mybatis缓存有一级缓存和二级缓存,一级缓存的作用域是sqlSession,在一次会话内,默认是开启的,如果在一次会话内,查询的sql、参数相同,则
会从缓存中取数据,执行dml操作会清楚缓存,二级缓存的作用域是sqlSessionFactory,默认是关闭的,需要在mybatis-config.xml指定开启,在一个会话完成后,
会将所有的select的查询数据缓存,其他的会话如果以相同的sql和参数查询,有能够从缓存中拿到结果。
一:一级缓存的使用
测试用例如下:在同一个sqlSession会话内,执行两次相同的查询操作
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 将mybatis-config的配置文件读入内存,生成字符流对象
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
// 解析全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = builder.build(reader);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// PageHelper.startPage(1,2);
// 测试一级缓存:
List<User> list = userMapper.selectUser("hello105");
System.out.println("第一次查询结果:" + list.size());
List<User> list2 = userMapper.selectUser("hello105");
System.out.println("第二次查询结果:" + list2.size());
}
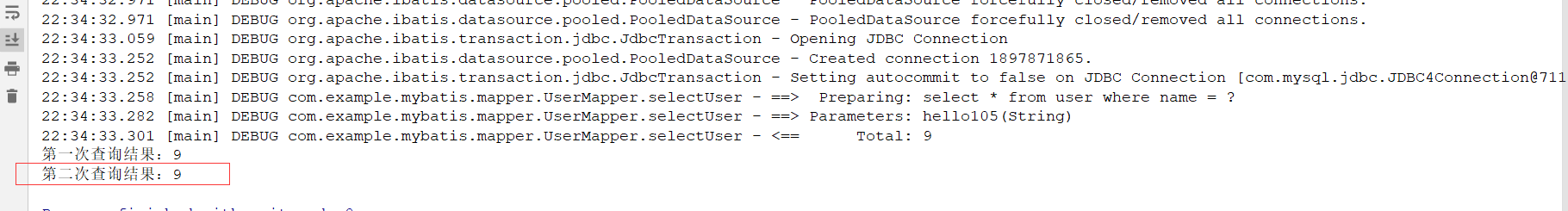
因为一级缓存默认开启,且缓存key值相同,从结果可以看到,第二次没有执行数据库select的操作,直接从缓存拿的数据。
二:从源码层面分析一下一级缓存
1:在看查询缓存之前,我们先来看一下Executor的创建,这个是SqlSessionFactory中的方法,看一下configuration.newExecutor
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
从代码可以看出,创建完成一个executor对象后,会把它包装成一个cacheExecutor,因为cacheEnabled默认是开启的
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
来看一下构造函数里面的逻辑:
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
会把真正的executor维护到cacheExecutor的属性delegate上。
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
2:executor的创建完成后,我们来看一下怎么缓存的,来到DefaultSqlSession类,因为要执行查询操作
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
这里会根据sql语句、参数、命名空间生成一个缓存key值
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
调用query方法,首先会判断mapper.xml或者mapper类上是否开启了二级缓存(sqlSessionFactory全局),这里我们没有开启,会跳过if语句,直接执行查询,delegate.query
就是创建execcutor的时候封装进去的SimpleExecutor对象
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
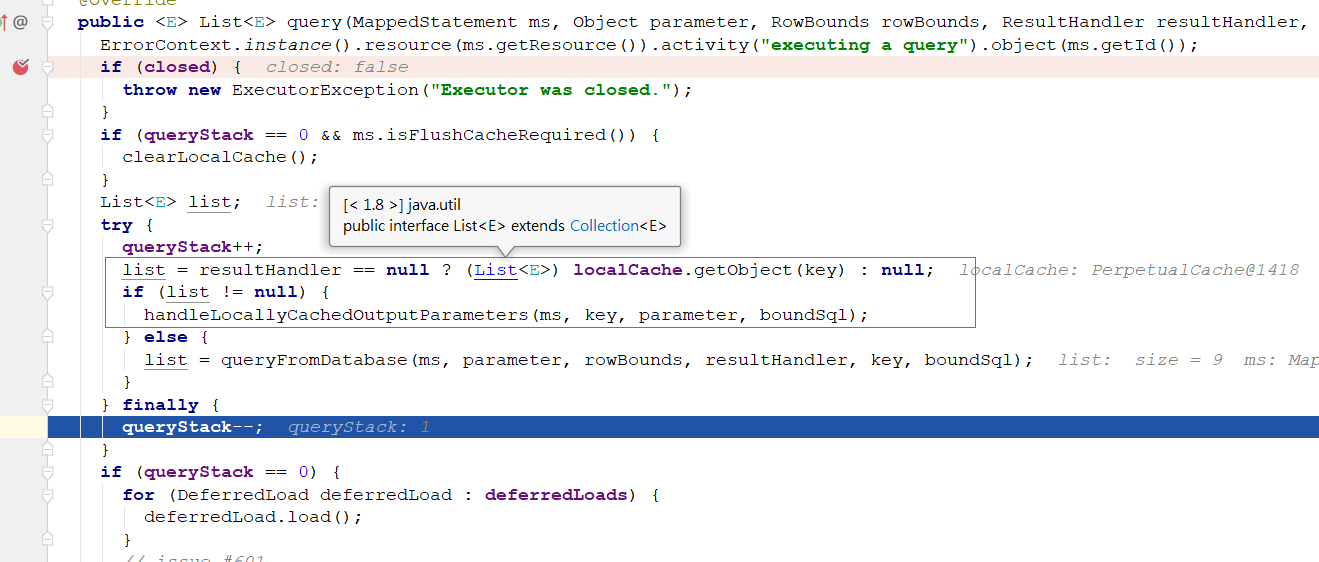
这里的查询,首先会到一级缓存localCache,第一次查询localCache中没有数据,返回null,然后会调用queryFromDatabase接口,去真正的执行数据库的查询操作
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
这个方法,首先设置了一个默认值放入localCache,查询完成后删除key值,然后将查询结果list放入缓存localCache
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
所以当第二次执行查询操作时,发现key值相同,就会到一级缓存中去查询,这样就会出现日志中查询两次,但是只会执行一次数据库操作的现象了
一级缓存的源码就是这样,下面来看一下二级缓存
三:二级缓存的使用
mybatis-config.xml可以配置也可以不配置
<settings>
<!-- 开启驼峰匹配:完成经典的数据库命名到java属性的映射
相当于去掉数据中的名字的下划线,和java进行匹配
-->
<!--<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true" /> 默认开启,可以不用配置-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
在mapper接口类配置注解或者在mapper.xml文件中配置cache标签

测试用例:创建2个不同的sqlSession,但是查询sql和参数相同
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 将mybatis-config的配置文件读入内存,生成字符流对象
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
// 解析全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = builder.build(reader);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// PageHelper.startPage(1,2);
// 测试一级缓存:
List<User> list = userMapper.selectUser("hello105");
System.out.println("第一次查询结果:" + list.size());
// List<User> list2 = userMapper.selectUser("hello105");
// System.out.println("第二次查询结果:" + list2.size());
// 只有sqlSession关闭时,数据才会缓存到二级缓存
sqlSession.close();
// 测试二级缓存:
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println("另外一个会话查询结果:"+userMapper2.selectUser("hello105").size());
}
执行结果,只查询了1次,第二次查询的缓存:

看一下注册,mybatis-config.xml中开启时,会在XMLConfigBuilder中解析设置:
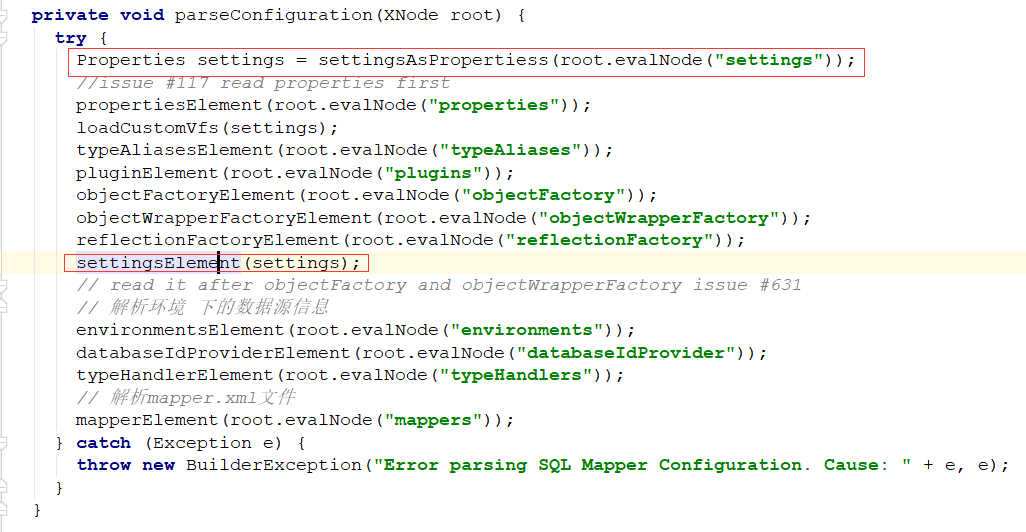
不配默认是true:

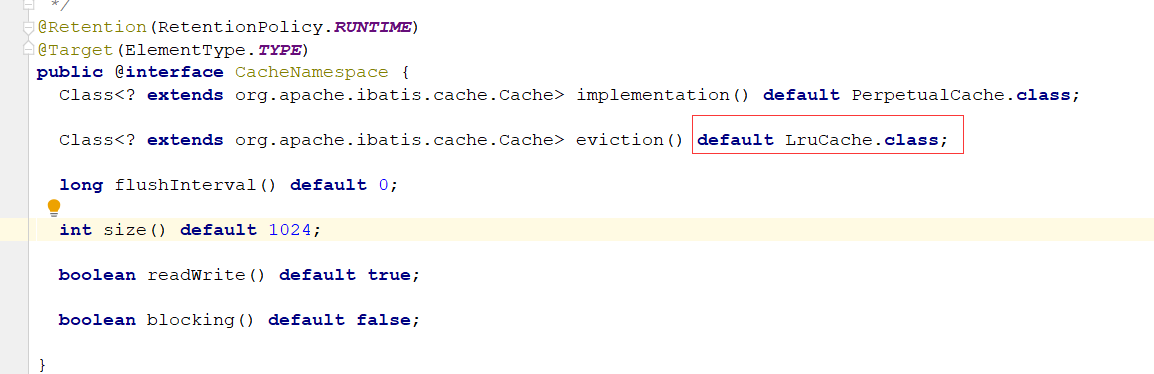
Mapper类上加注解@CacheNamespace 或者在Mapper.xml中配置Cache标签
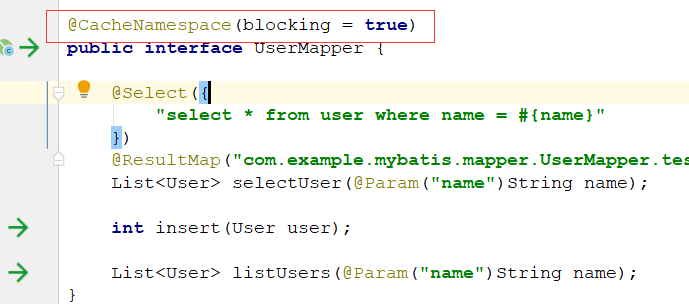
看一下解析:XMLMapperBuilder类中解析命名空间:
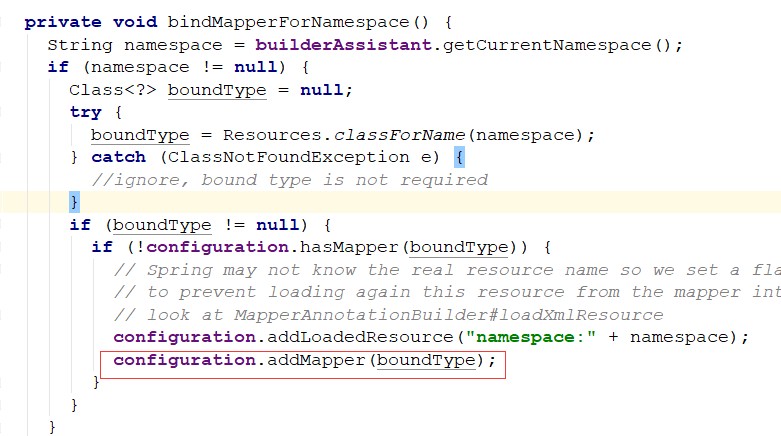
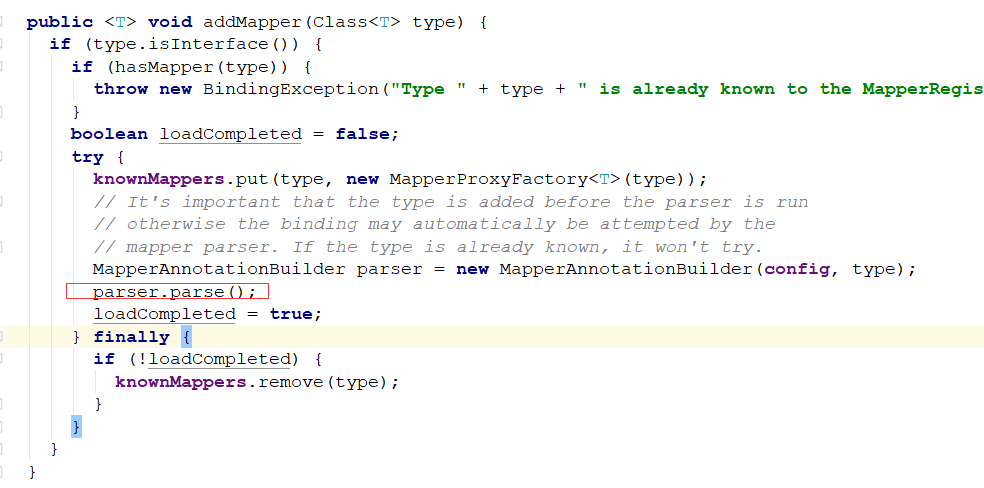
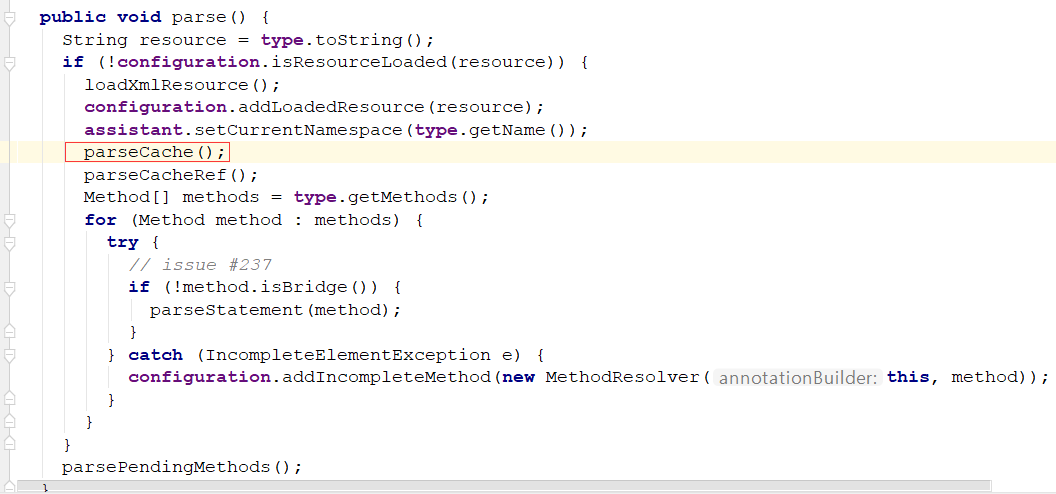
解析CacheNamespace注解:
然后将解析后的元数据封装到Cache对象中,缓存到configuration中
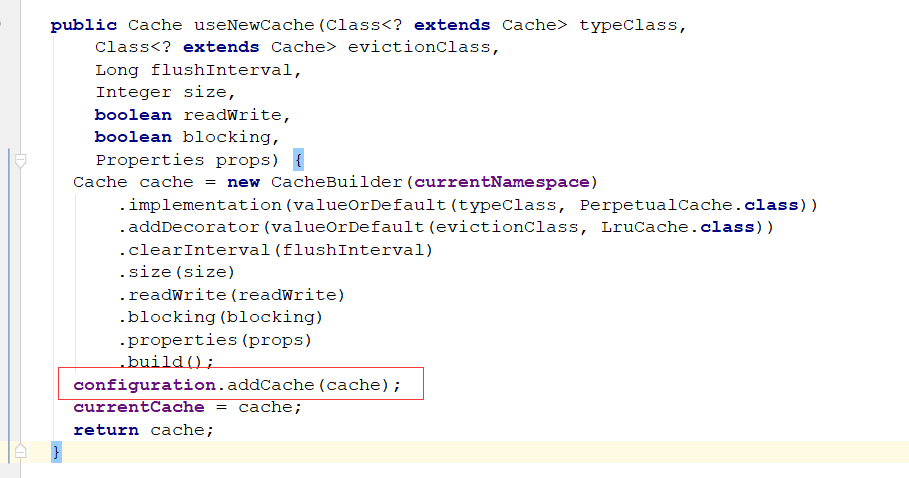
把cache对象 赋值给了currentCache,而在创建MapperStatement的时候会把currentCache赋值给cache属性

public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resulSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}

下面看看具体的查询,其实在分析一级缓存的时候有涉及到,这里我们详细看一下:
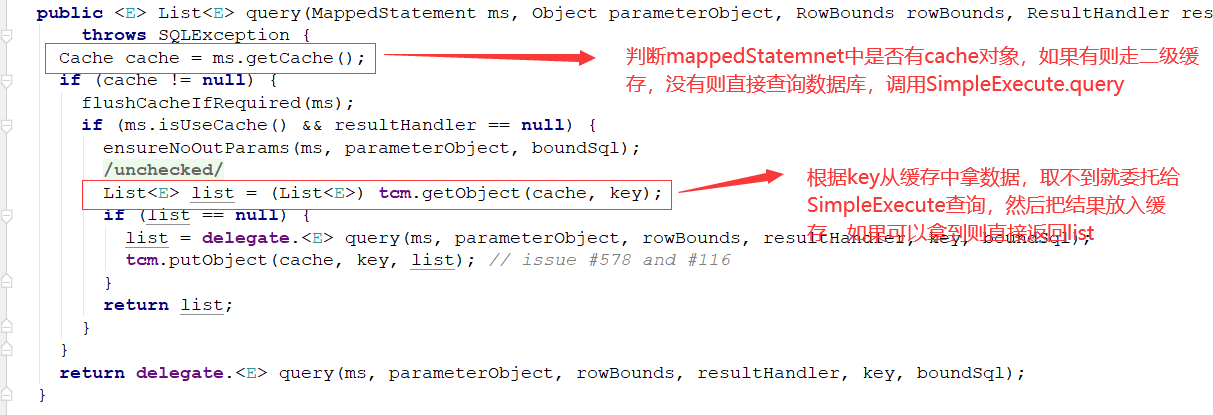
MappedStatement的getCache方法,如果配置Cache标签或者注解就不为null


默认用到缓存类型是LruCache:
存取数据
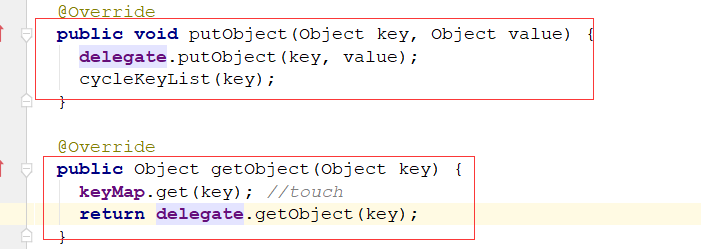
向二级缓存中放数据是在会话关闭这个动作放的

总结:mybatis缓存
在创建executor的时候,会对executor进行包装,包装成cacheExecutor,在DefaultSqlSession中调用query时,
会路由到CacheExecutor的query方法,首先判断二级缓存是否开启,如果开启,则到二级缓存中查询,看是否命中,
命中cacheKey则返回结果,如果没有命中则委托给simpleExecutor处理,simpleExecutor首先会到一级缓存中查询,如果
命中则返回,没有命中则执行数据库查询操作,从数据库查询到结果后把数据放到一级缓存中,当这个sqlSession关闭的
时候会向二级缓存中缓存数据,大致的查询流程就是这样
如果一级和二级缓存都开启,那么在同一个sqlSession内会取一级缓存,其他的sqlSession会到二级缓存中获取
| 一级缓存 | 二级缓存 | |
| 作用域 | sqlSession会话内 | sqlSessionFactory全局 |
| 开启情况 | 默认开启 | 需要在mapper接口或者mapper.xml配置 |