一、使用PreparedStatement预编译语句防止SQL注入
什么是SQL注入?
所谓SQL注入,就是通过把SQL命令插入到Web表单提交或输入域名或页面请求的查询字符串,最终达到欺骗服务器执行恶意的SQL命令。
举个例子:假如我们登录时执行的SQL语句为:select *from user where username='USERNAME' and password='PASSWORD';
但是我们可以把USERNAME填写为"tom';-- ",(注意--后有空格),PASSWORD随便写(假设这里写123),这样SQL语句就成了select *from user where username='tom';-- ' and password='123';
"-- "后的内容就被注释掉,现在就算密码不正确也能查询到相应的结果。利用SQL注入可以实现数据的盗取
在Java中使用PreparedStatement类防止SQL注入
防SQL注入的方法有很多,使用预编译语句是一种简单有效的方式
下面介绍如何使用这种方式来操作数据库
我已经在本地数据库mydb中创建了一个user表,并在表中插入数据
现在我们使用字符串拼接的方式来构造一个SQL语句,并在mysql客户端执行此SQL语句,结果如下:

通过图中我们发现这种方式SQL注入成功
下面使用预编译SQL语句的方式来执行此SQL语句
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
String username = "杜若' or 1=1; -- "; //'-- ' 是sql中的注释符号(注意后面的空格)
String pwd = "000";
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//构造sql语句
String sql = "select *from user where username=? and pwd =?";
PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, pwd);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
do{
String username = rs.getString(2);
String pwd = rs.getString(3);
System.out.println(username+":"+pwd);
}while(rs.next());
}else{
System.out.println("未查到相应的结果");
}
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if(pstmt!=null){
pstmt.close();
}
if(connection!=null){
connection.close();
}
测试运行之后的结果
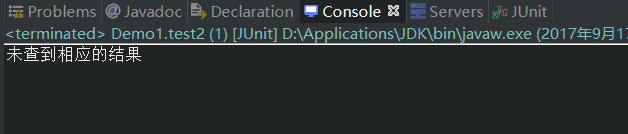
这样已经达到了防SQL注入的目的
那为什么它这样处理就能预防SQL注入提高安全性呢?其实是因为SQL语句在程序运行前已经进行了预编译,在程序运行时第一次操作数据库之前,SQL语句已经被数据库分析,编译和优化,对应的执行计划也会缓存下来并允许数据库已参数化的形式进行查询,当运行时动态地把参数传给PreprareStatement时,即使参数里有敏感字符如 or '1=1'也数据库会作为一个参数一个字段的属性值来处理而不会作为一个SQL指令
二,获取插入自增长值
有时候在插入一条记录的时候,我们需要获取插入这条数据的自增长值,以便在其他地方使用
直接上代码
//获取插入自增长
public class Demo1 {
private String user="root";
private String password="root";
private String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
String sql = "insert into user(username,pwd) values(?,?)";
//第二个参数是Statement类中的一个常量,指示是否应该返回自动生成的键的标志
PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
pstmt.setString(1, "mary");
pstmt.setString(2, "123456");
pstmt.executeUpdate();
ResultSet rs = pstmt.getGeneratedKeys();
if(rs.next()){
int key = rs.getInt(1);
System.out.println(key);
}
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if(pstmt!=null){
pstmt.close();
}
if(connection!=null){
connection.close();
}
}
}
三,批处理执行
有时候需要向数据库发送一批SQL语句执行,这时应避免向数据库一条条的发送执行,而应采用JDBC的批处理机制,以提升执行效率。
无论使用Statement对象还是使用PreparedStatement对象都可以实现
这里介绍使用PreparedStatement来实现的方式
- 获取PreparedStatement对象
- 设置每条批处理的参数
- 将一组参数添加到批处理命令中
下面上实例代码
public class Demo1 {
private String user="root";
private String password="root";
private String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("albee"+i);
user.setPwd("123456");
list.add(user);
}
sava(list);
}
public void sava(List<User> l) throws Exception{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
String sql = "insert into user(username,pwd) values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0;i<l.size();i++){
pstmt.setString(1, l.get(i).getUsername());
pstmt.setString(2, l.get(i).getPwd());
pstmt.addBatch();
// 每到五条就执行一次对象集合中的批处理命令,
if(i%5==0){
pstmt.executeBatch();
pstmt.clearBatch();
}
}
// 不足五条也要执行一次
pstmt.executeBatch();
pstmt.clearBatch();
if(pstmt!=null){
pstmt.close();
}
if(connection!=null){
connection.close();
}
}
}
四,事务的操作
有时候我们需要完成一组数据库操作,这其中的操作有一个失败则整个操作就回滚,即组成事务的每一个操作都执行成功整个事务才算成功执行
常见的例子就是银行转帐业务
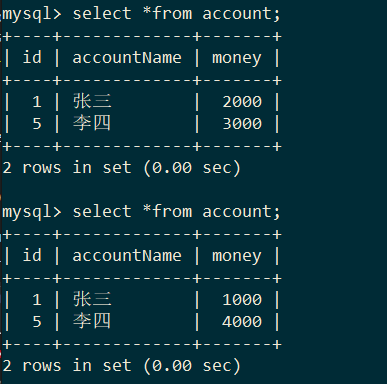
update account set money=money-1000 where accountName='张三';
update account set money=money+1000 where accountName='李四';
已经在mydb中创建了account表,包含accountName和money字段,并插入了两条记录
实例代码:
// 使用事务
@Test
public void test2(){
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
connection.setAutoCommit(false); //设置事务为手动提交
String sql_zs = "update account set money=money-1000 where accountName='张三'";
String sql_ls = "update account set money=money+1000 where accountName='李四'";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql_ls);
int count_ls = pstmt.executeUpdate();
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql_zs);
int count_zs = pstmt.executeUpdate();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
try {
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
if(pstmt!=null){
try {
pstmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
如果事务执行成功
执行前和执行后表的变动