Tutorial: Triplet Loss Layer Design for CNN
Xiao Wang 2016.05.02
Triplet Loss Layer could be a trick for further improving the accuracy of CNN. Today, I will introduce the whole process, and display the code for you. This tutorial mainly from the blog:
http://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/46812153
http://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/46788025
and the paper: <FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering>.
First, Let's talk about how to add the layer into caffe and make test this layer to check whether it works or not. And then, we will discuss the paper and introduce the process of how the triplet loss come from. In the new version of caffe framework, it mainly consists of these steps for add a new layer i.e.
step 1. add the paprameter message in the corresponding layer, which located in ./src/caffe/proto/caffe.proto ;
step 2. add the declaration information of the layer in ./include/caffe/***layers.hpp ;
step 3. add the corresponding .cpp and .cu files in ./src/caffe/layers/, realize the function of the new added layer;
step 4. add test code of new added layers in ./src/caffe/gtest/, test its foreward and back propagation and its computation speed.
Let's do it step by step.
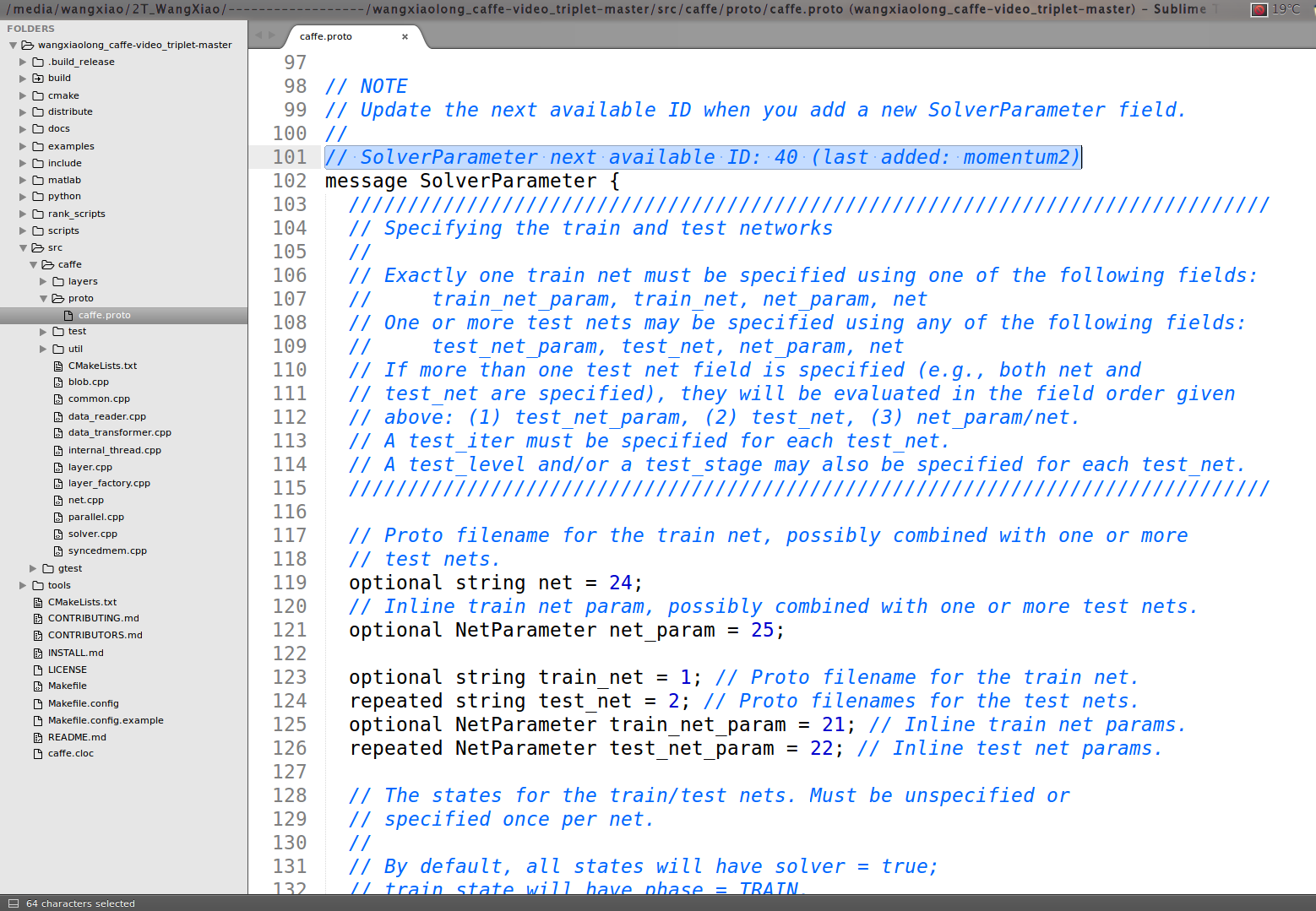
First, we add triplet loss layer in caffe.proto file:
we could found that in line 101, it said: SolverParameter next available ID: 40 (last added: momentum2), thus we add the ID: 40 as the new added information :
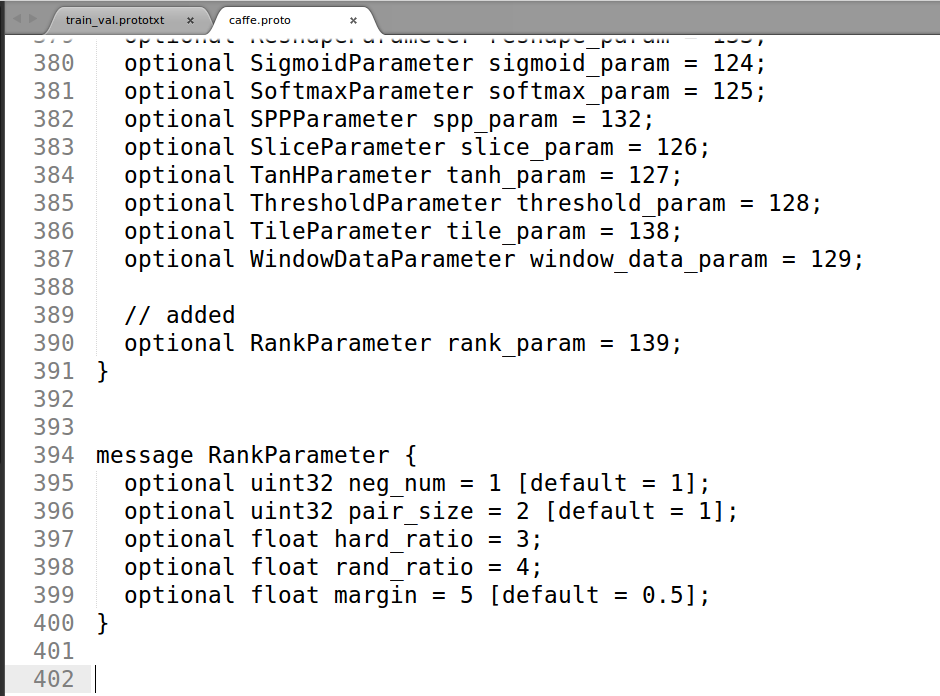
message RankParameter {
optional uint32 neg_num = 1 [default = 1];
optional uint32 pair_size = 2 [default = 1];
optional float hard_ratio = 3;
optional float rand_ratio = 4;
optional float margin = 5 [default = 0.5];
}
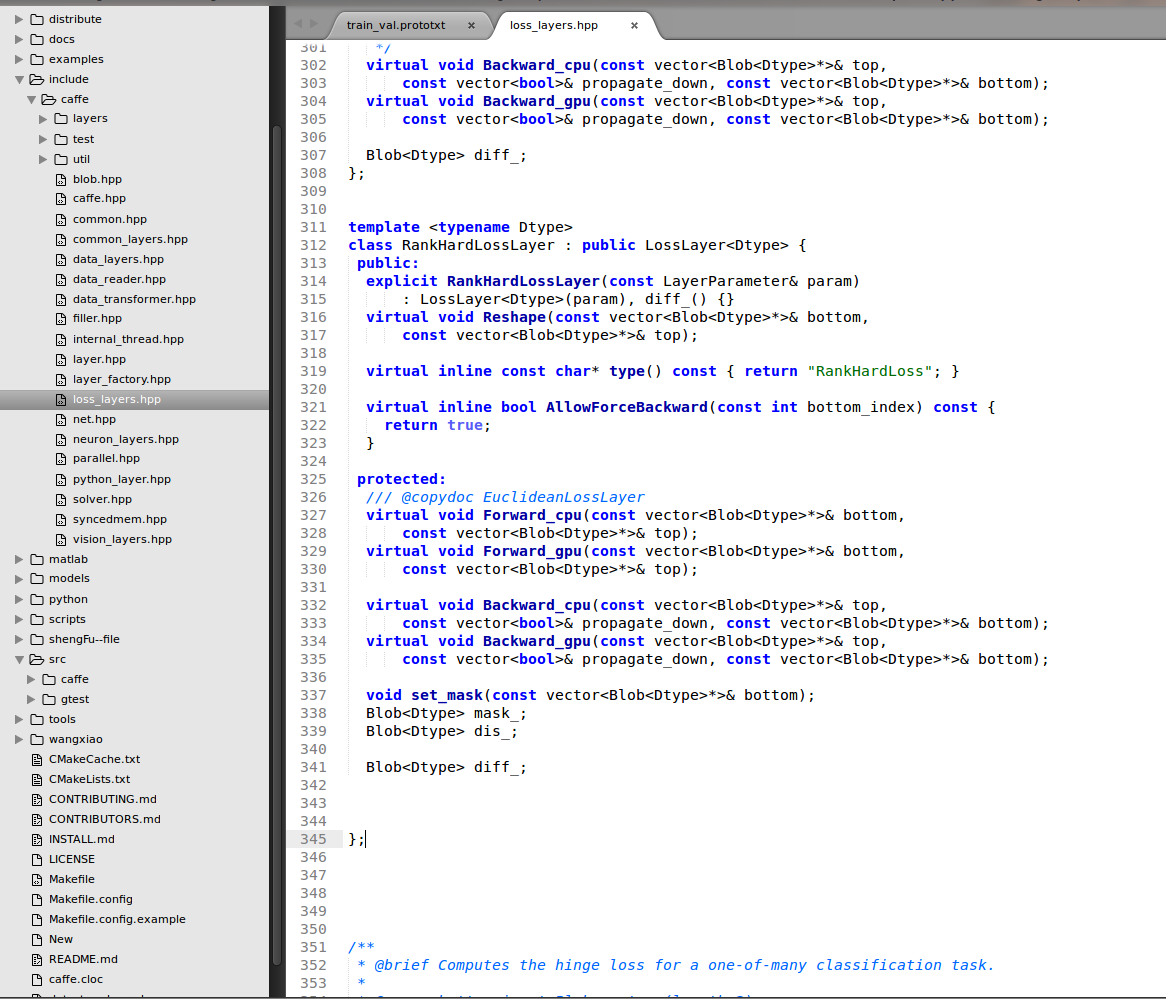
Second, we add the declearation information about triplet loss layer in ./include/caffe/TripletLoss_layers.hpp
Third, We compile the triplet loss layer of .cpp and .cu file
First of all is the .cpp file

1 #include <vector>
2
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <cmath>
5 #include <cfloat>
6
7 #include "caffe/layer.hpp"
8 #include "caffe/util/io.hpp"
9 #include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp"
10 #include "caffe/vision_layers.hpp"
11
12 using std::max;
13 using namespace std;
14 using namespace cv;
15
16 namespace caffe {
17
18 int myrandom (int i) { return caffe_rng_rand()%i;}
19
20
21 template <typename Dtype>
22 void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(
23 const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
24 LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(bottom, top);
25
26 diff_.ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]);
27 dis_.Reshape(bottom[0]->num(), bottom[0]->num(), 1, 1);
28 mask_.Reshape(bottom[0]->num(), bottom[0]->num(), 1, 1);
29 }
30
31
32 template <typename Dtype>
33 void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::set_mask(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom)
34 {
35
36 RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
37 int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num();
38 int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size();
39 float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
40 float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
41 float margin = rank_param.margin();
42
43 int hard_num = neg_num * hard_ratio;
44 int rand_num = neg_num * rand_ratio;
45
46 const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
47 const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
48 int count = bottom[0]->count();
49 int num = bottom[0]->num();
50 int dim = bottom[0]->count() / bottom[0]->num();
51 Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
52 Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data();
53
54 for(int i = 0; i < num * num; i ++)
55 {
56 dis_data[i] = 0;
57 mask_data[i] = 0;
58 }
59
60 // calculate distance
61 for(int i = 0; i < num; i ++)
62 {
63 for(int j = i + 1; j < num; j ++)
64 {
65 const Dtype* fea1 = bottom_data + i * dim;
66 const Dtype* fea2 = bottom_data + j * dim;
67 Dtype ts = 0;
68 for(int k = 0; k < dim; k ++)
69 {
70 ts += (fea1[k] * fea2[k]) ;
71 }
72 dis_data[i * num + j] = -ts;
73 dis_data[j * num + i] = -ts;
74 }
75 }
76
77 //select samples
78
79 vector<pair<float, int> >negpairs;
80 vector<int> sid1;
81 vector<int> sid2;
82
83
84 for(int i = 0; i < num; i += pair_size)
85 {
86 negpairs.clear();
87 sid1.clear();
88 sid2.clear();
89 for(int j = 0; j < num; j ++)
90 {
91 if(label[j] == label[i])
92 continue;
93 Dtype tloss = max(Dtype(0), dis_data[i * num + i + 1] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
94 if(tloss == 0) continue;
95
96 negpairs.push_back(make_pair(dis_data[i * num + j], j));
97 }
98 if(negpairs.size() <= neg_num)
99 {
100 for(int j = 0; j < negpairs.size(); j ++)
101 {
102 int id = negpairs[j].second;
103 mask_data[i * num + id] = 1;
104 }
105 continue;
106 }
107 sort(negpairs.begin(), negpairs.end());
108
109 for(int j = 0; j < neg_num; j ++)
110 {
111 sid1.push_back(negpairs[j].second);
112 }
113 for(int j = neg_num; j < negpairs.size(); j ++)
114 {
115 sid2.push_back(negpairs[j].second);
116 }
117 std::random_shuffle(sid1.begin(), sid1.end(), myrandom);
118 for(int j = 0; j < min(hard_num, (int)(sid1.size()) ); j ++)
119 {
120 mask_data[i * num + sid1[j]] = 1;
121 }
122 for(int j = hard_num; j < sid1.size(); j++)
123 {
124 sid2.push_back(sid1[j]);
125 }
126 std::random_shuffle(sid2.begin(), sid2.end(), myrandom);
127 for(int j = 0; j < min( rand_num, (int)(sid2.size()) ); j ++)
128 {
129 mask_data[i * num + sid2[j]] = 1;
130 }
131
132 }
133
134
135 }
136
137
138
139
140 template <typename Dtype>
141 void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
142 const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
143
144 const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
145 const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
146 int count = bottom[0]->count();
147 int num = bottom[0]->num();
148 int dim = bottom[0]->count() / bottom[0]->num();
149
150
151 RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
152 int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num(); // 4
153 int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size(); // 5
154 float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
155 float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
156 float margin = rank_param.margin();
157 Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
158 Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data();
159
160 set_mask(bottom);
161 Dtype loss = 0;
162 int cnt = neg_num * num / pair_size * 2;
163
164 for(int i = 0; i < num; i += pair_size)
165 {
166 for(int j = 0; j < num; j++)
167 {
168 if(mask_data[i * num + j] == 0)
169 continue;
170 Dtype tloss1 = max(Dtype(0), dis_data[i * num + i + 1] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
171 Dtype tloss2 = max(Dtype(0), dis_data[i * num + i + 1] - dis_data[(i + 1) * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
172 loss += tloss1 + tloss2;
173 }
174 }
175
176 loss = loss / cnt;
177 top[0]->mutable_cpu_data()[0] = loss;
178 }
179
180
181
182
183 template <typename Dtype>
184 void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
185 const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
186
187
188 const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
189 const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
190 Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
191 int count = bottom[0]->count();
192 int num = bottom[0]->num();
193 int dim = bottom[0]->count() / bottom[0]->num();
194
195 RankParameter rank_param = this->layer_param_.rank_param();
196 int neg_num = rank_param.neg_num();
197 int pair_size = rank_param.pair_size();
198 float hard_ratio = rank_param.hard_ratio();
199 float rand_ratio = rank_param.rand_ratio();
200 float margin = rank_param.margin();
201
202 Dtype* dis_data = dis_.mutable_cpu_data();
203 Dtype* mask_data = mask_.mutable_cpu_data();
204
205 for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ )
206 bottom_diff[i] = 0;
207
208 int cnt = neg_num * num / pair_size * 2;
209
210 for(int i = 0; i < num; i += pair_size)
211 {
212 const Dtype* fori = bottom_data + i * dim;
213 const Dtype* fpos = bottom_data + (i + 1) * dim;
214
215 Dtype* fori_diff = bottom_diff + i * dim;
216 Dtype* fpos_diff = bottom_diff + (i + 1) * dim;
217 for(int j = 0; j < num; j ++)
218 {
219 if(mask_data[i * num + j] == 0) continue;
220 Dtype tloss1 = max(Dtype(0), dis_data[i * num + i + 1] - dis_data[i * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
221 Dtype tloss2 = max(Dtype(0), dis_data[i * num + i + 1] - dis_data[(i + 1) * num + j] + Dtype(margin));
222
223 const Dtype* fneg = bottom_data + j * dim;
224 Dtype* fneg_diff = bottom_diff + j * dim;
225 if(tloss1 > 0)
226 {
227 for(int k = 0; k < dim; k ++)
228 {
229 fori_diff[k] += (fneg[k] - fpos[k]); // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
230 fpos_diff[k] += -fori[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
231 fneg_diff[k] += fori[k];
232 }
233 }
234 if(tloss2 > 0)
235 {
236 for(int k = 0; k < dim; k ++)
237 {
238 fori_diff[k] += -fpos[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
239 fpos_diff[k] += fneg[k]-fori[k]; // / (pairNum * 1.0 - 2.0);
240 fneg_diff[k] += fpos[k];
241 }
242 }
243
244 }
245 }
246
247 for (int i = 0; i < count; i ++)
248 {
249 bottom_diff[i] = bottom_diff[i] / cnt;
250 }
251
252 }
253
254 #ifdef CPU_ONLY
255 STUB_GPU(RankHardLossLayer);
256 #endif
257
258 INSTANTIATE_CLASS(RankHardLossLayer);
259 REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS(RankHardLoss);
260
261 } // namespace caffe
and the .cu file

1 #include <vector>
2
3 #include "caffe/layer.hpp"
4 #include "caffe/util/io.hpp"
5 #include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp"
6 #include "caffe/vision_layers.hpp"
7
8 namespace caffe {
9
10 template <typename Dtype>
11 void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
12 const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
13 Forward_cpu(bottom, top);
14 }
15
16 template <typename Dtype>
17 void RankHardLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
18 const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
19 Backward_cpu(top, propagate_down, bottom);
20 }
21
22 INSTANTIATE_LAYER_GPU_FUNCS(RankHardLossLayer);
23
24 } // namespace caffe
Finally, we make the caffe file and check whether have some mistakes about it.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
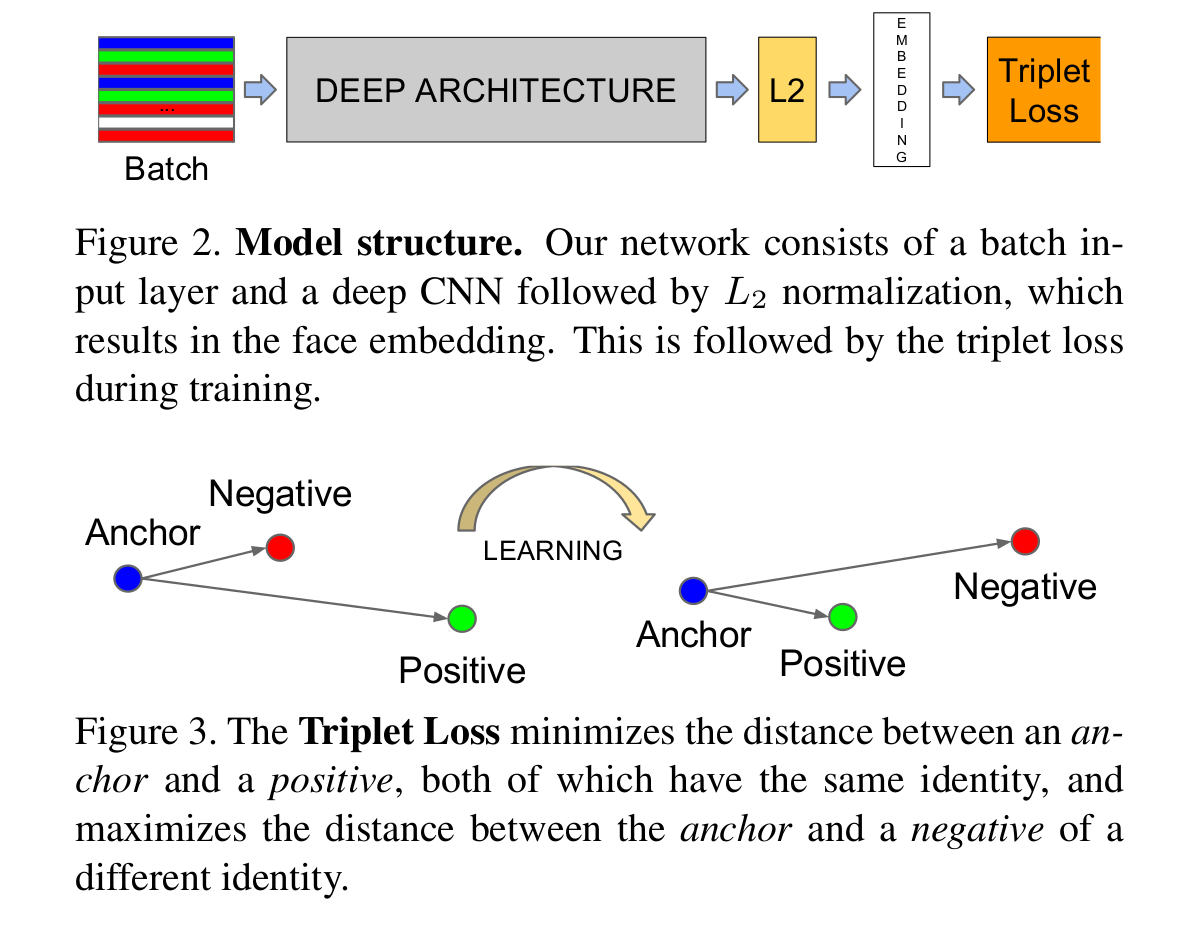
Let's continue to talk about the triplet loss:
Just like the above figure showns, the triplet loss usually have three components, i.e. the anchors, the positive, and the negative. What we are going to do is try to reduce the distance between the archor and the same, and push the different from the anchors.
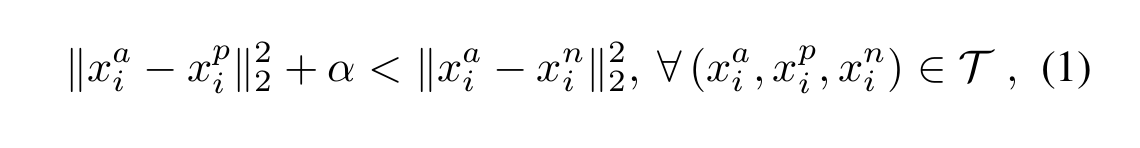
Thus, the whole loss could be described as following:
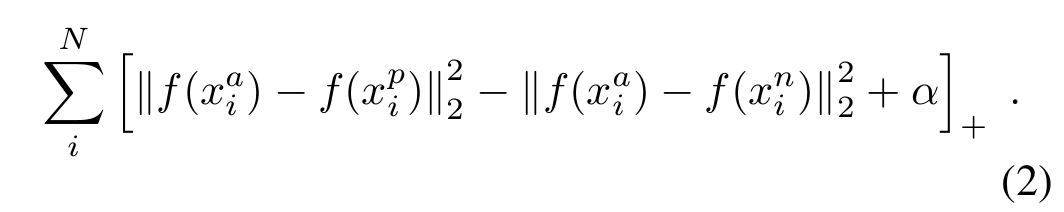
Only select triplets randomly may lead to slow converage of the network, and we need to find those hard triplets, that are active and can therefore contribute to improving the model. The following section will give you an explanination about the approach.
Triplet Selection:
There are two appproaches for generate triplets, i.e.
1. Generate triplets offline every n steps, using the most recent newwork checkpoint and computing the argmin and argmax on a subset of the data.
2. Generate the triplets online. This can be done by selecting the hard positive/negative exemplars form within a mini-batch.
This paper use all anchor-positive pairs in a mini-batch while still selecting the hard negatives. the all anchor-positive method was more stable and converaged slightly faster at the begining of training.
The code could refer the github page: https://github.com/wangxiao5791509/caffe-video_triplet
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "RankHardLoss"
rank_param{
neg_num: 4
pair_size: 2
hard_ratio: 0.5
rand_ratio: 0.5
margin: 1
}
bottom: "norml2"
bottom: "label"
}
Triplet Loss Implementation using Pytorch:
the following document comes from: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#tripletmarginloss
Creates a criterion that measures the triplet loss given an input tensors x1, x2, x3 and a margin with a value greater than 0. This is used for measuring a relative similarity between samples. A triplet is composed by a, p and n: anchor, positive examples and negative example respectively. The shapes of all input tensors should be (N,D)(N,D).
The distance swap is described in detail in the paper Learning shallow convolutional feature descriptors with triplet losses by V. Balntas, E. Riba et al.
The loss function for each sample in the mini-batch is:
where d(xi,yi)=∥xi−yi∥pd(xi,yi)=‖xi−yi‖p.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
- Shape:
-
- Input: (N,D)(N,D) where D is the vector dimension.
- Output: scalar. If reduce is False, then (N).
>>> triplet_loss = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2)
>>> input1 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> input2 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> input3 = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
>>> output = triplet_loss(input1, input2, input3)
>>> output.backward()
import torch.nn as nn triplet_loss = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.2, p=2) # 计算特征向量 anchor = model.forward(data[0]) positive = model.forward(data[1]) negative = model.forward(data[2]) # 计算三元组loss loss = triplet_loss.forward(anchor, positive, negative) loss.backward() optimizer.step()
