
g函数返回后,f函数对应的栈中的数据没有任何变化,这就是回溯算法的核心。
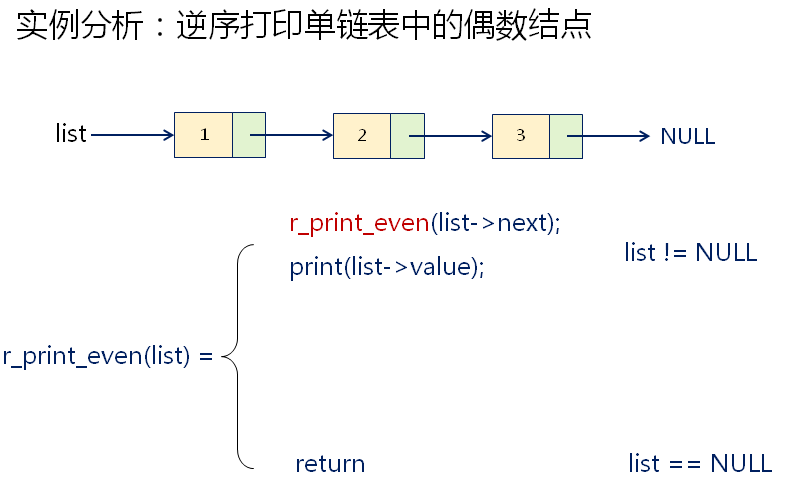
可以这样思考,先逆序打印从第二个节点开始的子表,最后再将第一个节点打印出来。
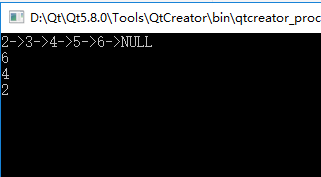
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include "DTString.h" 4 5 using namespace std; 6 using namespace DTLib; 7 8 struct Node 9 { 10 int value; 11 Node* next; 12 }; 13 14 Node* create_list(int v, int len) // v:数据元素从哪一个之开始。 len:长度 15 { 16 Node* ret = NULL; 17 Node* slider = NULL; 18 19 for(int i=0; i<len; i++) 20 { 21 Node* n = new Node(); 22 23 n->value = v++; 24 n->next = NULL; 25 26 if( slider == NULL ) 27 { 28 slider = n; 29 ret = n; 30 } 31 else 32 { 33 slider->next = n; 34 slider = n; 35 } 36 } 37 38 return ret; 39 } 40 41 void destroy_list(Node* list) 42 { 43 while( list ) 44 { 45 Node* del = list; 46 47 list = list->next; 48 49 delete del; 50 } 51 } 52 53 void print_list(Node* list) 54 { 55 while( list ) 56 { 57 cout << list->value << "->"; 58 59 list = list->next; 60 } 61 62 cout << "NULL" << endl; 63 } 64 65 66 67 void r_print_even(Node* list) 68 { 69 if( list != NULL) 70 { 71 r_print_even(list->next); 72 73 if( (list->value % 2) == 0 ) 74 { 75 cout << list->value << endl; 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 80 int main() 81 { 82 Node* list = create_list(2, 5); 83 84 print_list(list); 85 86 r_print_even(list); 87 88 destroy_list(list); 89 90 return 0; 91 }
逆序打印栈的增长与退栈示意图:
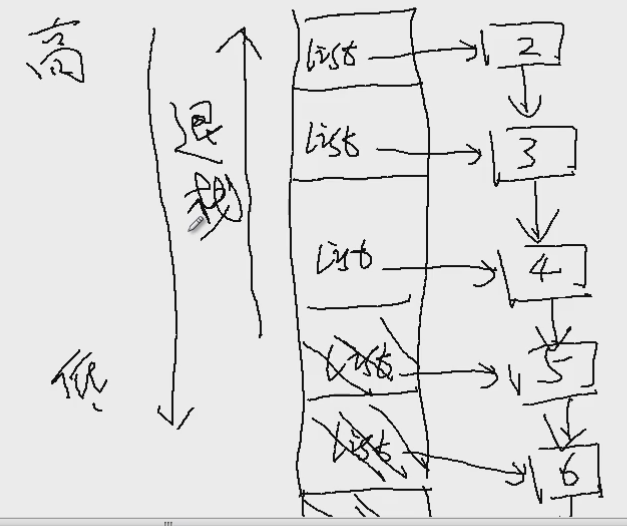
退栈打印的过程就是回溯的过程。
递归调用的时候只是先将参数保存在栈上,这时这个参数还没有用到,只是让指针指向了相应的节点,退栈的时候才用到。
类似于走迷宫,走到一个路口时先做个标记,这个标记暂时不用,回来的时候再用。根据标记找来时的路。
回溯的本质就是做标记,这样方便回退。
八皇后:

放皇后的时候只需要关注箭头的方向,因为其他的方向还没有放任何东西。
当我们发现某一行的任何一个位置都不能放皇后的时候,就开始要回溯了。因为,这证明了上一行放置皇后的地方是错误的。
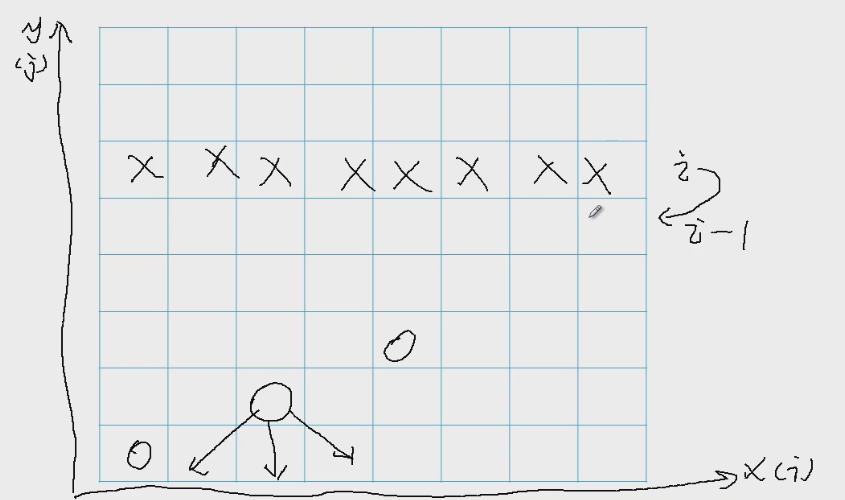
当我们发现第i行的任何一个位置都不能放置皇后了,这就证明了第i-1行放置的位置是错误的。
如果发现第i-1行也没有地方可以放置皇后了,这意味着还要继续回退,退到i-2行,这就是回溯。


理论上,每放置一个皇后要判断8个方向,但是我们从第一行开始放置皇后,有规律的放,因此,只需要考虑三个方向。

如果判断一个位置的左下角对角线是否已经放置了皇后,那就在这个位置的基础上,在xy坐标上不断的减一。因此,方向数据很重要。左下角方向数据是(-1,-1)。


1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include "DTString.h" 4 #include "LinkList.h" 5 6 using namespace std; 7 using namespace DTLib; 8 9 struct Node 10 { 11 int value; 12 Node* next; 13 }; 14 15 Node* create_list(int v, int len) // v:数据元素从哪一个之开始。 len:长度 16 { 17 Node* ret = NULL; 18 Node* slider = NULL; 19 20 for(int i=0; i<len; i++) 21 { 22 Node* n = new Node(); 23 24 n->value = v++; 25 n->next = NULL; 26 27 if( slider == NULL ) 28 { 29 slider = n; 30 ret = n; 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 slider->next = n; 35 slider = n; 36 } 37 } 38 39 return ret; 40 } 41 42 void destroy_list(Node* list) 43 { 44 while( list ) 45 { 46 Node* del = list; 47 48 list = list->next; 49 50 delete del; 51 } 52 } 53 54 void print_list(Node* list) 55 { 56 while( list ) 57 { 58 cout << list->value << "->"; 59 60 list = list->next; 61 } 62 63 cout << "NULL" << endl; 64 } 65 66 67 68 void r_print_even(Node* list) 69 { 70 if( list != NULL) 71 { 72 r_print_even(list->next); 73 74 if( (list->value % 2) == 0 ) 75 { 76 cout << list->value << endl; 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 81 template <int SIZE> 82 class QueueSolution : public Object 83 { 84 protected: 85 enum { N = SIZE + 2}; //设置边界用 86 87 struct Pos : public Object 88 { 89 Pos(int px = 0, int py = 0) : x(px),y(py){} 90 int x; 91 int y; 92 }; 93 94 int m_chessboard[N][N]; 95 Pos m_direction[3]; //方向数组 96 LinkList<Pos> m_solution; // 使用链表存储解决方案(放置皇后的位置) 97 int m_count; 98 99 void init() 100 { 101 m_count = 0; 102 103 for(int i = 0; i < N; i+=(N-1)) 104 { 105 for(int j = 0; j<N; j++) 106 { 107 m_chessboard[i][j] = 2; 108 m_chessboard[j][i] = 2; 109 } 110 } 111 112 for(int i=1; i<=SIZE; i++) 113 { 114 for(int j = 1; j <= SIZE; j++) 115 { 116 m_chessboard[i][j] = 0; 117 } 118 } 119 120 m_direction[0].x = -1; 121 m_direction[0].y = -1; 122 m_direction[1].x = 0; 123 m_direction[1].y = -1; 124 m_direction[2].x = 1; 125 m_direction[2].y = -1; 126 } 127 128 void print() 129 { 130 for(m_solution.move(0); !m_solution.end(); m_solution.next()) 131 { 132 cout << "(" << m_solution.current().x << "," << m_solution.current().y << ") "; 133 } 134 135 cout << endl; 136 137 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 138 { 139 for(int j=0; j<N; j++) 140 { 141 switch(m_chessboard[i][j]) 142 { 143 case 0 : cout << " " ; break; 144 case 1 : cout << "#" ; break; //有皇后 145 case 2 : cout << "*" ; break; 146 } 147 } 148 149 cout << endl; 150 } 151 152 cout << endl; 153 } 154 155 bool check(int x, int y, int d) 156 { 157 bool flag = true; 158 159 do 160 { 161 x += m_direction[d].x; 162 y += m_direction[d].y; 163 flag = flag && (m_chessboard[x][y] == 0); 164 } 165 while( flag ); 166 167 return (m_chessboard[x][y] == 2); //do while退出时,如果到达了边界说明这个方向没有皇后 168 } 169 170 void run(int j) //检查第j行有没有可以放置皇后的位置 171 { 172 if( j <= SIZE ) 173 { 174 for(int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++) 175 { 176 if( check(i, j, 0) && check(i, j, 1) &&check(i, j, 2) ) 177 { 178 m_chessboard[i][j] = 1; 179 180 m_solution.insert(Pos(i, j)); 181 182 run(j + 1); // 看下一行能不能放皇后,如果返回,意味着i,j位置不能放皇后,要回溯 183 184 m_chessboard[i][j] = 0; 185 186 m_solution.remove(m_solution.length() - 1); 187 188 } 189 } 190 } 191 else 192 { 193 //到这里意味着找到了解决方案 194 m_count++; 195 196 print(); 197 } 198 } 199 public: 200 QueueSolution() 201 { 202 init(); 203 } 204 205 void run() 206 { 207 run(1); 208 209 cout << "Total : " << m_count << endl; 210 } 211 }; 212 213 int main() 214 { 215 QueueSolution<8> qs; 216 217 qs.run(); 218 219 return 0; 220 }

共92种解法。
小结:
