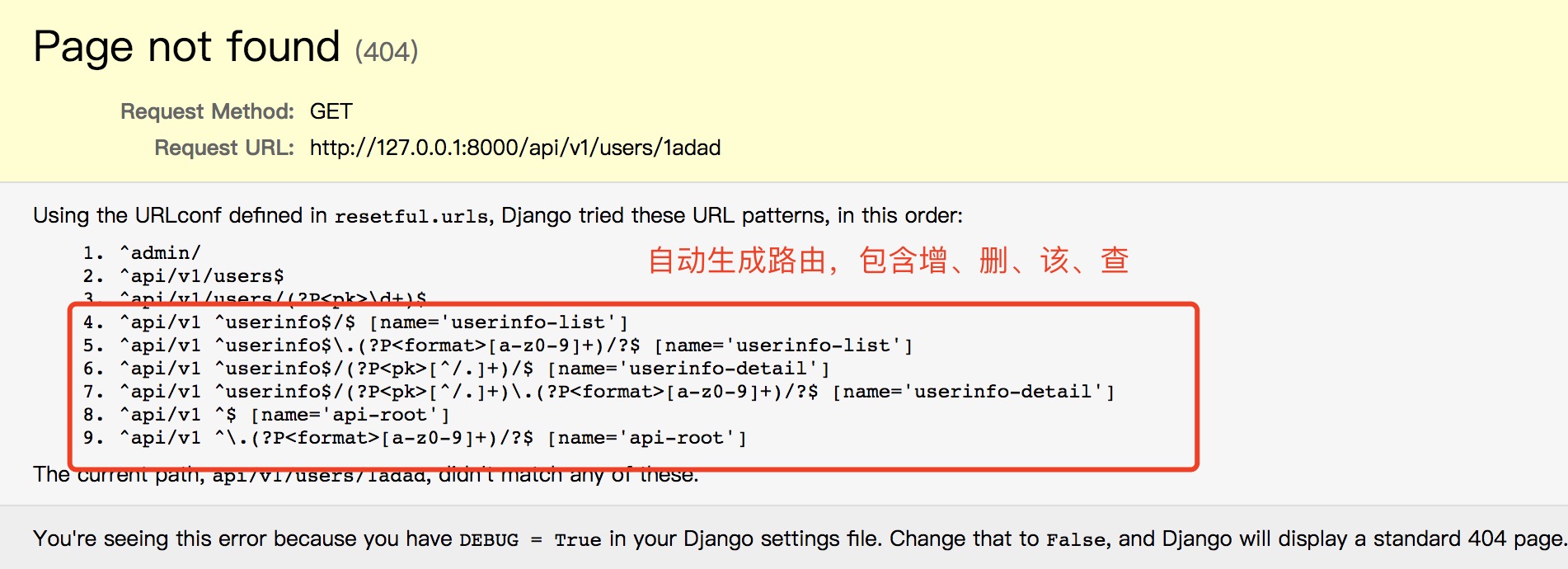
| 四、源码剖析 |
需要知道的知识点:
- 子类拥有父类的所有功能
由于视图类较多,所以我们对源码的剖析就不一一分析了,这里以一个常用的GenericAPIView为例子分析下源码。首先从继承角度来说,GenericAPIView继承了APIView,而APIView又继承了View,而APIView是对django原生的View类的dispatch方法进行了重写(在认证的篇章已经说明),所以GenericAPIView具有APIView和View的所有功能,下面是GenericAPIView源码,分析部分请看注释:
class GenericAPIView(views.APIView): """ Base class for all other generic views. """ # You'll need to either set these attributes, # or override `get_queryset()`/`get_serializer_class()`. # If you are overriding a view method, it is important that you call # `get_queryset()` instead of accessing the `queryset` property directly, # as `queryset` will get evaluated only once, and those results are cached # for all subsequent requests. queryset = None # queryset数据配置,这就是为什么我们示例中的queryset = models.UserInfo.objects.all() serializer_class = None # 序列化类配置 # If you want to use object lookups other than pk, set 'lookup_field'. # For more complex lookup requirements override `get_object()`. lookup_field = 'pk' # 浏览条数据使用的pk lookup_url_kwarg = None # The filter backend classes to use for queryset filtering filter_backends = api_settings.DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS # 过滤配置 # The style to use for queryset pagination. pagination_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS #分页配置 def get_queryset(self): # 获取queryset方法 """ Get the list of items for this view. This must be an iterable, and may be a queryset. Defaults to using `self.queryset`. This method should always be used rather than accessing `self.queryset` directly, as `self.queryset` gets evaluated only once, and those results are cached for all subsequent requests. You may want to override this if you need to provide different querysets depending on the incoming request. (Eg. return a list of items that is specific to the user) """ assert self.queryset is not None, ( "'%s' should either include a `queryset` attribute, " "or override the `get_queryset()` method." % self.__class__.__name__ ) queryset = self.queryset # 将配置querset 转化为类属性 if isinstance(queryset, QuerySet): # 判断配置queryset是不是QuerySet类型 # Ensure queryset is re-evaluated on each request. queryset = queryset.all() # 返回所有该Queryset类型的数据 return queryset def get_object(self): # 获取单个的对象,需要在url中配置pk,其中pk的参数一般是ID """ Returns the object the view is displaying. You may want to override this if you need to provide non-standard queryset lookups. Eg if objects are referenced using multiple keyword arguments in the url conf. """ queryset = self.filter_queryset(self.get_queryset()) # Perform the lookup filtering. lookup_url_kwarg = self.lookup_url_kwarg or self.lookup_field assert lookup_url_kwarg in self.kwargs, ( 'Expected view %s to be called with a URL keyword argument ' 'named "%s". Fix your URL conf, or set the `.lookup_field` ' 'attribute on the view correctly.' % (self.__class__.__name__, lookup_url_kwarg) ) filter_kwargs = {self.lookup_field: self.kwargs[lookup_url_kwarg]} obj = get_object_or_404(queryset, **filter_kwargs) # May raise a permission denied self.check_object_permissions(self.request, obj) # 检查请求是否有该对象权限,也就是权限篇章定义权限时候不可少的方法,如不过没定义会,执行权限验证的时候就会抛出异常。 return obj def get_serializer(self, *args, **kwargs): # 获取序列化类 """ Return the serializer instance that should be used for validating and deserializing input, and for serializing output. """ serializer_class = self.get_serializer_class() # 执行get_serializer_class用于获取序列化类 kwargs['context'] = self.get_serializer_context() return serializer_class(*args, **kwargs) # 序列化数据,返回序列化以后的结果 def get_serializer_class(self): # 获取序列化类 ,也就是serialzier_class配置 """ Return the class to use for the serializer. Defaults to using `self.serializer_class`. You may want to override this if you need to provide different serializations depending on the incoming request. (Eg. admins get full serialization, others get basic serialization) """ assert self.serializer_class is not None, ( # 判断序列化类是否存在 "'%s' should either include a `serializer_class` attribute, " "or override the `get_serializer_class()` method." % self.__class__.__name__ ) return self.serializer_class def get_serializer_context(self): """ Extra context provided to the serializer class. """ return { 'request': self.request, 'format': self.format_kwarg, 'view': self } def filter_queryset(self, queryset): # 过滤,参数为queryset """ Given a queryset, filter it with whichever filter backend is in use. You are unlikely to want to override this method, although you may need to call it either from a list view, or from a custom `get_object` method if you want to apply the configured filtering backend to the default queryset. """ for backend in list(self.filter_backends): queryset = backend().filter_queryset(self.request, queryset, self) return queryset @property def paginator(self): #属性方法,用于获取分页对象 """ The paginator instance associated with the view, or `None`. """ if not hasattr(self, '_paginator'): # 判断分页对象是否存在 if self.pagination_class is None: self._paginator = None #不存在返回none else: self._paginator = self.pagination_class() # 存在返回分页对象 return self._paginator def paginate_queryset(self, queryset): """ Return a single page of results, or `None` if pagination is disabled. """ if self.paginator is None: return None return self.paginator.paginate_queryset(queryset, self.request, view=self) # 调用分页对象的分页方法,返回分页数据 def get_paginated_response(self, data): # 使用分页对象响应请求,页面显示时候比较美观提供一些操作方法,除此之外无其他作用 """ Return a paginated style `Response` object for the given output data. """ assert self.paginator is not None return self.paginator.get_paginated_response(data)
| 五、总结 |
使用建议:
1.对于简单的数据模型来说,建议使用modelViewSet,因为它已经帮我们写好了增删该查接口。
2.对于复杂的数据模型,比如涉及多个表操作或有事务要求时,此时更建议使用APIView或者GenericAPIView,这样可以根据需求我们自己写增删该查接口。