1.foreach[对一些数组或集合进行遍历]
foreach(类型 变量名 in 集合对象){语句体}

1 //定义一个数组 2 int [] sNum1={19,33,27,57,45,43 }; 3 foreach(var i in sNum1) 4 { 5 Console.WriteLine(i); 6 }
for循环

1 int[] str1 = {19,33,27,57,45,43 }; 2 //for循环遍历 3 for (int i=0;i<str1.length;i++) 4 { 5 Console.WriteLine(str1[i]); 6 }
2.异常
1)异常和错误的区别:
错误:语法错误根本没有编译成功
异常:在程序运行过程中产生使程序终止正常运行的事件,编译成功,运行的时候出了问题
2)为什么要写异常?假如web.config里面的用户名和密码要与数据库交互,如果用户名或密码写错,它就会将后台代码展示到了网页上,一是不安全,二是不美观
eg:

1 class Program 2 { 3 static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 int[] iNum1 ={19, 33, 27, 57, 45, 43}; 6 //数组越界 7 Console.WriteLine(iNum1[6]); 8 } 9 }
3)我们怎么写异常处理

1 try 2 { 3 要发生异常的代码 4 } 5 catch(异常类型,异常对象名) 6 { 7 处理的代码 8 } 9 finaly //可选 10 { 11 无论是否发生异常,都要执行的代码 12 }
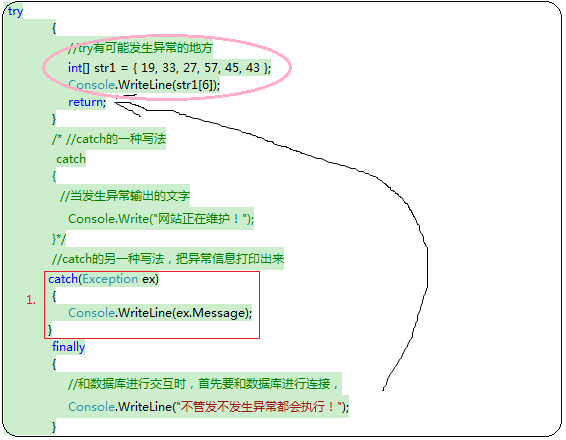
return是跳出方法体的意思,这边它的执行顺序是:
执行try里面可能发生异常的地方,如果发生异常,执行catch里面的语句,反之,从上而下执行再执行return。finally不管有没有return都会执行。finally在return之前执行。
3.数组
数组和集合都是用来存放数据的,存放数据的用处

假如我们要做一个列表,这么多课程,首先是在数据库里面的得到它的列表,然后对这个列表进行循环,然后才把循环的结果显示到页面里面
ⅰ.一维数组
声明一个一维数组:int [] iNum1={1,2,3};//常用
int [] iNum1=new int[3];a[0]=1;a[1]=2; //声明一个长度为3的数组,指定第一个数为1,第二个数为2
int [] iNum1=new int[3]{1,2,3};//[3]可以省去
ⅱ.二维数组
定义一个二维数组:int [,]a={{1,2},{2,3},{3,4}};
int [,]a=new int[3,2];a[0,0]=1;//a的一行一列为1
int [,]a=new int[3,2]{{1,1},{1,1},{1,1}};//[3,2]不能省

1 int[] iNum1 = { 1,6,7,32,21,12}; 2 Console.WriteLine("数组的长度为:"+iNum1.Length);
4.集合
比数组更加强大的东西,假如我们要对一组数组里面的元素进行删除,数组做不到,这是我们就可以使用ArrayList
使用ArrayList,HashTable等都要加上命名空间"using System.Collections;"
Ⅰ.ArrayList操作
它的用法,我们可以看一下它的代码

1 int[] iNum1 = { 1,6,7,32,21,12}; 2 //创建一个ArrayList对象 3 ArrayList aList = new ArrayList(); 4 //把数组里面的东西加到alist里面去,对数组进行foreach循环 5 foreach(var a in iNum1) 6 { 7 aList.Add(a);//将a添加到alist中 8 } 9 aList.RemoveAt(0);//删除它所对应的索引 10 aList.Add(0);//在alist数组的末尾添加一个0 11 aList.Insert(1,20);//在索引为1的位置处添加一个20 12 //aList.Clear();//清除所有的现有元素 13 //加进去之后再对它进行遍历 14 foreach(var a in aList) 15 { 16 Console.WriteLine(a); 17 }
ArraylList尽管对集合里面的内容很强大,但是它有一个弊端:

它添加的类型是object类型[任何一中类型的父类],object是引用类型,上面传的是值类型,值类型转为引用类型,这个过程叫着装箱,在程序中,我们要尽量避免装箱操作,如果是大数据,100w+条数据, 它每个都装箱一次,那它会有多大啊损耗。
ArrayList的用法看情况,比如一个集合里面,它要存一个字符串,int类型,数组,bool类型

1 ArrayList aList = new ArrayList(); 2 aList.Add("abc");//存字符串 3 aList.Add(123); //存int 4 aList.Add(iNum1);//存数组 5 aList.Add(true);//存bool类型
Ⅱ .为了避免装箱操作,引用了它的泛型形式把它改为:List <int> aList=new List<int>();
注:<int>只是它的一种泛型形式[对数据类型进行约束],表示这个集合只能存int类型

这时候就变成了值类型,就不会存在装箱操作,效益更高。
它也可以存任何数据类型的集合:

1 List<object> aList = new List<object>(); 2 aList.Add("abc");//存字符串 3 aList.Add(123); //存int 4 aList.Add(iNum1);//存数组 5 aList.Add(true);//存bool类型
1).public int UserId;与public int UserId{get;set;}的区别
ⅰ.public int UserId是字段
ⅱ.public int UserId{get;set;}//属性,get是读,set写。全写出来是这样的

1 public int UserId 2 { 3 get{return UserId;} 4 set{UserId=value;} 5 }
属性更加灵活,可以控制它的读和写,i字段只是一个简单的变量,不能控制读和写
eg:我们新建一个UserInfor类,program里面调用

1 class UserInfor 2 { 3 public int UserId {get; set;} 4 public string UserName {get;set;} 5 public string Pwd { get; set; } 6 public int Qq { get; set; } 7 }

1 class Program 2 { 3 static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 //得到一个集合 6 List<UserInfor> list = new List<UserInfor>() 7 { 8 //先得到它的对象 9 new UserInfor(){UserId=1,UserName="zhangsan",Pwd="zhangsan123",Qq=76895423}, 10 new UserInfor(){UserId=1,UserName="lisi",Pwd="lisi123",Qq=7115423}, 11 new UserInfor(){UserId=1,UserName="wang",Pwd="wang123",Qq=7575423}, 12 new UserInfor(){UserId=1,UserName="zhaoqian",Pwd="zhaoqian123",Qq=466683926}, 13 new UserInfor(){UserId=1,UserName="sunli",Pwd="sunli123",Qq=12123445} 14 }; 15 //遍历集合user表示上面每一个对象 16 foreach(var user in list) 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine(string.Format("用户名是:{0},密码是:{1}", user.UserName, user.Pwd)); 19 } 20 }
Ⅲ.hashtable
1.我们为什么要用hashTable?
在List<>,ArrayList,数组中,假设我们要对alist[3]-->4这个值,进行删除,然后又添加,又删除,找这个4。
那大数据100w+,用循环遍历循环10w次?这些都不可取,操作起来不方便,我们要对一个数组进行非常频繁的操作,那这时候我们就用到了hashtable。
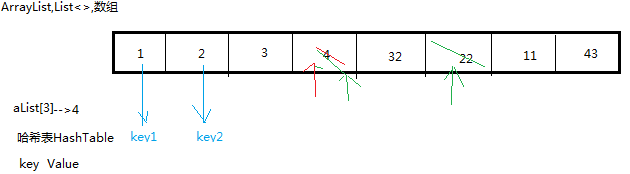
2.hashTable是怎样的存储方式?
一个key,一个value.以上图中,1这个值得key就是key1,1就是它的value,2这个值得key就是key2,value就是2,每个value对应一个key,即使内容顺序打乱也没关系,我们可以通过key去查找,所以就算对集 合里面的内容进行多频繁的操作,我们只要知道这个key就可以通过key去查找,就可以知道里面的value。
3.hashTable操作:

1 Hashtable ht = new Hashtable(); 2 ht.Add("key1", "aa"); 3 ht.Add("key2", "bb"); 4 ht.Add("key3", "cc"); 5 ht.Add("key4", "dd"); 6 ht.Add("key5", "ee"); 7 foreach (var key in ht.Keys)//ht.Keys找到ht里面的所有key 8 { 9 Console.WriteLine(ht[key]);//通过key去找value 10 }
hashTable没有插入,因为它不是通过位置去添加的。
Ⅳ.hashTable泛型形式
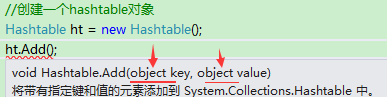
hashTable中,它也是object类型,object类型就存在装箱,拆箱的问题
hashTable的泛型形式,
Dictionary<string,int> ht=new Dictionary<string,int>();//实例化一个对象,<string,int> 里面必须是string,int

1.hashTable泛型形式操作,遍历

1 Dictionary<string, int> ht = new Dictionary<string, int>(); 2 ht.Add("key1", 10); 3 ht.Add("key2", 20); 4 ht.Add("key3", 30); 5 ht.Add("key4", 40); 6 foreach (var key in ht.Keys)//ht.Keys找到ht里面的所有key 7 { 8 Console.WriteLine(ht[key]);//通过key去找value 9 }
