本博客已搬家至个人网站 在路上 - On the way 下面的 技术 分类。
你可以通过点击 更新帖子 【已解决】Python中,用eval强制将字符串转换为字典变量时候出错:NameError: name 'null' is not defined 找到当前帖子的新地址。
----------------------------------搬家声明--------------------------------------
【已解决】Python中,用eval强制将字符串转换为字典变量时候出错:NameError: name 'null' is not defined
【背景】
在python中,对于一个已经存在的字符串:
|
{ ..., "title":“”, } |
其内容的形式很类似于字典类型的变量,所以,希望去将其强制转换为字典类型变量,以便于后续处理。
后来找到了介绍,说是用eval强制转换即可。然后去试了,用了eval去转换,发现的确是可以的。
但是,后来去用eval强制转换另外别的一个字符串:
|
{ ..., "title":null, } |
却出现错误:
| Traceback (most recent call last): File "D: mpWordPressOthers o_wphi-baidu-mover_v2hi-baidu-mover_v2.py", line 446, in <module> main() File "D: mpWordPressOthers o_wphi-baidu-mover_v2hi-baidu-mover_v2.py", line 384, in main i=fetchEntry(permalink,datetimepattern,mode) File "D: mpWordPressOthers o_wphi-baidu-mover_v2hi-baidu-mover_v2.py", line 98, in fetchEntry cmt_err_msg = eval(cmt_soup_uni_removeHtmlTag) File "<string>", line 1, in <module> NameError: name 'null' is not defined |
【解决过程】
1. 网上找了半天,只是看到很多解释,说是最好有节制的使用,尽量少用eval函数,其好像存在一些安全隐患。
推荐使用ast模块。但是ast是python 2.6中才有,而我装得正好只是python 2.5,暂时不方便重新安装升级为2.6,所以继续折腾,看看eval转换为何会出现这个错误。
2.后来通过google搜索到这个:
Running JSON through Python's eval()? - Stack Overflow
“So, as I'm working with Python 2.4 (i.e. no json module), eval() is ... out by SilentGhost: eval doesn't handle true -> True, false -> False, null -> None correctly. ... line 1, in <module> NameError: name 'false' is not defined ”
其中,注意到其解释说,eval不支持null,true,false等,没法正确转换为None,True,False等,所以,才明白,此处的错误,是由于上面的字符串中,包含了“title”:null,eval函数无法正确解析,所以报错“NameError: name 'null' is not defined”。
知道了这个原因后,那就明白了,没法继续再用eval了,只有想办法升级python到2.6+的版本了,然后用
ast.literal_eval
去取代eval,即可。
3。刚又找到官方的解释:
http://docs.python.org/library/functions.html#eval
| eval(expression[, globals[, locals]])?
The arguments are a string and optional globals and locals. If provided,globals must be a dictionary. If provided, locals can be any mapping object. Changed in version 2.4: formerly locals was required to be a dictionary. The expression argument is parsed and evaluated as a Python expression (technically speaking, a condition list) using the globals and localsdictionaries as global and local namespace. If the globals dictionary is present and lacks ‘__builtins__’, the current globals are copied into globalsbefore expression is parsed. This means that expressionnormally has full access to the standard __builtin__ module and restricted environments are propagated. If the locals dictionary is omitted it defaults to theglobalsdictionary. If both dictionaries are omitted, the expression is executed in the environment where eval() is called. The return value is the result of the evaluated expression. Syntax errors are reported as exceptions. Example: >>>
>>> x = 1 >>> print eval('x+1') 2
This function can also be used to execute arbitrary code objects (such as those created by compile()). In this case pass a code object instead of a string. If the code object has been compiled with 'exec' as themode argument, eval()‘s return value will be None. Hints: dynamic execution of statements is supported by the execstatement. Execution of statements from a file is supported by theexecfile() function. The globals() andlocals() functions returns the current global and local dictionary, respectively, which may be useful to pass around for use by eval() or execfile(). See ast.literal_eval() for a function that can safely evaluate strings with expressions containing only literals. |
【总结】
(1)以后安装python尽量装python的新版本,至少是>=2.6,因为其支持ast模块。
(2)以后尽量少用eval函数,用ast.literal_eval取代eval。
(3)关于ast.literal_eval的解释,详情参见:http://docs.python.org/library/ast.html#ast.literal_eval
【后记 2011-12-20】
后来的经验,证明上述结论,是不准确的。
实际情况是,在用ast.literal_eval的时候,遇到很多字典形式的字符串,转换为字典的时候,结果都会出错,但是用eval,却是可以正常解析的。
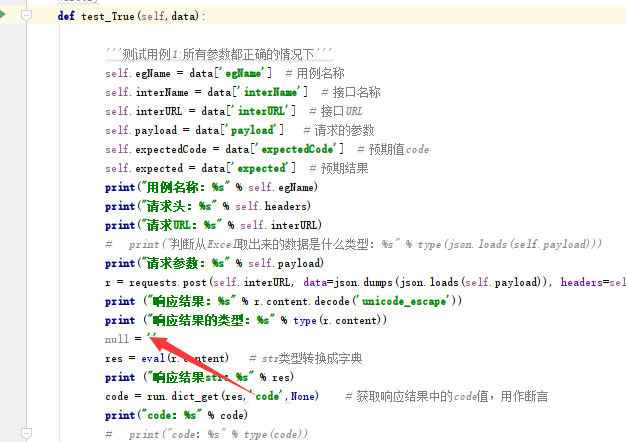
而对于null没有定义的问题,不论是ast.literal_eval和eval,两者都不支持的,因为本身python不支持null,python中的变量“空”,不是null,也不是NULL,而是None。所以,一个解决办法是,定义一个全局变量:
null = '' #因为此处处理的是字符,所以此处定义为空字符串
然后在函数里面,加上
global null
然后再去调用eval,就可以正常使用了。
实际证明,至少此处我遇到的,eval处理很多字典类字符串转换为字典变量的时候,还是很好用的。
【结论 2011-12-20】
1.将字典形式字符串转换为字典变量的时候,eval比ast.literal_eval更好用。
2.eval和ast.literal_eval,都不支持null。可以通过,在全局定义一个 null='',在函数内加上global null,以解决此问题。
转自:http://againinput4.blog.163.com/blog/static/172799491201111143108624/?suggestedreading&wumii