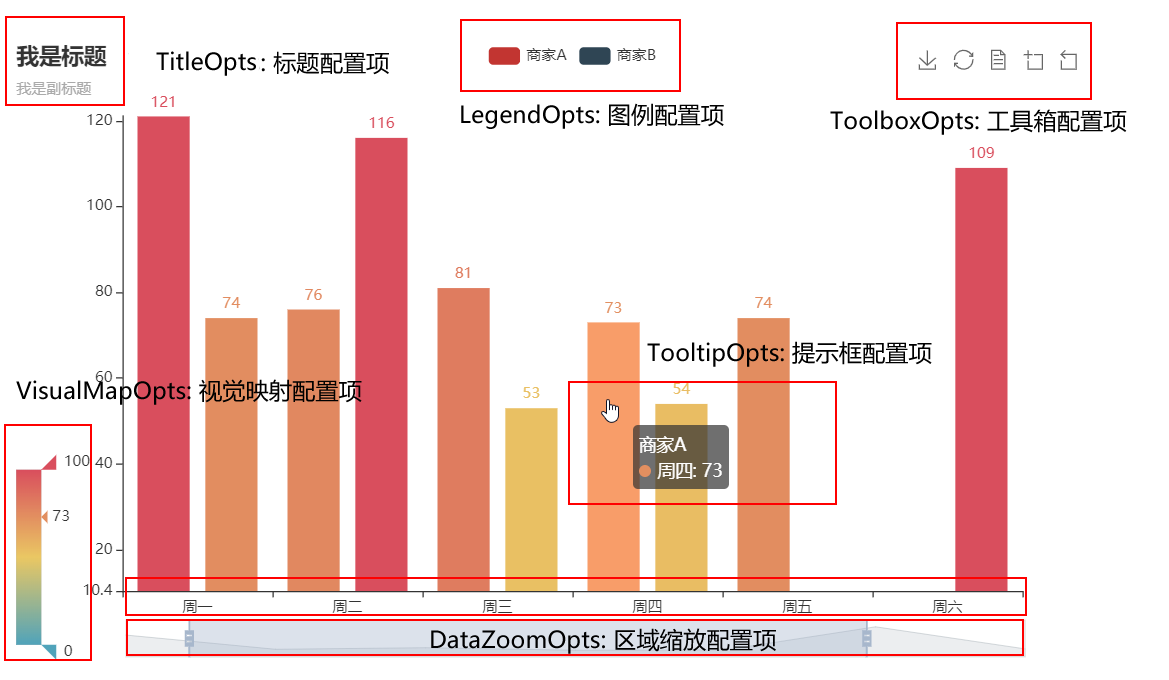
可视化可以直接利用:
init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width="800px",height="600px", # animation_opts=opts.AnimationOpts(animation_delay=1000, animation_easing="elasticOut")
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False)) .set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Geo-Lines-background",subtitle="我是副标题",pos_left="center",pos_top="0px"), legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(pos_top="35px"), tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(formatter="{a}:{b}") # dataZoomOpts=opts.DataZoomOpts(is_show=True) )
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Geo
from pyecharts.globals import ChartType, SymbolType
c = (
Geo(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width="800px",height="600px",
# animation_opts=opts.AnimationOpts(animation_delay=1000, animation_easing="elasticOut")
)
)
.add_schema(
maptype="china",
itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(color="#323c48", border_color="#111"),
)
.add(
"",
[("广州", 55), ("北京", 66), ("杭州", 77), ("重庆", 88)],
type_=ChartType.EFFECT_SCATTER,
color="white",
)
.add(
"geo",
b,
type_=ChartType.LINES,
effect_opts=opts.EffectOpts(
symbol=SymbolType.ARROW, symbol_size=6, color="blue"
),
linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(curve=0.2),
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Geo-Lines-background",subtitle="我是副标题",pos_left="center",pos_top="0px"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(pos_top="35px"),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(formatter="{a}:{b}")
# dataZoomOpts=opts.DataZoomOpts(is_show=True)
)
)
c.render_notebook()
a=["广州","上海","北京","杭州","乌鲁木齐"]
for i in range(len(a)):
for j in range(i+1,len(a)):
b.append((a[i],a[j]))