0.前言
在c语言并行程序设计之路(一)(初探多线程)中,变量A、x、y设置成了全局共享变量,是较理想的存储访问方式。现在考虑多个线程更新同一内存单元的数据。
相关环境同上一篇。
本篇主要学习忙等待与锁。
1.问题描述
以下是估算(pi)值的一个最简单的方法:
[pi=(1-frac{1}{3}+frac{1}{5}-frac{1}{7}+...+(-1)^nfrac{1}{2n+1}+...)
]
2.串行程序
书中给出的串行程序为:

计算项数越多,结果越精准
//pi.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
double factor = 1.0;
double sum = 0.0;
double pi;
int n;
int main(int argc,char *argv[]) {
n = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i,factor=-factor) {
sum+=factor/(2*i+1);
}
pi = 4.0*sum;
printf("pi:%.8lf",pi);
}
3.并行程序
3.1 尝试并行
首先尝试用并行化矩阵-向量乘法的方法来并行化这个程序:将for循环分块后交给各个线程处理,并将sum设为全局变量。同样的,为了简化计算,假设线程数thread_count,简称t能够整除项目总数n。如果(overline n =n/t),那么线程0加上第一部分的(overline n)项,循环变量的范围是(overline n sim overline{2n}-1)。一般的,对于线程q,循环变量的范围是
[overline {qn},overline {qn}+1,overline {qn}+2,...overline {(q+1)n}-1
]
而且,第一项也就是(overline {qn}),为偶数时符号为正,为奇数时符号为负,得到以下的并行代码:

3.2 并行计算
//thread_pi.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#define ll long long
double factor = 1.0;
double sum = 0.0;
double pi;
int n,thread_count;
void* Thread_sum(void* rank) {
ll my_rank = (ll)rank;
double factor;
int my_n = n/thread_count;
int my_first_i = my_n*my_rank;
int my_last_i = my_first_i+my_n;
if(my_first_i%2==0) {
factor = 1.0;
} else {
factor = -1.0;
}
for(int i=my_first_i;i<my_last_i;++i,factor=-factor){
sum+=factor/(2*i+1);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]) {
n = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
thread_count = strtol(argv[2],NULL,10);
ll thread;
pthread_t* thread_handles = (pthread_t *)malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
for(thread=0;thread<thread_count;++thread){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[thread],NULL,Thread_sum,(void*) thread);
}
for(thread=0;thread<thread_count;++thread){
pthread_join(thread_handles[thread],NULL);
}
free(thread_handles);
pi = 4.0*sum;
printf("pi:%.8lf",pi);
}
3.3 计算结果
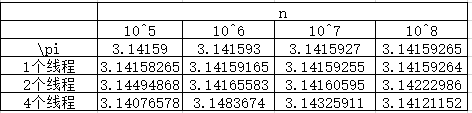
可以看到,随着n的增加,单线程的估算结果越来越准确。然而多线程的结果反而变遭,其实多次运行也会得到不一样的结果。
是的,当多个线程尝试更新同一个共享变量时,会出问题。
原因是因为线程函数中对sum的加法操作不是原子性的。

4 改良设计
4.1忙等待
//thread_pi_busywaiting.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<sys/time.h>
#include<stdint.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define ll long long
double factor = 1.0;
double sum = 0.0;
double pi;
int n,thread_count;
ll flag=0;//新增一个共享的标志变量
int64_t now() {
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return tv.tv_sec * 1000000 + tv.tv_usec;
}
void* Thread_sum(void* rank) {
ll my_rank = (ll)rank;
double factor;
int my_n = n/thread_count;
int my_first_i = my_n*my_rank;
int my_last_i = my_first_i+my_n;
if(my_first_i%2==0) {
factor = 1.0;
} else {
factor = -1.0;
}
for(int i=my_first_i;i<my_last_i;++i,factor=-factor){
while(flag!=my_rank);//忙等待
sum+=factor/(2*i+1);
flag=(flag+1)%thread_count;//改变标志量
usleep(500);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]) {
n = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
thread_count = strtol(argv[2],NULL,10);
ll thread;
int64_t start = now();
pthread_t* thread_handles = (pthread_t *)malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
for(thread=0;thread<thread_count;++thread){
pthread_create(&thread_handles[thread],NULL,Thread_sum,(void*) thread);
}
for(thread=0;thread<thread_count;++thread){
pthread_join(thread_handles[thread],NULL);
}
free(thread_handles);
pi = 4.0*sum;
int64_t end = now();
double sec = (end-start)/1000000.0;
printf("pi:%.8lf %f sec
",pi,sec);
}
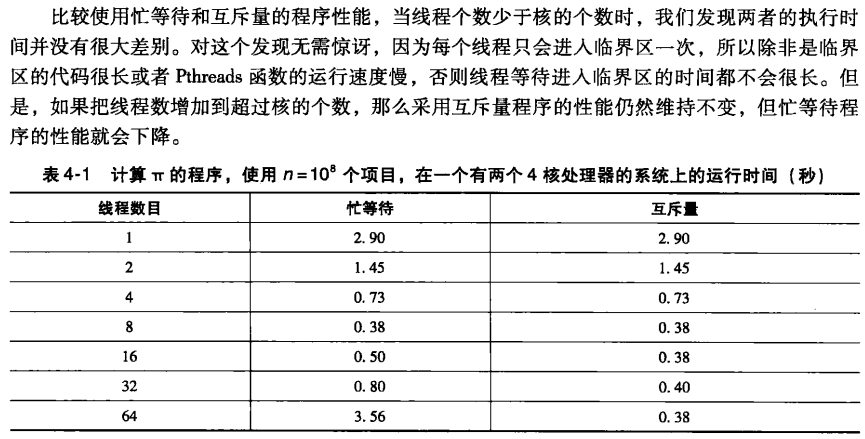
修改后多个线程的计算结果也是对的。但是,在(n=10^8)时,明显的感觉到时间要花的多的多。时间主要耗费在线程不停地在等待和运行之间切换。
4.2互斥量
因为处于忙等待的线程仍然在持续使用cpu,所以忙等待不是限制临界区访问的最理想方式。这里引入互斥量(互斥锁),它是一个特殊类型的变量,通过某些特殊的函数,可以限制每次只有一个线程能进入临界区。
//thread_pi_mutex.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<sys/time.h>
#include<stdint.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define ll long long
double factor = 1.0;
double sum = 0.0;
double pi;
int n,thread_count;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//静态初始化一个锁
int64_t now() {
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return tv.tv_sec * 1000000 + tv.tv_usec;
}
void* Thread_sum(void* rank) {
ll my_rank = (ll)rank;
double factor;
int my_n = n/thread_count;
int my_first_i = my_n*my_rank;
int my_last_i = my_first_i+my_n;
double my_sum = 0.0;
if(my_first_i%2==0) {
factor = 1.0;
} else {
factor = -1.0;
}
for(int i=my_first_i; i<my_last_i; ++i,factor=-factor) {
my_sum+=factor/(2*i+1);
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
sum+=my_sum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]) {
n = strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);
thread_count = strtol(argv[2],NULL,10);
ll thread;
//pthread_mutex_init(mutex,NULL);//动态初始化
int64_t start = now();
pthread_t* thread_handles = (pthread_t *)malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
for(thread=0; thread<thread_count; ++thread) {
pthread_create(&thread_handles[thread],NULL,Thread_sum,(void*) thread);
}
for(thread=0; thread<thread_count; ++thread) {
pthread_join(thread_handles[thread],NULL);
}
free(thread_handles);
pi = 4.0*sum;
int64_t end = now();
double sec = (end-start)/1000000.0;
printf("pi:%.8lf %f sec
",pi,sec);
}
在使用互斥量的多线程程序中,多个线程进入临界区的顺序是随机的。
5.后记