


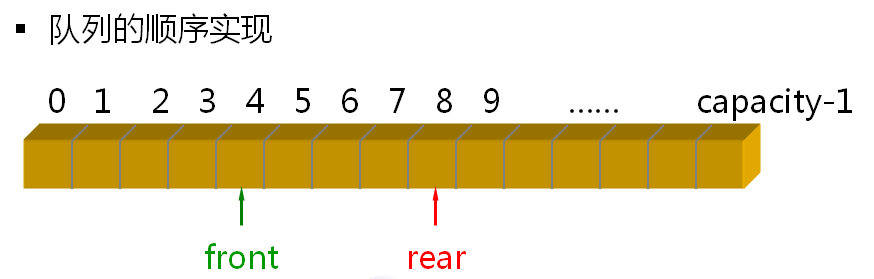


使用循环计数法的目的是为了高效。
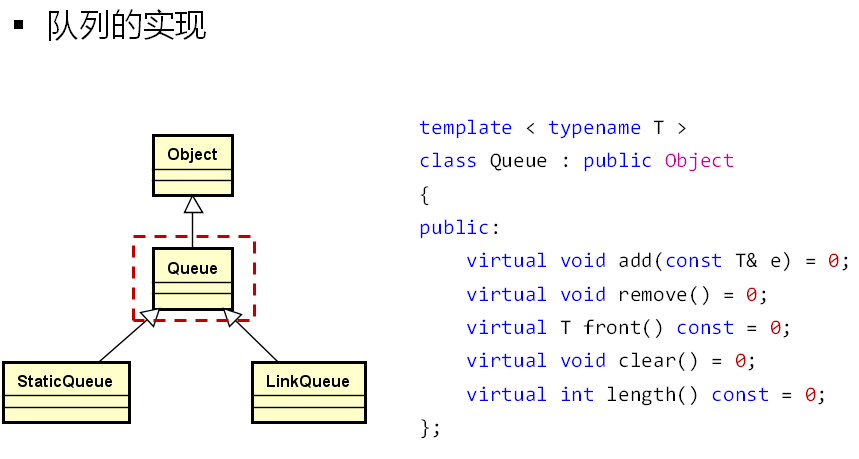
添加Queue.h文件:
1 #ifndef QUEUE_H 2 #define QUEUE_H 3 4 #include "Object.h" 5 6 namespace DTLib 7 { 8 9 template < typename T > 10 class Queue : public Object 11 { 12 public: 13 virtual void add(const T& e) = 0; 14 virtual void remove() = 0; 15 virtual T front() const = 0; 16 virtual void clear() = 0; 17 virtual int length() const = 0; 18 }; 19 20 } 21 22 #endif // QUEUE_H
添加StaticQueue.h文件:
1 #ifndef STATICQUEUE_H 2 #define STATICQUEUE_H 3 4 #include "Queue.h" 5 #include "Exception.h" 6 7 namespace DTLib 8 { 9 10 template < typename T, int N > 11 class StaticQueue : public Queue<T> 12 { 13 protected: 14 T m_space[N]; 15 int m_front; 16 int m_rear; 17 int m_length; 18 public: 19 StaticQueue() 20 { 21 m_front = 0; 22 m_rear = 0; 23 m_length = 0; 24 } 25 26 int capacity() const 27 { 28 return N; 29 } 30 31 void add(const T& e) 32 { 33 if( m_length < N ) 34 { 35 m_space[m_rear] = e; 36 m_rear = (m_rear + 1) % N; 37 m_length++; 38 } 39 else 40 { 41 THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No space in current queue..."); 42 } 43 } 44 45 void remove() 46 { 47 if( m_length > 0 ) 48 { 49 m_front = (m_front + 1) % N; 50 m_length--; 51 } 52 else 53 { 54 THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No element in current queue..."); 55 } 56 } 57 58 T front() const 59 { 60 if( m_length > 0 ) 61 { 62 return m_space[m_front]; 63 } 64 else 65 { 66 THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No element in current queue..."); 67 } 68 } 69 70 void clear() 71 { 72 m_front = 0; 73 m_rear = 0; 74 m_length = 0; 75 } 76 77 int length() const 78 { 79 return m_length; 80 } 81 82 ~StaticQueue() 83 { 84 clear(); 85 } 86 }; 87 88 } 89 90 #endif // STATICQUEUE_H
测试程序如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "StaticQueue.h" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 using namespace DTLib; 6 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 StaticQueue<int, 5> queue; 11 12 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 13 { 14 queue.add(i); 15 } 16 17 while( queue.length() > 0 ) 18 { 19 cout << queue.front() << endl; 20 21 queue.remove(); 22 } 23 24 return 0; 25 }
运行结果如下:

小结:
