Real-Time MDNet
ECCV 2018 2018-10-22 15:52:01
Code (PyTorch): https://github.com/IlchaeJung/RT-MDNet
PyTorch 1.0 Python3 version: https://github.com/BossBobxuan/RT-MDNet
Reference Paper:
1. Learning Multi-Domain Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Tracking CVPR-2016 paper code
2. BranchOut: Regularization for Online Ensemble Tracking with Convolutional Neural Networks CVPR-2017 paper
3. "Meta-Tracker: Fast and Robust Online Adaptation for Visual Object Trackers." ECCV-2018 Paper Code
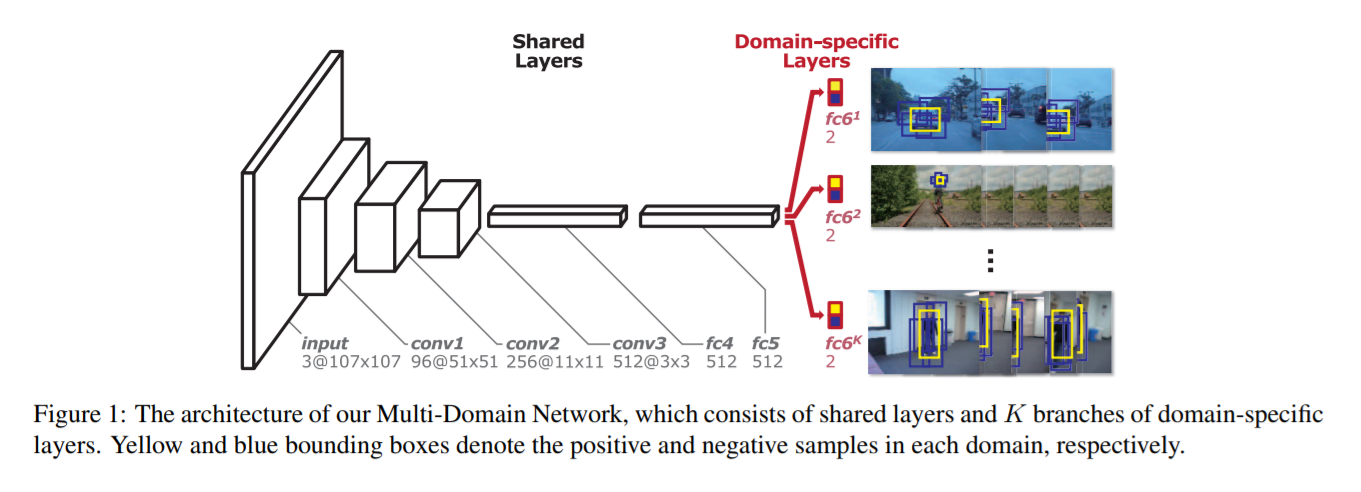
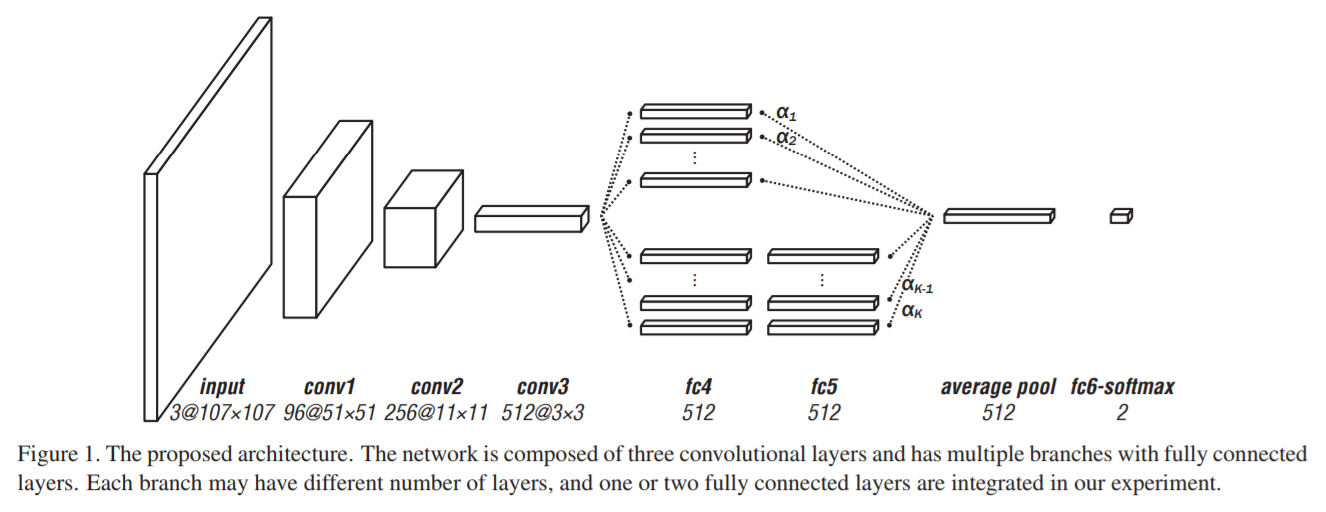
上面两个流程图分别是 MDNet 以及 MDNet 的一个改进 Branchout。本文是基于 MDNet 进行改进的,主要是在速度上进行大幅度的提升,因为原始的 MDNet 采用的是 RCNN 的思路,暴力的进行特征的提取,而本文采用改进的 ROI Align 的方法进行更加高效的特征提取。此外,作者提出一种新的 loss function 使其能够取更好的区分前景背景。主要的贡献如下:
本文所提出的网络结构如下所示:
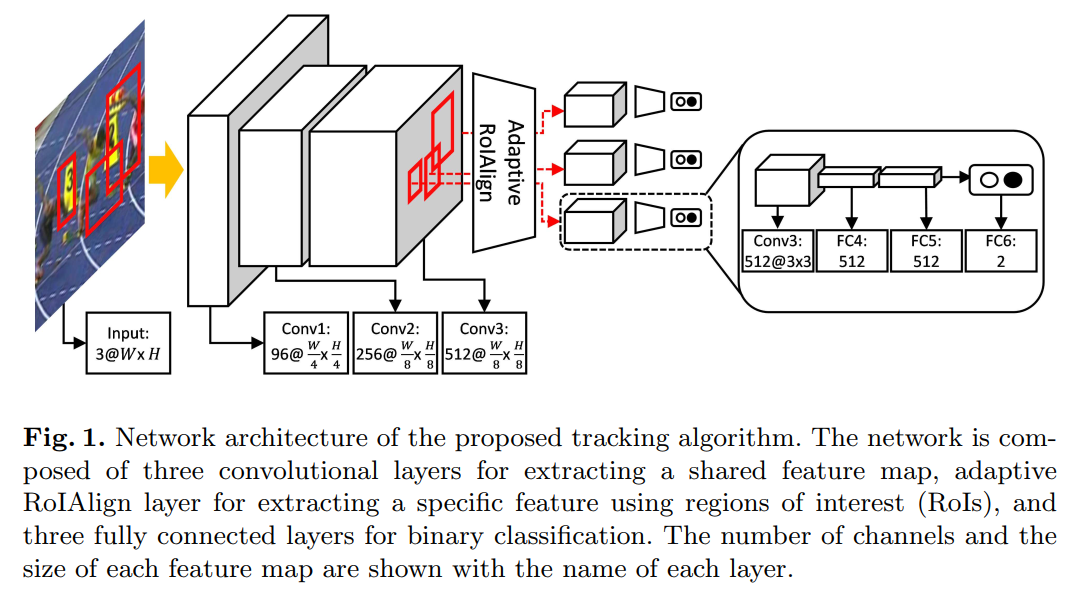
Efficient Feature Extraction and Discriminative Feature Learning:
1. Network Architecture:
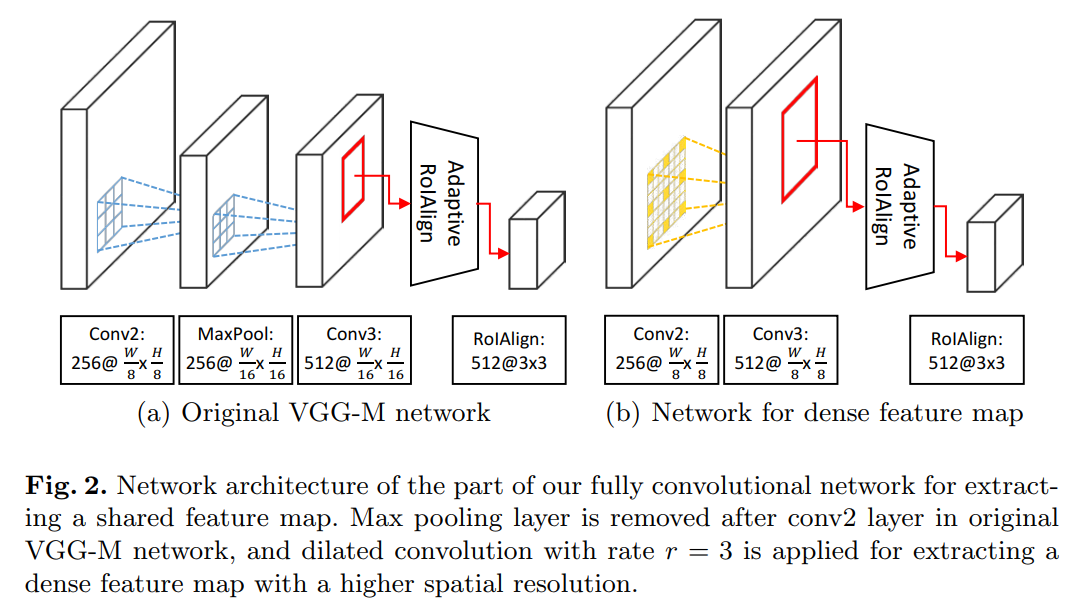
如图1所示,网络结构上与 MDNet 基本一致,最大的改动就是采用 改进的 ROI Align 算法 替换掉了原本的暴力的特征提取流程。所以,该网络结构就变成了:3 conv + Adaptive ROI Align layer + fc layers 。
2. Improved RoIAlign for Visual Tracking:
直接采用 RoIAlign 算法得到的 feature map 是比较粗糙的( compared to the ones from individual proposal bounding box)。为了提升 RoIs 的质量,我们需要构建一个 feature map,使得该 feature map 有较高的分辨率 以及 丰富的语义信息。这些需求可以通过获取更加 dense 的全卷机特征图以及扩张每一个激活的感受野来实现(by computing a denser fully convolutional feature map and enlarging the receptive field of each activitation)。所以,我们移除了 a max pooling layer followed by conv2 layer in VGG-M network,然后利用空洞卷积来提升分辨率(with rate r =3)。这个策略可以得到比常规的卷积更大的 feature map。它可以提取到更大的 feature maps,可以很大程度上改善表达的质量。图2展示了常规的 MDNet 与 加入了 dilated layers 之后的网络,进行了对比。
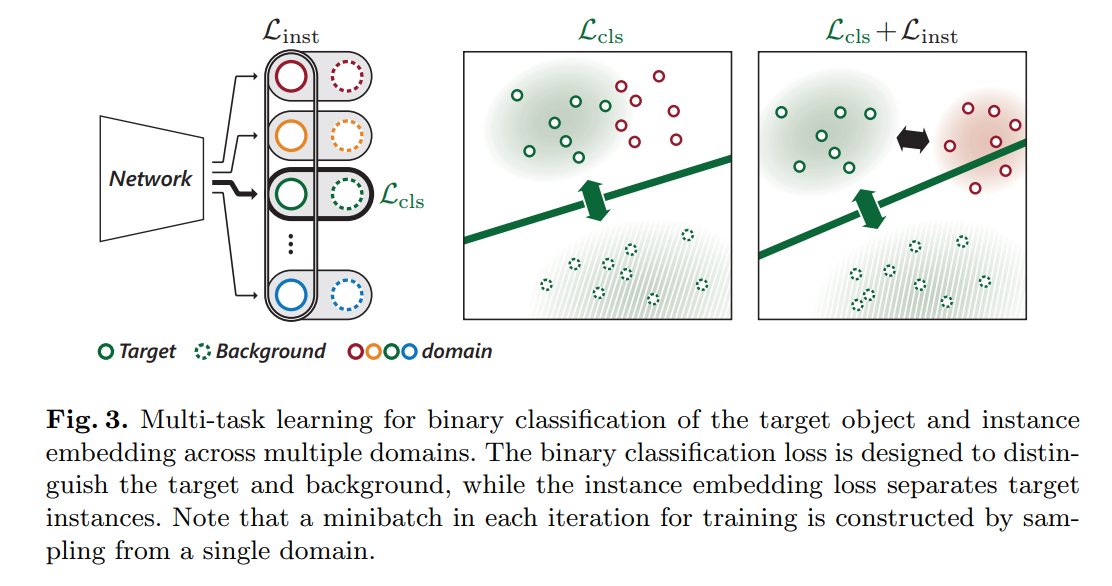
3. Pretraining for Dsicriminative Instance Embedding:
我们的学习算法的目标是训练一个判别性的特征映射,来应用到 multiple domains。MDNet 划分出 shared and domain separate layers 来学习表示以区分出前景和背景。除了这个目标之外,我们提出一种新的 loss,即:instance embedding loss,enforces target objects in different domains to be embedded far from each other in a shared feature space and enables to learn discriminative represenations of the unseen target objects in new test sequences. 换句话说,MDNet 仅仅考虑在单独的 domain 来区分 target 和 background,可能在不同 domains 之间来判断 foreground objects 没那么好,特别是当前景物体属于同一个 semantic class 或者 有类似的外观时。这可能是由于原始的 CNN 是用来训练做分类的。为了解决这个问题,我们的算法将额外的约束考虑进来,对前景物体进行 embedding,使得在不同 videos 之间彼此远离(embeds foreground objects from multiple videos to be apart from each other)。
给定一张图像 $x_d$,在domain d,以及 BBox R,网络输出的得分,记为 fd, 通过 concatenating 最后的 fc layers 的激活来构成:
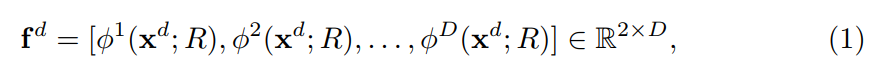
其中,![]() 是一个 2D binary classification score in domain d,D 是训练结合中 domain 的个数。输出的 feature 被送到 softmax function 中进行二分类,来确定是否一个 BBox R 是前景或者背景图像 in domain d。另外,输出的 feature 通过另一个 softmax operator 来进行 multiple domains 的 instances 判断。这两个 softmax 可以表达为:
是一个 2D binary classification score in domain d,D 是训练结合中 domain 的个数。输出的 feature 被送到 softmax function 中进行二分类,来确定是否一个 BBox R 是前景或者背景图像 in domain d。另外,输出的 feature 通过另一个 softmax operator 来进行 multiple domains 的 instances 判断。这两个 softmax 可以表达为:

其中,![]() 比较了在每一个 domain 中,目标物体和背景物体之间的得分,
比较了在每一个 domain 中,目标物体和背景物体之间的得分,![]() 对比了所有 domains 的物体的 pos score。
对比了所有 domains 的物体的 pos score。
我们网络优化一个多任务的 loss L,可以表达为:

其中,$L_{cls}$ 以及 $L_{inst}$ 分别是 binary classification 与 discriminative instance embedding 的 loss function。详细的表达式,可以分别记为:
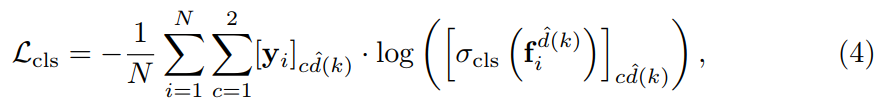

注意到,the instance embedding loss 仅仅对 positive examples 进行处理。
Online Tracking Algorithm:
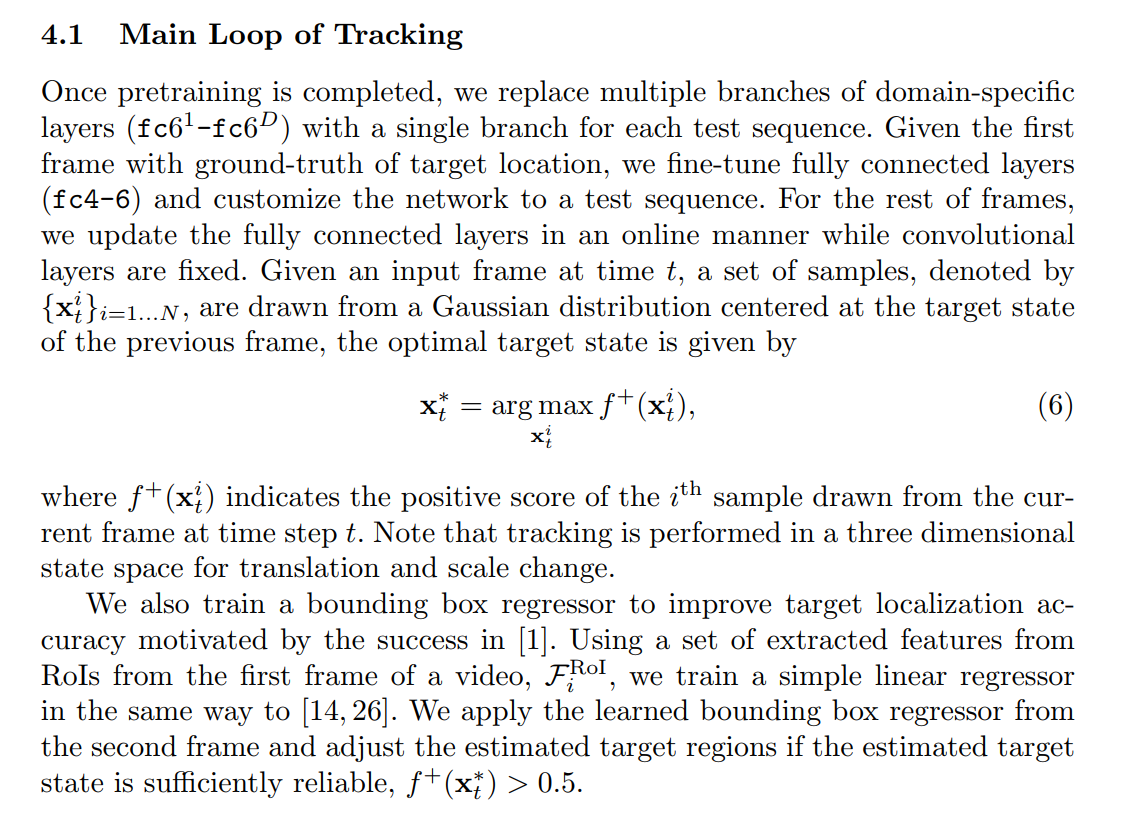
4.2 Online Model Updates:
We perform two complementary update strategies as in MDNet [1]: long-term and short-term updates to maintain robustness and adaptiveness, respectively. Long-term updates are regularly applied using the samples collected for a long period of time, while short-term updates are triggered whenever the score of the estimated target is below a threshold and the result is unreliable.
与 MDNet 不同的是,作者并没有利用 VOT 训练 OTB 测试 或者相反的思路,而是用 ImageNet-VID 上的视频,将近有 4500 个视频,作者随机挑选了 100 videos 来进行offline pretraining。
5. Experiments:
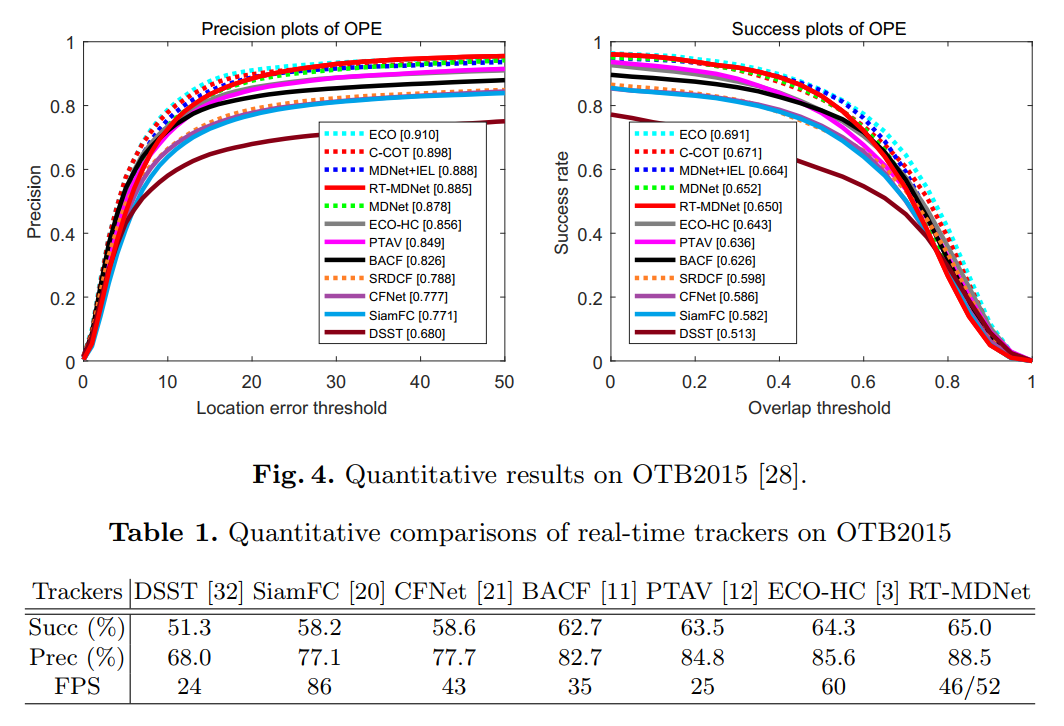
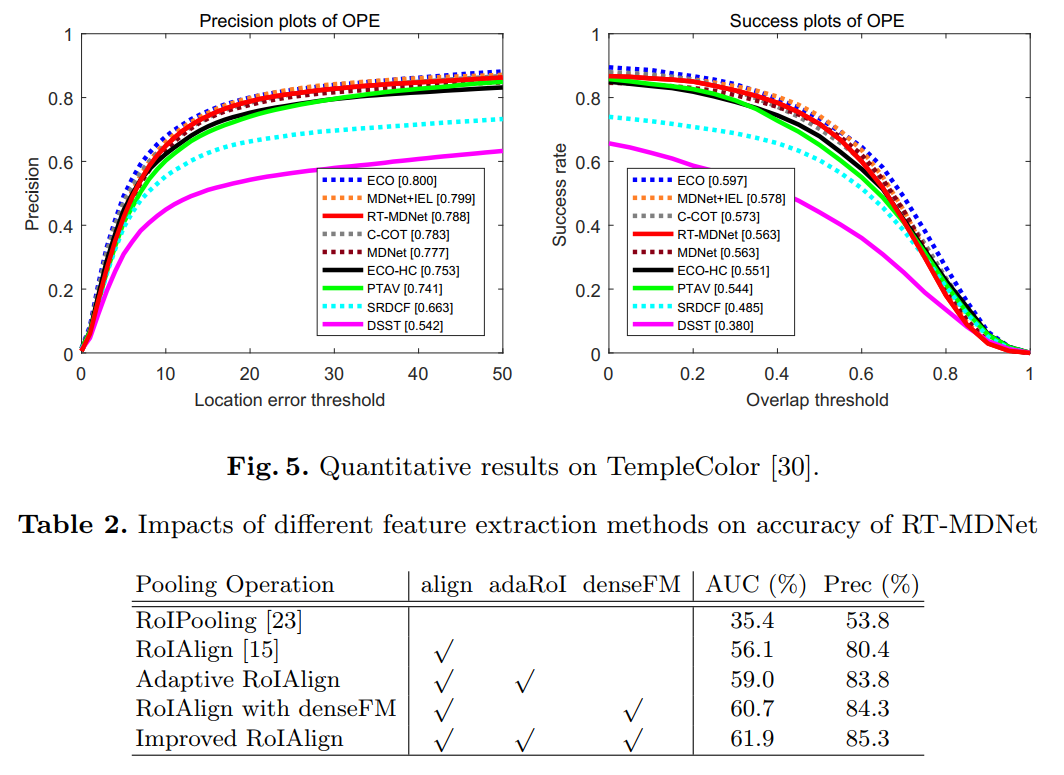
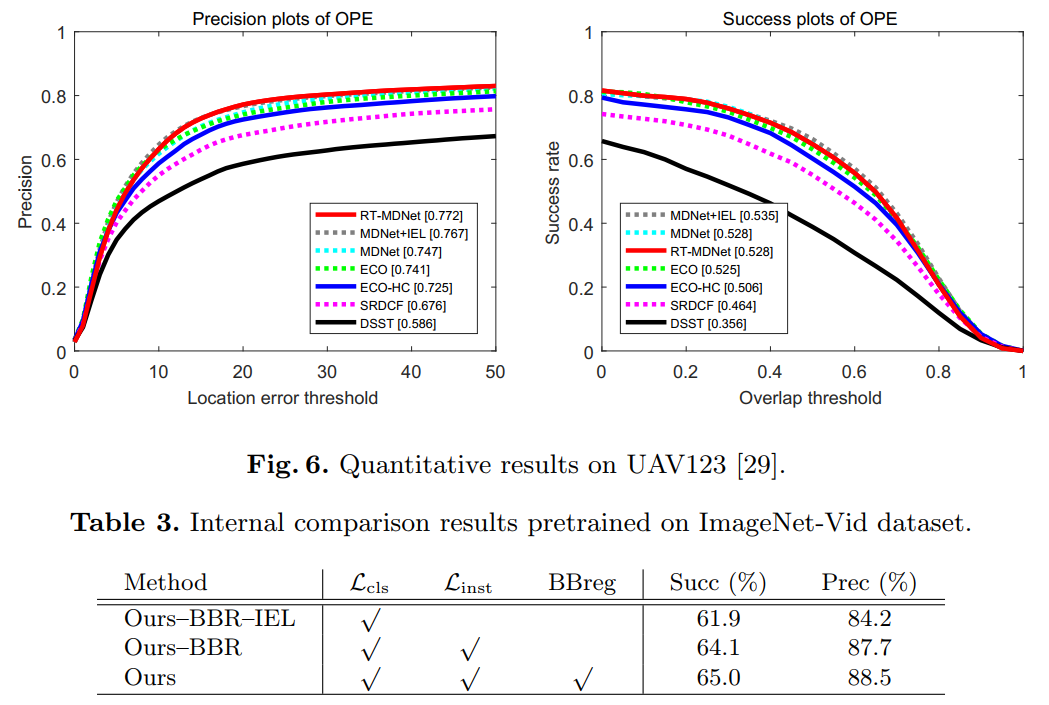

可以看到,作者在后续跟踪过程中,采用了 BBox regression 的技术,但是没有提到是否采用了 MDNet 中用到的 Hard Negative Mining(没有说,默认就是没有用咯 o(╯□╰)o)。