环境准备
1、系统版本
CentOS7.5 + docker ee
2、配置阿里云yum源
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
cat /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-main.repo
[docker-main-repo]
name=Docker main Repository
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-engine/yum/repo/main/centos/7
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-engine/yum/gpg
yum clean all && yum makecache
3、安装常用软件
yum install -y vim wget openssl openssl-devel openssl pcre pcre-devel telnet setuptool ntsysv git python-urllib3 sqlite sqlite-devel bzip2 bzip2-devel gcc gcc-c++ cmake lsof sysstat bind-utils ntp iftop iotop tree screen iftop ntpdate nettools
4、配置主机名及hosts
# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.10.101 linux-reancher1.exmaple.com linux-reancher1
192.168.10.102 linux-k8s-master1.exmaple.com linux-k8s-master1
192.168.10.103 linux-k8s-node1.exmaple.com linux-k8s-node1
# cat /etc/hostname
linux-reancher1
....
5、停止防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
6、关闭selinux
# cat /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
7、开启ipv4转发
# cat /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
8、下载rancher的docker安装脚本,并修改docker的yum源为aliyun
curl -O 1.13.sh https://releases.rancher.com/install-docker/1.13.sh
#!/bin/sh
set -e
docker_version=1.13.1
#
# This script is meant for quick & easy install via:
# 'curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh'
# or:
# 'wget -qO- https://get.docker.com/ | sh'
#
# For test builds (ie. release candidates):
# 'curl -fsSL https://test.docker.com/ | sh'
# or:
# 'wget -qO- https://test.docker.com/ | sh'
#
# For experimental builds:
# 'curl -fsSL https://experimental.docker.com/ | sh'
# or:
# 'wget -qO- https://experimental.docker.com/ | sh'
#
# Docker Maintainers:
# To update this script on https://get.docker.com,
# use hack/release.sh during a normal release,
# or the following one-liner for script hotfixes:
# aws s3 cp --acl public-read hack/install.sh s3://get.docker.com/index
#
url="https://get.docker.com/"
apt_url="https://apt.dockerproject.org"
yum_url="http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-engine/yum"
gpg_fingerprint="58118E89F3A912897C070ADBF76221572C52609D"
key_servers="
ha.pool.sks-keyservers.net
pgp.mit.edu
keyserver.ubuntu.com
"
command_exists() {
command -v "$@" > /dev/null 2>&1
}
echo_docker_as_nonroot() {
if command_exists docker && [ -e /var/run/docker.sock ]; then
(
set -x
$sh_c 'docker version'
) || true
fi
your_user=your-user
[ "$user" != 'root' ] && your_user="$user"
# intentionally mixed spaces and tabs here -- tabs are stripped by "<<-EOF", spaces are kept in the output
cat <<-EOF
If you would like to use Docker as a non-root user, you should now consider
adding your user to the "docker" group with something like:
sudo usermod -aG docker $your_user
Remember that you will have to log out and back in for this to take effect!
EOF
}
# Check if this is a forked Linux distro
check_forked() {
# Check for lsb_release command existence, it usually exists in forked distros
if command_exists lsb_release; then
# Check if the `-u` option is supported
set +e
lsb_release -a -u > /dev/null 2>&1
lsb_release_exit_code=$?
set -e
# Check if the command has exited successfully, it means we're in a forked distro
if [ "$lsb_release_exit_code" = "0" ]; then
# Print info about current distro
cat <<-EOF
You're using '$lsb_dist' version '$dist_version'.
EOF
# Get the upstream release info
lsb_dist=$(lsb_release -a -u 2>&1 | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]' | grep -E 'id' | cut -d ':' -f 2 | tr -d '[[:space:]]')
dist_version=$(lsb_release -a -u 2>&1 | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]' | grep -E 'codename' | cut -d ':' -f 2 | tr -d '[[:space:]]')
# Print info about upstream distro
cat <<-EOF
Upstream release is '$lsb_dist' version '$dist_version'.
EOF
else
if [ -r /etc/debian_version ] && [ "$lsb_dist" != "ubuntu" ] && [ "$lsb_dist" != "raspbian" ]; then
# We're Debian and don't even know it!
lsb_dist=debian
dist_version="$(cat /etc/debian_version | sed 's//.*//' | sed 's/..*//')"
case "$dist_version" in
9)
dist_version="stretch"
;;
8|'Kali Linux 2')
dist_version="jessie"
;;
7)
dist_version="wheezy"
;;
esac
fi
fi
fi
}
rpm_import_repository_key() {
local key=$1; shift
local tmpdir=$(mktemp -d)
chmod 600 "$tmpdir"
for key_server in $key_servers ; do
gpg --homedir "$tmpdir" --keyserver "$key_server" --recv-keys "$key" && break
done
gpg --homedir "$tmpdir" -k "$key" >/dev/null
gpg --homedir "$tmpdir" --export --armor "$key" > "$tmpdir"/repo.key
rpm --import "$tmpdir"/repo.key
rm -rf "$tmpdir"
}
semverParse() {
major="${1%%.*}"
minor="${1#$major.}"
minor="${minor%%.*}"
patch="${1#$major.$minor.}"
patch="${patch%%[-.]*}"
}
do_install() {
case "$(uname -m)" in
*64)
;;
armv6l|armv7l)
;;
*)
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
Error: you are not using a 64bit platform or a Raspberry Pi (armv6l/armv7l).
Docker currently only supports 64bit platforms or a Raspberry Pi (armv6l/armv7l).
EOF
exit 1
;;
esac
if command_exists docker; then
version="$(docker -v | awk -F '[ ,]+' '{ print $3 }')"
MAJOR_W=1
MINOR_W=10
semverParse $version
shouldWarn=0
if [ $major -lt $MAJOR_W ]; then
shouldWarn=1
fi
if [ $major -le $MAJOR_W ] && [ $minor -lt $MINOR_W ]; then
shouldWarn=1
fi
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
Warning: the "docker" command appears to already exist on this system.
If you already have Docker installed, this script can cause trouble, which is
why we're displaying this warning and provide the opportunity to cancel the
installation.
If you installed the current Docker package using this script and are using it
EOF
if [ $shouldWarn -eq 1 ]; then
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
again to update Docker, we urge you to migrate your image store before upgrading
to v1.10+.
You can find instructions for this here:
https://github.com/docker/docker/wiki/Engine-v1.10.0-content-addressability-migration
EOF
else
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
again to update Docker, you can safely ignore this message.
EOF
fi
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
You may press Ctrl+C now to abort this script.
EOF
( set -x; sleep 20 )
fi
user="$(id -un 2>/dev/null || true)"
sh_c='sh -c'
if [ "$user" != 'root' ]; then
if command_exists sudo; then
sh_c='sudo -E sh -c'
elif command_exists su; then
sh_c='su -c'
else
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
Error: this installer needs the ability to run commands as root.
We are unable to find either "sudo" or "su" available to make this happen.
EOF
exit 1
fi
fi
curl=''
if command_exists curl; then
curl='curl -sSL'
elif command_exists wget; then
curl='wget -qO-'
elif command_exists busybox && busybox --list-modules | grep -q wget; then
curl='busybox wget -qO-'
fi
# check to see which repo they are trying to install from
if [ -z "$repo" ]; then
repo='main'
if [ "https://test.docker.com/" = "$url" ]; then
repo='testing'
elif [ "https://experimental.docker.com/" = "$url" ]; then
repo='experimental'
fi
fi
# perform some very rudimentary platform detection
lsb_dist=''
dist_version=''
if command_exists lsb_release; then
lsb_dist="$(lsb_release -si)"
fi
if [ -z "$lsb_dist" ] && [ -r /etc/lsb-release ]; then
lsb_dist="$(. /etc/lsb-release && echo "$DISTRIB_ID")"
fi
if [ -z "$lsb_dist" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_version ]; then
lsb_dist='debian'
fi
if [ -z "$lsb_dist" ] && [ -r /etc/fedora-release ]; then
lsb_dist='fedora'
fi
if [ -z "$lsb_dist" ] && [ -r /etc/oracle-release ]; then
lsb_dist='oracleserver'
fi
if [ -z "$lsb_dist" ] && [ -r /etc/centos-release ]; then
lsb_dist='centos'
fi
if [ -z "$lsb_dist" ] && [ -r /etc/redhat-release ]; then
lsb_dist='redhat'
fi
if [ -z "$lsb_dist" ] && [ -r /etc/os-release ]; then
lsb_dist="$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$ID")"
fi
lsb_dist="$(echo "$lsb_dist" | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]')"
# Special case redhatenterpriseserver
if [ "${lsb_dist}" = "redhatenterpriseserver" ]; then
# Set it to redhat, it will be changed to centos below anyways
lsb_dist='redhat'
fi
case "$lsb_dist" in
ubuntu)
if command_exists lsb_release; then
dist_version="$(lsb_release --codename | cut -f2)"
fi
if [ -z "$dist_version" ] && [ -r /etc/lsb-release ]; then
dist_version="$(. /etc/lsb-release && echo "$DISTRIB_CODENAME")"
fi
;;
debian|raspbian)
dist_version="$(cat /etc/debian_version | sed 's//.*//' | sed 's/..*//')"
case "$dist_version" in
8)
dist_version="jessie"
;;
7)
dist_version="wheezy"
;;
esac
;;
oracleserver)
# need to switch lsb_dist to match yum repo URL
lsb_dist="oraclelinux"
dist_version="$(rpm -q --whatprovides redhat-release --queryformat "%{VERSION}
" | sed 's//.*//' | sed 's/..*//' | sed 's/Server*//')"
;;
fedora|centos|redhat)
dist_version="$(rpm -q --whatprovides ${lsb_dist}-release --queryformat "%{VERSION}
" | sed 's//.*//' | sed 's/..*//' | sed 's/Server*//' | sort | tail -1)"
;;
*)
if command_exists lsb_release; then
dist_version="$(lsb_release --codename | cut -f2)"
fi
if [ -z "$dist_version" ] && [ -r /etc/os-release ]; then
dist_version="$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_ID")"
fi
;;
esac
# Check if this is a forked Linux distro
check_forked
# Run setup for each distro accordingly
case "$lsb_dist" in
amzn)
(
set -x
$sh_c 'sleep 3; yum -y -q install docker'
)
echo_docker_as_nonroot
exit 0
;;
'opensuse project'|opensuse)
echo 'Going to perform the following operations:'
if [ "$repo" != 'main' ]; then
echo ' * add repository obs://Virtualization:containers'
fi
echo ' * install Docker'
$sh_c 'echo "Press CTRL-C to abort"; sleep 3'
if [ "$repo" != 'main' ]; then
# install experimental packages from OBS://Virtualization:containers
(
set -x
zypper -n ar -f obs://Virtualization:containers Virtualization:containers
rpm_import_repository_key 55A0B34D49501BB7CA474F5AA193FBB572174FC2
)
fi
(
set -x
zypper -n install docker
)
echo_docker_as_nonroot
exit 0
;;
'suse linux'|sle[sd])
echo 'Going to perform the following operations:'
if [ "$repo" != 'main' ]; then
echo ' * add repository obs://Virtualization:containers'
echo ' * install experimental Docker using packages NOT supported by SUSE'
else
echo ' * add the "Containers" module'
echo ' * install Docker using packages supported by SUSE'
fi
$sh_c 'echo "Press CTRL-C to abort"; sleep 3'
if [ "$repo" != 'main' ]; then
# install experimental packages from OBS://Virtualization:containers
echo >&2 'Warning: installing experimental packages from OBS, these packages are NOT supported by SUSE'
(
set -x
zypper -n ar -f obs://Virtualization:containers/SLE_12 Virtualization:containers
rpm_import_repository_key 55A0B34D49501BB7CA474F5AA193FBB572174FC2
)
else
# Add the containers module
# Note well-1: the SLE machine must already be registered against SUSE Customer Center
# Note well-2: the `-r ""` is required to workaround a known issue of SUSEConnect
(
set -x
SUSEConnect -p sle-module-containers/12/x86_64 -r ""
)
fi
(
set -x
zypper -n install docker
)
echo_docker_as_nonroot
exit 0
;;
ubuntu|debian|raspbian)
export DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
did_apt_get_update=
apt_get_update() {
if [ -z "$did_apt_get_update" ]; then
( set -x; $sh_c 'sleep 3; apt-get update' )
did_apt_get_update=1
fi
}
if [ "$lsb_dist" = "raspbian" ]; then
# Create Raspbian specific systemd drop-in file, use overlay by default
( set -x; $sh_c "mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d" )
( set -x; $sh_c "echo '[Service]
ExecStart=
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd --storage-driver overlay -H fd://' > /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/overlay.conf" )
else
# aufs is preferred over devicemapper; try to ensure the driver is available.
if ! grep -q aufs /proc/filesystems && ! $sh_c 'modprobe aufs'; then
if uname -r | grep -q -- '-generic' && dpkg -l 'linux-image-*-generic' | grep -qE '^ii|^hi' 2>/dev/null; then
kern_extras="linux-image-extra-$(uname -r) linux-image-extra-virtual"
apt_get_update
( set -x; $sh_c 'sleep 3; apt-get install -y -q '"$kern_extras" ) || true
if ! grep -q aufs /proc/filesystems && ! $sh_c 'modprobe aufs'; then
echo >&2 'Warning: tried to install '"$kern_extras"' (for AUFS)'
echo >&2 ' but we still have no AUFS. Docker may not work. Proceeding anyways!'
( set -x; sleep 10 )
fi
else
echo >&2 'Warning: current kernel is not supported by the linux-image-extra-virtual'
echo >&2 ' package. We have no AUFS support. Consider installing the packages'
echo >&2 ' linux-image-virtual kernel and linux-image-extra-virtual for AUFS support.'
( set -x; sleep 10 )
fi
fi
fi
# install apparmor utils if they're missing and apparmor is enabled in the kernel
# otherwise Docker will fail to start
if [ "$(cat /sys/module/apparmor/parameters/enabled 2>/dev/null)" = 'Y' ]; then
if command -v apparmor_parser >/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo 'apparmor is enabled in the kernel and apparmor utils were already installed'
else
echo 'apparmor is enabled in the kernel, but apparmor_parser is missing. Trying to install it..'
apt_get_update
( set -x; $sh_c 'sleep 3; apt-get install -y -q apparmor' )
fi
fi
if [ ! -e /usr/lib/apt/methods/https ]; then
apt_get_update
( set -x; $sh_c 'sleep 3; apt-get install -y -q apt-transport-https ca-certificates' )
fi
if [ -z "$curl" ]; then
apt_get_update
( set -x; $sh_c 'sleep 3; apt-get install -y -q curl ca-certificates' )
curl='curl -sSL'
fi
if [ ! -e /usr/bin/gpg ]; then
apt_get_update
( set -x; $sh_c 'sleep 3; apt-get install -y -q gnupg2 || apt-get install -y -q gnupg' )
fi
if ! command -v gpg > /dev/null; then
apt_get_update
( set -x; $sh_c 'sleep 3; apt-get install -y -q gnupg2 || apt-get install -y -q gnupg' )
fi
# dirmngr is a separate package in ubuntu yakkety; see https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/apt/+bug/1634464
if ! command -v dirmngr > /dev/null; then
apt_get_update
( set -x; $sh_c 'sleep 3; apt-get install -y -q dirmngr' )
fi
(
set -x
for key_server in $key_servers ; do
$sh_c "apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://${key_server}:80 --recv-keys ${gpg_fingerprint}" && break
done
$sh_c "apt-key adv -k ${gpg_fingerprint} >/dev/null"
$sh_c "mkdir -p /etc/apt/sources.list.d"
$sh_c "echo deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture)] ${apt_url}/repo ${lsb_dist}-${dist_version} ${repo} > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list"
$sh_c "sleep 3; apt-get update"
$sh_c "apt-get install -y -q docker-engine=$(apt-cache madison docker-engine | grep ${docker_version} | head -n 1 | cut -d ' ' -f 3)"
)
echo_docker_as_nonroot
exit 0
;;
fedora|centos|redhat|oraclelinux)
if [ "${lsb_dist}" = "redhat" ]; then
# we use the centos repository for both redhat and centos releases
lsb_dist='centos'
fi
$sh_c "cat >/etc/yum.repos.d/docker-${repo}.repo" <<-EOF
[docker-${repo}-repo]
name=Docker ${repo} Repository
baseurl=${yum_url}/repo/${repo}/${lsb_dist}/${dist_version}
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=${yum_url}/gpg
EOF
if [ "$lsb_dist" = "fedora" ] && [ "$dist_version" -ge "22" ]; then
(
set -x
$sh_c "sleep 3; dnf -y -q install docker-engine-${docker_version}"
)
else
(
set -x
$sh_c "sleep 3; yum -y -q install docker-engine-${docker_version}"
)
fi
echo_docker_as_nonroot
exit 0
;;
gentoo)
if [ "$url" = "https://test.docker.com/" ]; then
# intentionally mixed spaces and tabs here -- tabs are stripped by "<<-'EOF'", spaces are kept in the output
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
You appear to be trying to install the latest nightly build in Gentoo.'
The portage tree should contain the latest stable release of Docker, but'
if you want something more recent, you can always use the live ebuild'
provided in the "docker" overlay available via layman. For more'
instructions, please see the following URL:'
https://github.com/tianon/docker-overlay#using-this-overlay'
After adding the "docker" overlay, you should be able to:'
emerge -av =app-emulation/docker-9999'
EOF
exit 1
fi
(
set -x
$sh_c 'sleep 3; emerge app-emulation/docker'
)
exit 0
;;
rancheros)
(
set -x
$sh_c "sleep 3; ros engine switch -f $(sudo ros engine list | grep ${docker_version} | head -n 1 | cut -d ' ' -f 2)"
)
exit 0
;;
esac
# intentionally mixed spaces and tabs here -- tabs are stripped by "<<-'EOF'", spaces are kept in the output
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
Either your platform is not easily detectable, is not supported by this
installer script (yet - PRs welcome! [hack/install.sh]), or does not yet have
a package for Docker. Please visit the following URL for more detailed
installation instructions:
https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/
EOF
exit 1
}
# wrapped up in a function so that we have some protection against only getting
# half the file during "curl | sh"
do_install
安装randcher
1、执行命令
sudo docker run -d --restart=unless-stopped -p 8080:8080 rancher/server
2、登陆验证,用户名,密码admin,admin
http://<ip>:8080
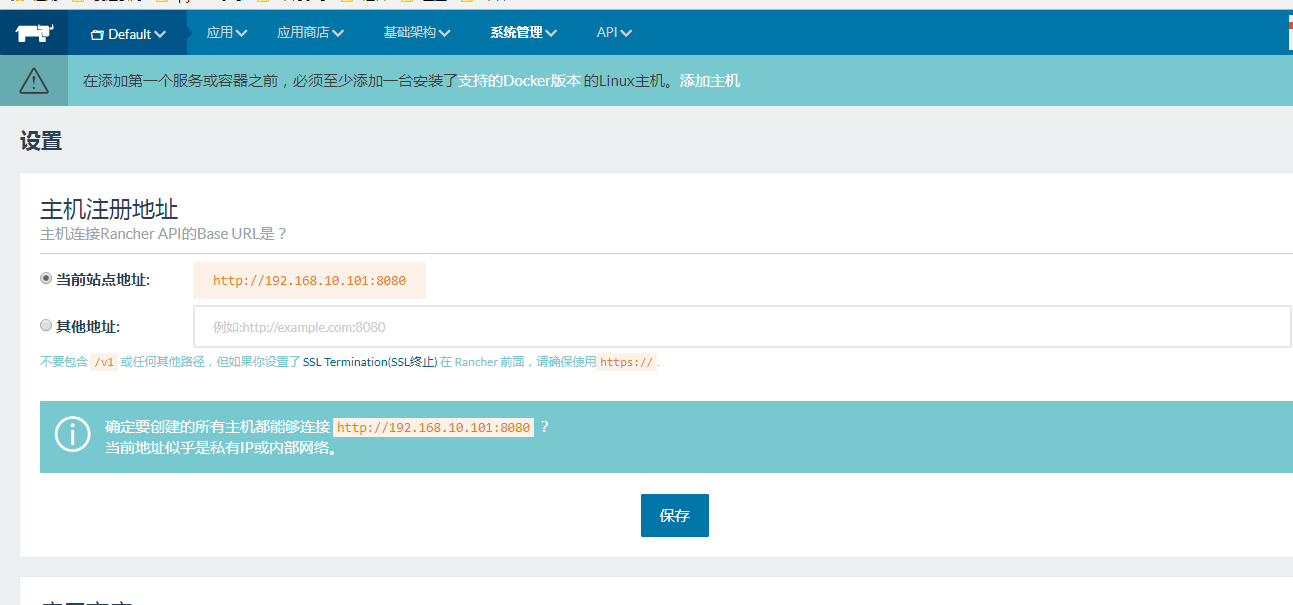
3、配置系统管理
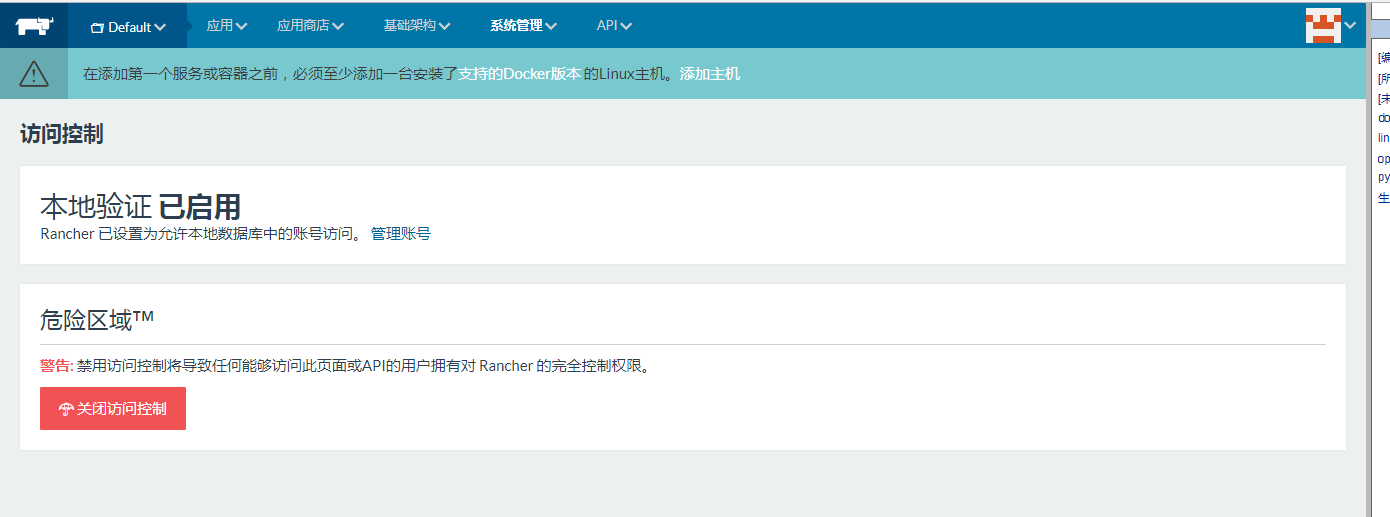
4、配置访问控制启用
5、添加环境配置
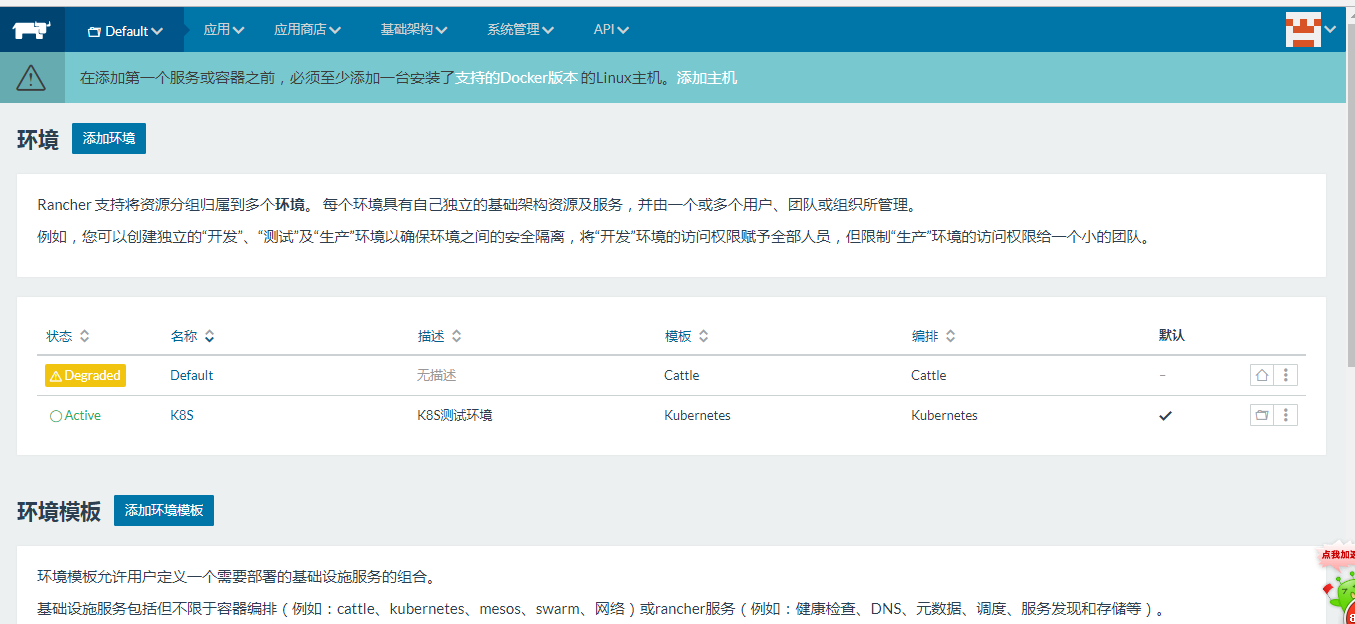
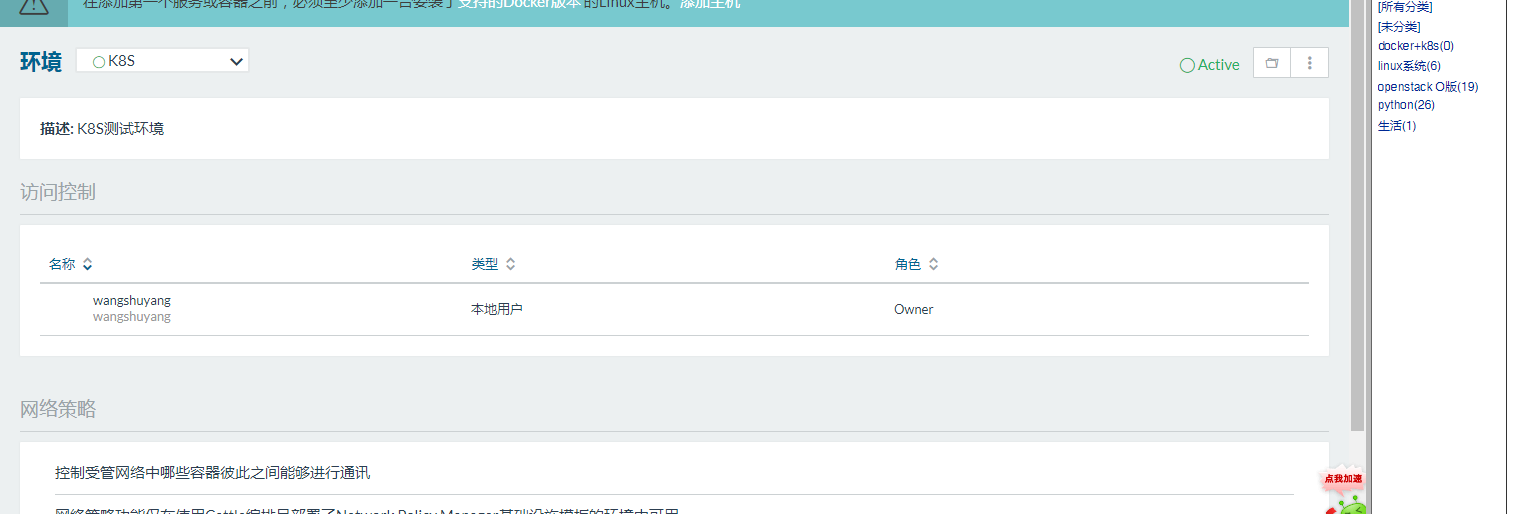
k8s集群创建
1、添加主机
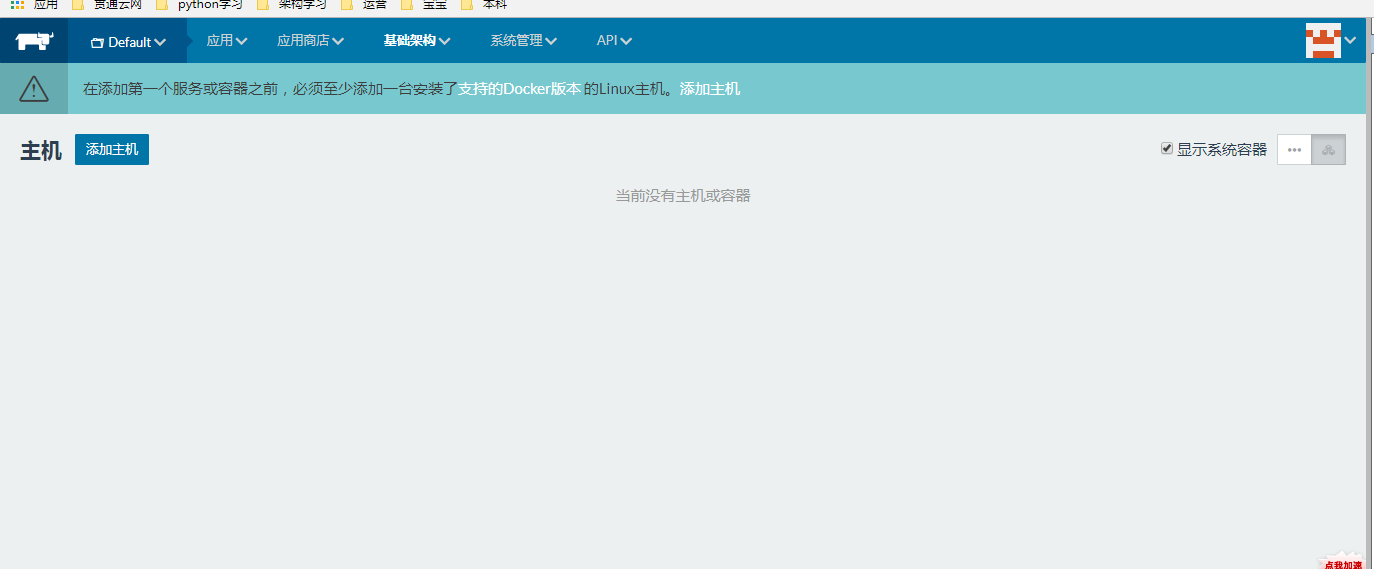
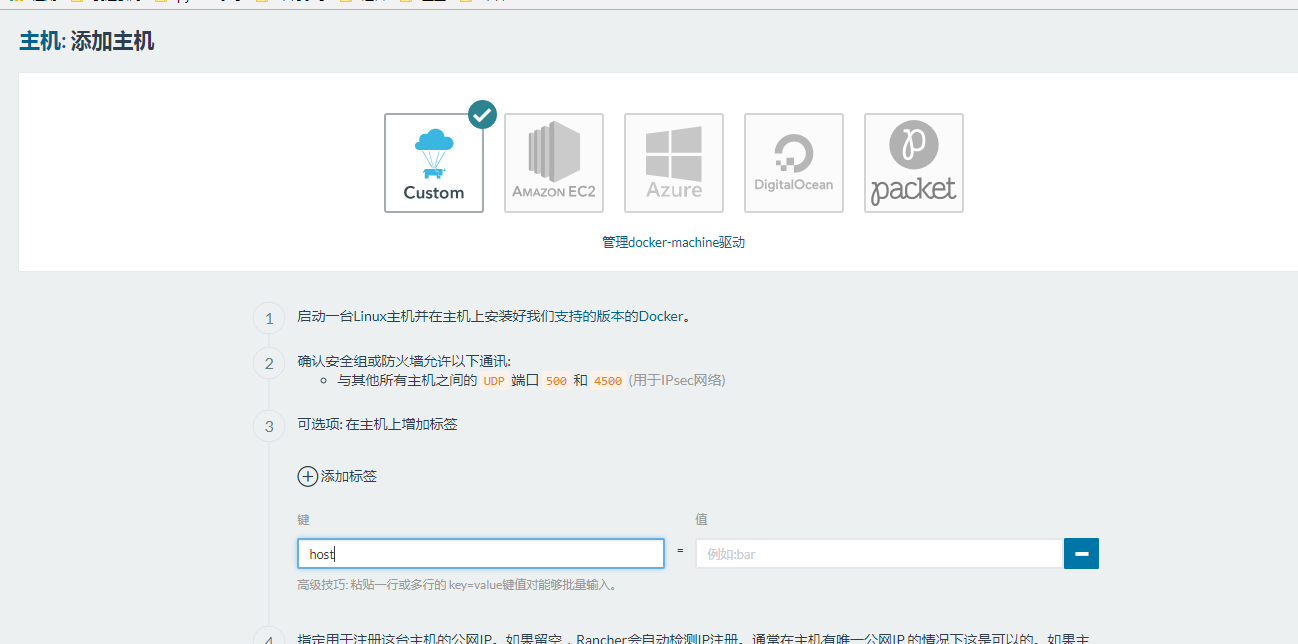
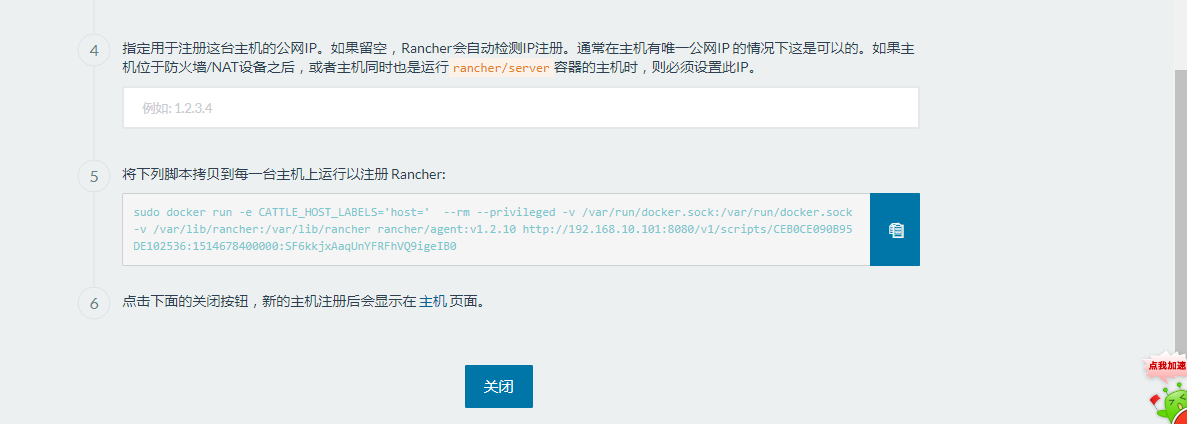
2、等待完成。
3、环境切换为K8s
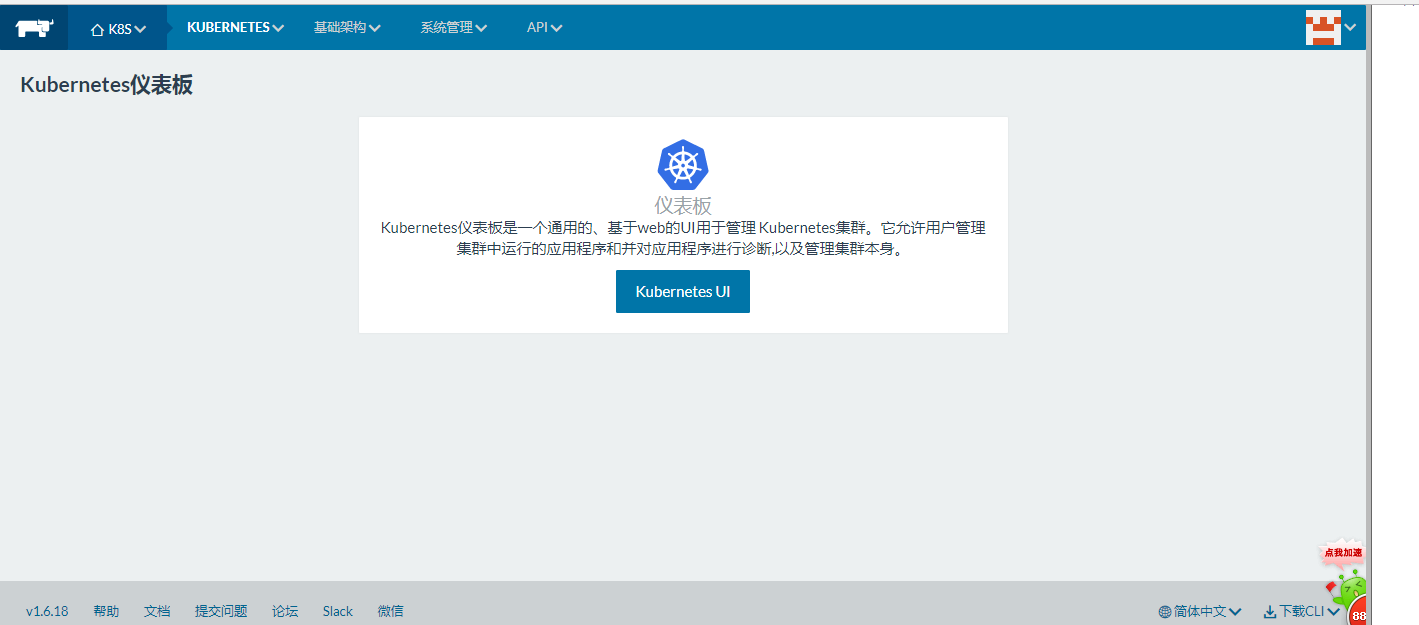
4、k8s服务