这篇题解原发于我的blog
据说这是一道模拟退火的题
那我也来做一做乱搞
模拟退火模板
t=初始温度;
while(t>eps)
{
tmp=从当前找到的最优转态随机找到的一个转态;
d=calc(now)-calc(ans);
if(d<0)
ans=tmp;
else if(exp(d/t)*RAND_MAX>rand())
ans=now;
t*=cold;
}
总之这个算法全靠(rp++)
理论上运气好的话你可以AK
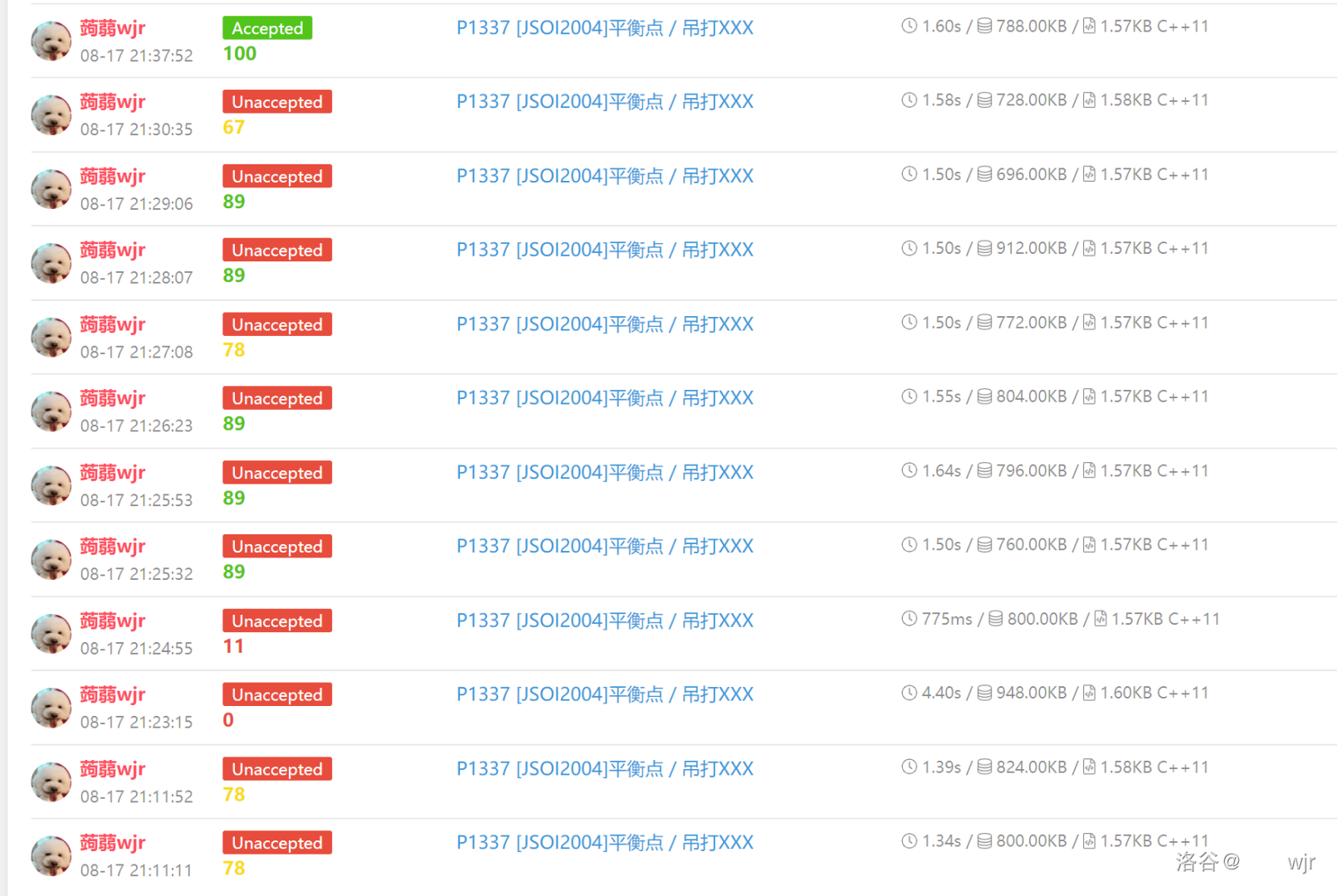
蒟蒻调试的代码不堪入目
接下来讨论此题:
当解最优时
所算的势能
[sum^{n}_{i=1}sqrt {(ans_x-x[i])^2+(ans_y-y[i])^2}*w[i]
]
一定尽量小
于是乎,就可以调模拟退火了
总之
模拟退火是一个极为玄学的算法,全靠(rp) !!!
最后贴上代码知道你们只看这个:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
inline void read(T&x)
{
x=0;
char s=getchar();
bool f=false;
while(!(s>='0'&&s<='9'))
{
if(s=='-')
f=true;
s=getchar();
}
while(s>='0'&&s<='9')
{
x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+s-'0';
s=getchar();
}
if(f)
x=(~x)+1;
return;
}
#define re register
#define temperature 1e5
#define cold 0.996
const int N=1e3+10;
int n;
double ans,ansx,ansy;
struct node
{
int x,y,w;
} a[N];
inline double calc(double x,double y)//计算势能,势能越小解越优
{
double energy=0.0;
for(re int i=1; i<=n; i++)
energy+=sqrt((x-a[i].x)*(x-a[i].x)+(y-a[i].y)*(y-a[i].y))*a[i].w;
return energy;
}
inline void solve()
{
double t=temperature;
while(t>1e-18)
{
double tmpx=ansx+(rand()+rand()-RAND_MAX)*t,tmpy=ansy+(rand()+rand()-RAND_MAX)*t;
double tmp=calc(tmpx,tmpy);
double d=tmp-ans;
if(d<0.0)
ans=tmp,ansx=tmpx,ansy=tmpy;
else if(exp(-d/t)*RAND_MAX>rand())
ansx=tmpx,ansy=tmpy;
t*=cold;
}
}
int main()
{
srand(rand());
read(n);
for(re int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
read(a[i].x),read(a[i].y),read(a[i].w);
ansx+=a[i].x;
ansy+=a[i].y;
}
ansx/=n,ansy/=n,ans=calc(ansx,ansy);//乱搞一个初始值
for(re int i=1; i<=4; i++)//多搞几次
solve();
printf("%.3lf %.3lf
",ansx,ansy);
return 0;
}
马蜂差评
建议大家请别忙着抄,因为管理员可能会加强数据,程序还要自己打,但是我的代码确实是(AC)代码。