enable_shared_from_this是一个模板类,定义于头文件<memory>,其原型为:
template< class T > class enable_shared_from_this;
std::enable_shared_from_this 能让一个对象(假设其名为 t ,且已被一个 std::shared_ptr 对象 pt 管理)安全地生成其他额外的 std::shared_ptr 实例(假设名为 pt1, pt2, ... ) ,它们与 pt 共享对象 t 的所有权。
若一个类 T 继承 std::enable_shared_from_this<T> ,则会为该类 T 提供成员函数: shared_from_this 。 当 T 类型对象 t 被一个为名为 pt 的 std::shared_ptr<T> 类对象管理时,调用 T::shared_from_this 成员函数,将会返回一个新的 std::shared_ptr<T> 对象,它与 pt 共享 t 的所有权。
一.使用场合
当类A被share_ptr管理,且在类A的成员函数里需要把当前类对象作为参数传给其他函数时,就需要传递一个指向自身的share_ptr。
1.为何不直接传递this指针
使用智能指针的初衷就是为了方便资源管理,如果在某些地方使用智能指针,某些地方使用原始指针,很容易破坏智能指针的语义,从而产生各种错误。
2.可以直接传递share_ptr<this>么?
答案是不能,因为这样会造成2个非共享的share_ptr指向同一个对象,未增加引用计数导对象被析构两次。例如:
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
class Bad
{
public:
std::shared_ptr<Bad> getptr() {
return std::shared_ptr<Bad>(this);
}
~Bad() { std::cout << "Bad::~Bad() called" << std::endl; }
};
int main()
{
// 错误的示例,每个shared_ptr都认为自己是对象仅有的所有者
std::shared_ptr<Bad> bp1(new Bad());
std::shared_ptr<Bad> bp2 = bp1->getptr();
// 打印bp1和bp2的引用计数
std::cout << "bp1.use_count() = " << bp1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "bp2.use_count() = " << bp2.use_count() << std::endl;
} // Bad 对象将会被删除两次
输出结果如下:
当然,一个对象被删除两次会导致崩溃。
正确的实现如下:
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
struct Good : std::enable_shared_from_this<Good> // 注意:继承
{
public:
std::shared_ptr<Good> getptr() {
return shared_from_this();
}
~Good() { std::cout << "Good::~Good() called" << std::endl; }
};
int main()
{
// 大括号用于限制作用域,这样智能指针就能在system("pause")之前析构
{
std::shared_ptr<Good> gp1(new Good());
std::shared_ptr<Good> gp2 = gp1->getptr();
// 打印gp1和gp2的引用计数
std::cout << "gp1.use_count() = " << gp1.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << "gp2.use_count() = " << gp2.use_count() << std::endl;
}
system("pause");
}
输出结果如下:
二.为何会出现这种使用场合
因为在异步调用中,存在一个保活机制,异步函数执行的时间点我们是无法确定的,然而异步函数可能会使用到异步调用之前就存在的变量。为了保证该变量在异步函数执期间一直有效,我们可以传递一个指向自身的share_ptr给异步函数,这样在异步函数执行期间share_ptr所管理的对象就不会析构,所使用的变量也会一直有效了(保活)。
C++智能指针 weak_ptr
weak_ptr 是一种不控制对象生命周期的智能指针, 它指向一个 shared_ptr 管理的对象. 进行该对象的内存管理的是那个强引用的 shared_ptr. weak_ptr只是提供了对管理对象的一个访问手段.
weak_ptr 设计的目的是为配合 shared_ptr 而引入的一种智能指针来协助 shared_ptr 工作, 它只可以从一个 shared_ptr 或另一个 weak_ptr 对象构造, 它的构造和析构不会引起引用记数的增加或减少.
定义在 memory 文件中(非memory.h), 命名空间为 std.
weak_ptr 使用:
std::shared_ptr<int> sp(new int(10));
std::weak_ptr<int> wp(sp);
wp = sp;
printf("%d
", wp.use_count()); // 1
wp.reset();
printf("%d
", wp); // 0
// 检查 weak_ptr 内部对象的合法性.
if (std::shared_ptr<int> sp = wp.lock())
{
}
成员函数
weak_ptr 没有重载*和->但可以使用 lock 获得一个可用的 shared_ptr 对象. 注意, weak_ptr 在使用前需要检查合法性.
expired 用于检测所管理的对象是否已经释放, 如果已经释放, 返回 true; 否则返回 false.
lock 用于获取所管理的对象的强引用(shared_ptr). 如果 expired 为 true, 返回一个空的 shared_ptr; 否则返回一个 shared_ptr, 其内部对象指向与 weak_ptr 相同.
use_count 返回与 shared_ptr 共享的对象的引用计数.
reset 将 weak_ptr 置空.
weak_ptr 支持拷贝或赋值, 但不会影响对应的 shared_ptr 内部对象的计数.
使用 weak_ptr 解决 shared_ptr 因循环引有不能释放资源的问题
使用 shared_ptr 时, shared_ptr 为强引用, 如果存在循环引用, 将导致内存泄露. 而 weak_ptr 为弱引用, 可以避免此问题, 其原理:
对于弱引用来说, 当引用的对象活着的时候弱引用不一定存在. 仅仅是当它存在的时候的一个引用, 弱引用并不修改该对象的引用计数, 这意味这弱引用它并不对对象的内存进行管理.
weak_ptr 在功能上类似于普通指针, 然而一个比较大的区别是, 弱引用能检测到所管理的对象是否已经被释放, 从而避免访问非法内存。
注意: 虽然通过弱引用指针可以有效的解除循环引用, 但这种方式必须在程序员能预见会出现循环引用的情况下才能使用, 也可以是说这个仅仅是一种编译期的解决方案, 如果程序在运行过程中出现了循环引用, 还是会造成内存泄漏.
例子
#include <iostream> #include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp> using namespace std; using namespace boost; class BB; class AA { public: AA() { cout << "AA::AA() called" << endl; } ~AA() { cout << "AA::~AA() called" << endl; } shared_ptr<BB> m_bb_ptr; //! }; class BB { public: BB() { cout << "BB::BB() called" << endl; } ~BB() { cout << "BB::~BB() called" << endl; } shared_ptr<AA> m_aa_ptr; //! }; int main() { shared_ptr<AA> ptr_a (new AA); shared_ptr<BB> ptr_b ( new BB); cout << "ptr_a use_count: " << ptr_a.use_count() << endl; cout << "ptr_b use_count: " << ptr_b.use_count() << endl; //下面两句导致了AA与BB的循环引用,结果就是AA和BB对象都不会析构 ptr_a->m_bb_ptr = ptr_b; ptr_b->m_aa_ptr = ptr_a; cout << "ptr_a use_count: " << ptr_a.use_count() << endl; cout << "ptr_b use_count: " << ptr_b.use_count() << endl; }
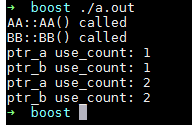
结果造成崩溃
可以看到由于AA和BB内部的shared_ptr各自保存了对方的一次引用,所以导致了ptr_a和ptr_b销毁的时候都认为内部保存的指针计数没有变成0,所以AA和BB的析构函数不会被调用。解决方法就是把一个shared_ptr替换成weak_ptr。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
class BB;
class AA
{
public:
AA() { cout << "AA::AA() called" << endl; }
~AA() { cout << "AA::~AA() called" << endl; }
weak_ptr<BB> m_bb_ptr; //!
};
class BB
{
public:
BB() { cout << "BB::BB() called" << endl; }
~BB() { cout << "BB::~BB() called" << endl; }
shared_ptr<AA> m_aa_ptr; //!
};
int main()
{
shared_ptr<AA> ptr_a (new AA);
shared_ptr<BB> ptr_b ( new BB);
cout << "ptr_a use_count: " << ptr_a.use_count() << endl;
cout << "ptr_b use_count: " << ptr_b.use_count() << endl;
//下面两句导致了AA与BB的循环引用,结果就是AA和BB对象都不会析构
ptr_a->m_bb_ptr = ptr_b;
ptr_b->m_aa_ptr = ptr_a;
cout << "ptr_a use_count: " << ptr_a.use_count() << endl;
cout << "ptr_b use_count: " << ptr_b.use_count() << endl;
}
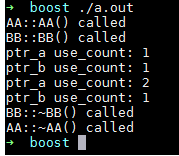
因此,如果代码比较复杂,我们在使用shared_ptr的时候其实很难知道是否会有循环引用,所以即使有weak_ptr来解决这个问题,我们也不太容易知道何时能用到,除非清楚非常清楚类之间的关系,所以,在我们编程的时候尽量使用一个指针控制生命周期(即使用shared_ptr),而多个指针控制访问(即使用weak_ptr)。