5种IO模型分别如下:
1、阻塞IO模型

当上层应用app1调用recv系统调用时,如果对等方没有发送数据(缓冲区没有数据),上层app1将阻塞(默认行为,被linux内核阻塞)。
当对等方发送了数据,linux内核recv端缓冲区有数据后,内核会把数据copy给用户空间。然后上层应用app1解除阻塞,执行下一步操作。
2、非阻塞IO模型
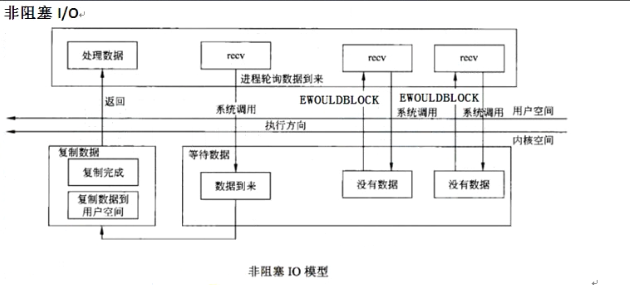
上层应用程序app2将套接字设置成非阻塞模式。
上层应用程序app2轮询调用recv函数,接收数据,若缓冲区没有数据,上层程序app2不会阻塞,recv返回值-1,错误码是EWOULDBLOCK。
上层应用程序不断轮询有没有数据到来,会造成上层应用忙等待,大量的消耗CPU时间,很少直接用,应用范围小,一般和select IO复用配合使用。
阻塞IO和非阻塞IO是两个极端,一个是没有数据就死等,另一个极端是轮询。
有没有这样一种机制去管理n个文件描述符,当文件描述符状态发生变化了,会通知应用程序呢?这就是IO复用技术,也叫作多路复用。
3、IO复用模型
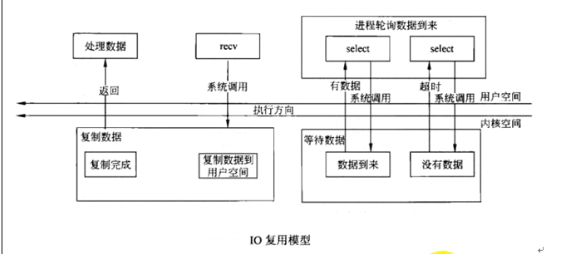
上层应用程序app3调用select机制(该机制由linux内核支持,避免了app3忙等待),进行轮询文件描述符的状态变化。
当select管理的文件描述符没有数据(或者状态没有变化时),上层应用程序app3也会阻塞。
好处是select会管理多个文件描述符。
select可以看成一个管理者,用select来管理多个IO。
一旦检测到一个IO或者多个IO有我们感兴趣的事件发生,select函数将返回,返回值为检测到的事件个数,继而可以利用select相关api函数,具体操作事件。
select函数可以设置等待时间,避免了上层应用程序app3长期僵死。
和阻塞IO模型相比,select IO复用模型相当于提前阻塞了,等到有数据到来时再调用recv就不会发生阻塞。
4、信号驱动模型:
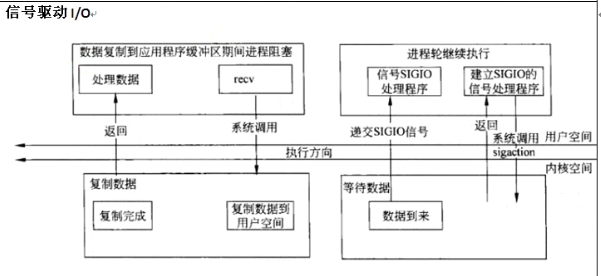
上层应用程序app4建立SIGIO信号处理程序,当缓冲区有数据到来时,内核会发送信号告诉上层应用程序app4。
上层应用程序app4接收到信号后,调用recv函数,因缓冲区有数据,recv函数一般不会阻塞。
这种模型用的也比较少,属于典型的“拉模式”,即上层应用程序app4需要调用recv函数把数据拉进来。
应用程序接收到信号有一个时间延迟,处理这个信号可能还有一个时间延迟,如果这些延迟比较长,内核空间数据有可能发生变化。存在隐患。因此,这种IO模型用的不多。
5、异步IO模型
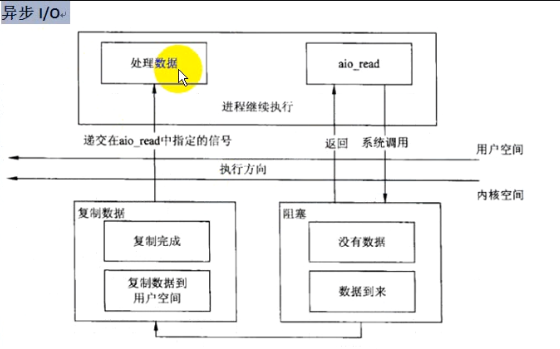
上层应用app5调用aio_read函数,同时提交一个应用层的缓冲区buf,调用完毕后不会阻塞,上层应用程序app5可以进行其他任务。
当TCP IP协议缓冲区有数据时,linux内核主动把内核缓冲区中的数据copy到用户空间,然后再给上层应用app5发送信号,告诉app5数据有了,赶快处理吧。
这是典型的推模式。
效率最高的一种形式,上层应用app5有异步处理的能力(在linux内核的支持下,言外之意:处理其他任务的同时,也可支持IO通讯)。
上层应用app5也可以在干别的活儿的同时接收数据。与信号驱动IO模型相比,上层应用程序app5不需要调用recv函数。
这种IO模型效率非常高,是高性能、高并发服务器常用的模型。
IO复用模型和异步IO模型是两种常用的模型。
重要概念:
阻塞IO:
数据没有准备好,读操作就会阻塞。
数据不能立即被收时,写操作就会阻塞。
打开文件时阻塞,直到某些条件发生。
非阻塞IO:
立即返回,并用错误值来表示当前的状态。
指定非阻塞方式:
打开时指定O_NONBLOCK标志。
使用fcntl打开或者关闭非阻塞方式
网络编程时,使用非阻塞,用轮询方式发送
使用多线程可以避免使用非阻塞IO,但是同步开销大
多路IO:
当程序需要同时从两个输入读数据时
使用多进程、多线程,同步复杂,进程线程开销
使用非阻塞IO,交替轮询
通过信号使用异步IO,无法判断哪个IO完成
多路IO:把关心的IO放入一个列表,调用多路函数
多路IO函数阻塞,直到有一个数据准备好后返回
返回后告诉调用者哪个描述符准备好了
IO复用模型分析:
select实现说明:
调用select时通过参数告诉内核用户感兴趣的IO描述符
关心的IO状态:输入、输出或者错误
调用者等待时间
返回之后内核告诉调用者多个描述符准备好了
哪些描述符发生了变化
调用返回后对准备好的描述符调用读写操作
不关心的描述符集传NULL
select函数原型如下:
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
监视readfs来查看是否read的时候会被阻塞,注意:即使到了end-of-file,fd也是可读的
监视writefds看写的时候会不会阻塞
监视excepted是否出现了异常,主要用来读取OOB数据,异常并不是指出错
注意当一个套接口出错时,它会变得既可读又可写
如果有了状态改变,会将其他fd清零,只有那些发生改变了的fd保持置位,以用来指示set中的哪一个改变了状态
参数n是所有set里的所有fd里面,具有最大值的那个fd的值加1
以下四个宏用来对fd_set进行操作:
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set); :把一个描述符从集合内移除
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set) :测试某个描述符是否在集合内
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set) : 把一个描述符加入集合
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set) :清空描述符集合
每个描述符在集合中只占一位,如下所示:


下面我们将客户端程序改成select形式,select用来监视标准输入描述符和套接字,服务器端程序还是用普通的多进程模型。只给出客户端程序如下:
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 #include <string.h> 6 #include <errno.h> 7 #include <signal.h> 8 #include <arpa/inet.h> 9 #include <sys/socket.h> 10 #include <netinet/in.h> 11 #include <sys/socket.h> 12 #include <netinet/ip.h> /* superset of previous */ 13 14 void handler(int num) 15 { 16 printf("signal num : %d ", num); 17 } 18 19 ssize_t readn(int fd, void *buf, size_t count) 20 { 21 size_t nleft = count; 22 ssize_t nread; 23 24 char *bufp = (char*)buf; 25 26 while(nleft > 0) 27 { 28 if( (nread = read(fd, bufp, nleft)) < 0 ) 29 { 30 if(errno == EINTR) 31 { 32 continue; 33 } 34 35 return -1; 36 } 37 else if(nread == 0) 38 { 39 return count - nleft; 40 } 41 42 bufp += nread; 43 nleft -= nread; 44 } 45 46 return count; 47 } 48 49 ssize_t writen(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count) 50 { 51 size_t nleft = count; 52 ssize_t nwritten; 53 54 char *bufp = (char*)buf; 55 56 while(nleft > 0) 57 { 58 if( (nwritten = write(fd, bufp, nleft)) < 0) 59 { 60 if(errno == EINTR) 61 { 62 continue; 63 } 64 65 return -1; 66 } 67 else if(nwritten == 0) 68 { 69 continue; 70 } 71 72 bufp += nwritten; 73 nleft -= nwritten; 74 } 75 76 return count; 77 } 78 79 ssize_t recv_peek(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len) 80 { 81 while(1) 82 { 83 int ret = recv(sockfd, buf, len, MSG_PEEK); 84 if(ret == -1 && errno == EINTR) 85 continue; 86 return ret; 87 } 88 } 89 90 ssize_t readline(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t maxline) 91 { 92 int ret; 93 int nread; 94 char *bufp = (char*)buf; 95 int nleft = maxline; 96 97 while(1) 98 { 99 ret = recv_peek(sockfd, bufp, nleft); 100 if(ret < 0) 101 { 102 return ret; 103 } 104 else if(ret == 0) 105 { 106 return ret; 107 } 108 109 nread = ret; 110 int i; 111 for(i = 0; i < nread; i++) 112 { 113 if(bufp[i] == ' ') 114 { 115 ret = readn(sockfd, bufp, i+1); 116 if(ret != i+1) 117 { 118 perror("readn error"); 119 exit(0); 120 } 121 122 return ret; 123 } 124 } 125 126 if(nread > nleft) 127 { 128 perror("FAILURE"); 129 exit(0); 130 } 131 132 nleft -= nread; 133 ret = readn(sockfd, bufp, nread); 134 if(ret != nread) 135 { 136 perror("readn error"); 137 exit(0); 138 } 139 bufp += nread; 140 } 141 142 return -1; 143 } 144 145 146 void echo_cli(int sock) 147 { 148 fd_set rset; 149 FD_ZERO(&rset); 150 151 int nready; 152 int maxfd; 153 int fd_stdin = fileno(stdin); 154 if(fd_stdin > sock) 155 maxfd = fd_stdin; 156 else 157 maxfd = sock; 158 159 char sendbuf[1024] = {0}; 160 char recvbuf[1024] = {0}; 161 162 int stdineof = 0; 163 164 while(1) 165 { 166 if (stdineof == 0) 167 FD_SET(fd_stdin, &rset); 168 FD_SET(sock, &rset); 169 170 nready = select(maxfd + 1, &rset, NULL, NULL, NULL); 171 172 if(nready == -1) 173 { 174 perror("select error"); 175 exit(0); 176 } 177 178 if(nready == 0) 179 { 180 continue; 181 } 182 183 if(FD_ISSET(sock, &rset)) 184 { 185 int ret = readline(sock, recvbuf, sizeof(recvbuf)); 186 if(ret == -1) 187 { 188 perror("readline error"); 189 exit(0); 190 } 191 else if(ret == 0) 192 { 193 printf("server closed "); 194 break; 195 } 196 197 fputs(recvbuf, stdout); 198 memset(recvbuf, 0, sizeof(recvbuf)); 199 } 200 201 if(FD_ISSET(fd_stdin, &rset)) 202 { 203 if(fgets(sendbuf, sizeof(sendbuf), stdin) == NULL) 204 { 205 printf("ctrl+d result fgets return "); 206 stdineof = 1; 207 close(sock); 208 } 209 else 210 { 211 writen(sock, sendbuf, strlen(sendbuf)); 212 memset(sendbuf, 0, sizeof(sendbuf)); 213 } 214 } 215 216 } 217 } 218 219 int main() 220 { 221 int sockfd; 222 223 signal(SIGPIPE, handler); 224 225 sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 226 227 struct sockaddr_in addr; 228 addr.sin_family = AF_INET; 229 addr.sin_port = htons(8001); 230 inet_aton("192.168.31.128", &addr.sin_addr); 231 //addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.31.128"); 232 233 if( connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)) == -1 ) 234 { 235 perror("connect error"); 236 exit(0); 237 } 238 239 struct sockaddr_in localaddr; 240 socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(localaddr); 241 if(getsockname(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&localaddr, &addrlen) < 0) 242 { 243 perror("getsockname error"); 244 exit(0); 245 } 246 247 printf("ip=%s port=%d ", inet_ntoa(localaddr.sin_addr), ntohs(localaddr.sin_port)); 248 249 echo_cli(sockfd); 250 251 return 0; 252 }
核心函数为echo_cli,其中调用了select函数,167、168将两个描述符加入到监视器中。fgets发生错误或者读到文件末尾时会返回NULL。读标准输入时ctrl+d代表文件末尾。
启动服务器和客户端,执行结果如下:
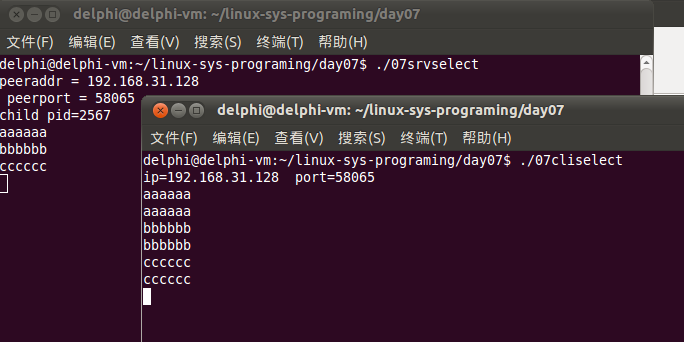
connect连接时,会阻塞进程,在公网上默认会等待75秒超时,但是一般应用不想等这么久,因此,需要优化一下。
网络模型中常用的操作:
1 #ifndef _SCK_UTIL_H_ 2 #define _SCK_UTIL_H_ 3 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <sys/select.h> 8 #include <sys/time.h> 9 #include <sys/socket.h> 10 #include <netinet/in.h> 11 #include <arpa/inet.h> 12 #include <netdb.h> 13 14 #include <stdio.h> 15 #include <errno.h> 16 #include <string.h> 17 #include <stdlib.h> 18 19 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 20 do 21 { 22 perror(m); 23 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 24 } 25 while (0) 26 27 void activate_nonblock(int fd); 28 void deactivate_nonblock(int fd); 29 30 int read_timeout(int fd, unsigned int wait_seconds); 31 int write_timeout(int fd, unsigned int wait_seconds); 32 int accept_timeout(int fd, struct sockaddr_in *addr, unsigned int wait_seconds); 33 int connect_timeout(int fd, struct sockaddr_in *addr, unsigned int wait_seconds); 34 35 36 ssize_t readn(int fd, void *buf, size_t count); 37 ssize_t writen(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); 38 ssize_t recv_peek(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len); 39 ssize_t readline(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t maxline); 40 41 #endif /* _SYS_UTIL_H_ */
1 #include "sckutil.h" 2 3 /* read函数的调用方法 4 int ret; 5 ret = read_timeout(fd, 5); 6 if (ret == 0) 7 { 8 read(fd, ...); 9 } 10 else if (ret == -1 && errno == ETIMEDOUT) 11 { 12 timeout.... 13 } 14 else 15 { 16 ERR_EXIT("read_timeout"); 17 } 18 */ 19 20 /** 21 * read_timeout - 读超时检测函数,不含读操作 22 * @fd: 文件描述符 23 * @wait_seconds: 等待超时秒数,如果为0表示不检测超时 24 * 成功(未超时)返回0,失败返回-1,超时返回-1并且errno = ETIMEDOUT 25 */ 26 int read_timeout(int fd, unsigned int wait_seconds) 27 { 28 int ret = 0; 29 if (wait_seconds > 0) 30 { 31 fd_set read_fdset; 32 struct timeval timeout; 33 34 FD_ZERO(&read_fdset); 35 FD_SET(fd, &read_fdset); 36 37 timeout.tv_sec = wait_seconds; 38 timeout.tv_usec = 0; 39 40 //select返回值三态 41 //1 若timeout时间到(超时),没有检测到读事件 ret返回=0 42 //2 若ret返回<0 && errno == EINTR 说明select的过程中被别的信号中断(可中断睡眠原理) 43 //2-1 若返回-1,select出错 44 //3 若ret返回值>0 表示有read事件发生,返回事件发生的个数 45 46 do 47 { 48 ret = select(fd + 1, &read_fdset, NULL, NULL, &timeout); 49 } while (ret < 0 && errno == EINTR); 50 51 if (ret == 0) 52 { 53 ret = -1; 54 errno = ETIMEDOUT; 55 } 56 else if (ret == 1) 57 ret = 0; 58 } 59 60 return ret; 61 } 62 63 /** 64 * write_timeout - 写超时检测函数,不含写操作 65 * @fd: 文件描述符 66 * @wait_seconds: 等待超时秒数,如果为0表示不检测超时 67 * 成功(未超时)返回0,失败返回-1,超时返回-1并且errno = ETIMEDOUT 68 */ 69 int write_timeout(int fd, unsigned int wait_seconds) 70 { 71 int ret = 0; 72 if (wait_seconds > 0) 73 { 74 fd_set write_fdset; 75 struct timeval timeout; 76 77 FD_ZERO(&write_fdset); 78 FD_SET(fd, &write_fdset); 79 80 timeout.tv_sec = wait_seconds; 81 timeout.tv_usec = 0; 82 do 83 { 84 ret = select(fd + 1, NULL, &write_fdset, NULL, &timeout); 85 } while (ret < 0 && errno == EINTR); 86 87 if (ret == 0) 88 { 89 ret = -1; 90 errno = ETIMEDOUT; 91 } 92 else if (ret == 1) 93 ret = 0; 94 } 95 96 return ret; 97 } 98 99 /** 100 * accept_timeout - 带超时的accept 101 * @fd: 套接字 102 * @addr: 输出参数,返回对方地址 103 * @wait_seconds: 等待超时秒数,如果为0表示正常模式 104 * 成功(未超时)返回已连接套接字,超时返回-1并且errno = ETIMEDOUT 105 */ 106 int accept_timeout(int fd, struct sockaddr_in *addr, unsigned int wait_seconds) 107 { 108 int ret; 109 socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in); 110 111 if (wait_seconds > 0) 112 { 113 fd_set accept_fdset; 114 struct timeval timeout; 115 FD_ZERO(&accept_fdset); 116 FD_SET(fd, &accept_fdset); 117 timeout.tv_sec = wait_seconds; 118 timeout.tv_usec = 0; 119 do 120 { 121 ret = select(fd + 1, &accept_fdset, NULL, NULL, &timeout); 122 } while (ret < 0 && errno == EINTR); 123 if (ret == -1) 124 return -1; 125 else if (ret == 0) 126 { 127 errno = ETIMEDOUT; 128 return -1; 129 } 130 } 131 132 //一但检测出 有select事件发生,表示对等方完成了三次握手,客户端有新连接建立 133 //此时再调用accept将不会堵塞 134 if (addr != NULL) 135 ret = accept(fd, (struct sockaddr*)addr, &addrlen); //返回已连接套接字 136 else 137 ret = accept(fd, NULL, NULL); 138 if (ret == -1) 139 ERR_EXIT("accept"); 140 141 return ret; 142 } 143 144 /** 145 * activate_noblock - 设置I/O为非阻塞模式 146 * @fd: 文件描符符 147 */ 148 void activate_nonblock(int fd) 149 { 150 int ret; 151 int flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL); 152 if (flags == -1) 153 ERR_EXIT("fcntl"); 154 155 flags |= O_NONBLOCK; 156 ret = fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags); 157 if (ret == -1) 158 ERR_EXIT("fcntl"); 159 } 160 161 /** 162 * deactivate_nonblock - 设置I/O为阻塞模式 163 * @fd: 文件描符符 164 */ 165 void deactivate_nonblock(int fd) 166 { 167 int ret; 168 int flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL); 169 if (flags == -1) 170 ERR_EXIT("fcntl"); 171 172 flags &= ~O_NONBLOCK; 173 ret = fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags); 174 if (ret == -1) 175 ERR_EXIT("fcntl"); 176 } 177 178 179 /** 180 * connect_timeout - connect 181 * @fd: 套接字 182 * @addr: 要连接的对方地址 183 * @wait_seconds: 等待超时秒数,如果为0表示正常模式 184 * 成功(未超时)返回0,失败返回-1,超时返回-1并且errno = ETIMEDOUT 185 */ 186 int connect_timeout(int fd, struct sockaddr_in *addr, unsigned int wait_seconds) 187 { 188 int ret; 189 socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in); 190 191 if (wait_seconds > 0) 192 activate_nonblock(fd); 193 194 ret = connect(fd, (struct sockaddr*)addr, addrlen); 195 if (ret < 0 && errno == EINPROGRESS) 196 { 197 //printf("11111111111111111111 "); 198 fd_set connect_fdset; 199 struct timeval timeout; 200 FD_ZERO(&connect_fdset); 201 FD_SET(fd, &connect_fdset); 202 timeout.tv_sec = wait_seconds; 203 timeout.tv_usec = 0; 204 do 205 { 206 // 一但连接建立,则套接字就可写 所以connect_fdset放在了写集合中 207 ret = select(fd + 1, NULL, &connect_fdset, NULL, &timeout); 208 } while (ret < 0 && errno == EINTR); 209 if (ret == 0) 210 { 211 ret = -1; 212 errno = ETIMEDOUT; 213 } 214 else if (ret < 0) 215 return -1; 216 else if (ret == 1) 217 { 218 //printf("22222222222222222 "); 219 /* ret返回为1(表示套接字可写),可能有两种情况,一种是连接建立成功,一种是套接字产生错误,*/ 220 /* 此时错误信息不会保存至errno变量中,因此,需要调用getsockopt来获取。 */ 221 int err; 222 socklen_t socklen = sizeof(err); 223 int sockoptret = getsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, &err, &socklen); 224 if (sockoptret == -1) 225 { 226 return -1; 227 } 228 if (err == 0) 229 { 230 //printf("3333333333333 "); 231 ret = 0; 232 } 233 else 234 { 235 //printf("4444444444444444:%d ", err); 236 errno = err; 237 ret = -1; 238 } 239 } 240 } 241 if (wait_seconds > 0) 242 { 243 deactivate_nonblock(fd); 244 } 245 return ret; 246 } 247 248 /** 249 * readn - 读取固定字节数 250 * @fd: 文件描述符 251 * @buf: 接收缓冲区 252 * @count: 要读取的字节数 253 * 成功返回count,失败返回-1,读到EOF返回<count 254 */ 255 ssize_t readn(int fd, void *buf, size_t count) 256 { 257 size_t nleft = count; 258 ssize_t nread; 259 char *bufp = (char*)buf; 260 261 while (nleft > 0) 262 { 263 if ((nread = read(fd, bufp, nleft)) < 0) 264 { 265 if (errno == EINTR) 266 continue; 267 return -1; 268 } 269 else if (nread == 0) 270 return count - nleft; 271 272 bufp += nread; 273 nleft -= nread; 274 } 275 276 return count; 277 } 278 279 /** 280 * writen - 发送固定字节数 281 * @fd: 文件描述符 282 * @buf: 发送缓冲区 283 * @count: 要读取的字节数 284 * 成功返回count,失败返回-1 285 */ 286 ssize_t writen(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count) 287 { 288 size_t nleft = count; 289 ssize_t nwritten; 290 char *bufp = (char*)buf; 291 292 while (nleft > 0) 293 { 294 if ((nwritten = write(fd, bufp, nleft)) < 0) 295 { 296 if (errno == EINTR) 297 continue; 298 return -1; 299 } 300 else if (nwritten == 0) 301 continue; 302 303 bufp += nwritten; 304 nleft -= nwritten; 305 } 306 307 return count; 308 } 309 310 /** 311 * recv_peek - 仅仅查看套接字缓冲区数据,但不移除数据 312 * @sockfd: 套接字 313 * @buf: 接收缓冲区 314 * @len: 长度 315 * 成功返回>=0,失败返回-1 316 */ 317 ssize_t recv_peek(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len) 318 { 319 while (1) 320 { 321 int ret = recv(sockfd, buf, len, MSG_PEEK); 322 if (ret == -1 && errno == EINTR) 323 continue; 324 return ret; 325 } 326 } 327 328 /** 329 * readline - 按行读取数据 330 * @sockfd: 套接字 331 * @buf: 接收缓冲区 332 * @maxline: 每行最大长度 333 * 成功返回>=0,失败返回-1 334 */ 335 ssize_t readline(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t maxline) 336 { 337 int ret; 338 int nread; 339 char *bufp = buf; 340 int nleft = maxline; 341 while (1) 342 { 343 ret = recv_peek(sockfd, bufp, nleft); 344 if (ret < 0) 345 return ret; 346 else if (ret == 0) 347 return ret; 348 349 nread = ret; 350 int i; 351 for (i=0; i<nread; i++) 352 { 353 if (bufp[i] == ' ') 354 { 355 ret = readn(sockfd, bufp, i+1); 356 if (ret != i+1) 357 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 358 359 return ret; 360 } 361 } 362 363 if (nread > nleft) 364 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 365 366 nleft -= nread; 367 ret = readn(sockfd, bufp, nread); 368 if (ret != nread) 369 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 370 371 bufp += nread; 372 } 373 374 return -1; 375 }
上述带超时的函数,具有一定的健壮性,将IO设置为阻塞或者非阻塞,主要是给connect_timeout函数用。先将fd设置为非阻塞,这样connect就可以立即返回,如果返回时fd还没有连接好,即errno == EINPROGRESS,则调用select去监控这个fd,要么指定时间内fd可用,要么超时。虽然connect立即返回了,但是三次握手内核还是会做的。fd可读可有两种可能,一种是连接建立了,真正可读了,另一种是发生错误了,这时候fd也可读了。因此,
我们需要调用getsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, &err, &socklen)来获取错误码,根据错误码进行进一步的判断。
connect_timeout总结如下图:

优化网络应用就是优化连接,可以通过在客户端建立连接池提供优化。TCP IP三次握手很浪费时间。
select三个应用场景:
1、用select封装超时(connect、accept、read、write)
2、用select优化客户端(stdin、confd)
3、用select优化服务器(用一个单进程去支持多个客户端)
select是一个管理机制,管理了多个IO,用单进程轮询的方式去查询n个IO是否发生了变化。