(1)说明:当y为一系列离散值时,问题转为分类问题。比如我们要根据一个肿瘤的大小判断肿瘤是为良性还是为恶性。
(2)假设函数:如下图,如果使用线性的方程作为假设函数,肿瘤大小作为横坐标,是否为恶性作为纵坐标。当y值小于0.5时判定为良性,大于0.5时判定为恶性。但有两个缺点:①经过计算会出现y值远大于1的情况,这是不符合常理的,因为概率不会大于1 ②假如在x轴很远的位置有一个数据,会导致斜率变小,本来应为恶性的肿瘤却被判定为良性。

下图为Logisitic回归的假设函数,可以看出他是一个增函数,并且值区间为0~1开区间,符合我们得要求。如果最终得出值为0.7,我们可以说有70%得概率为恶心肿瘤。
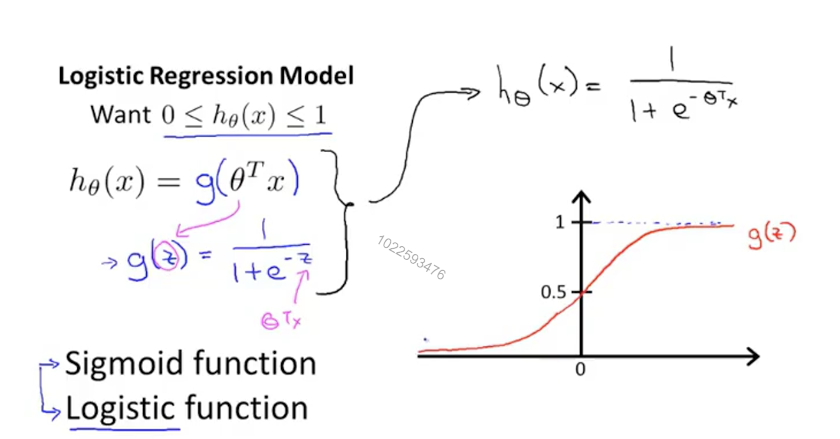
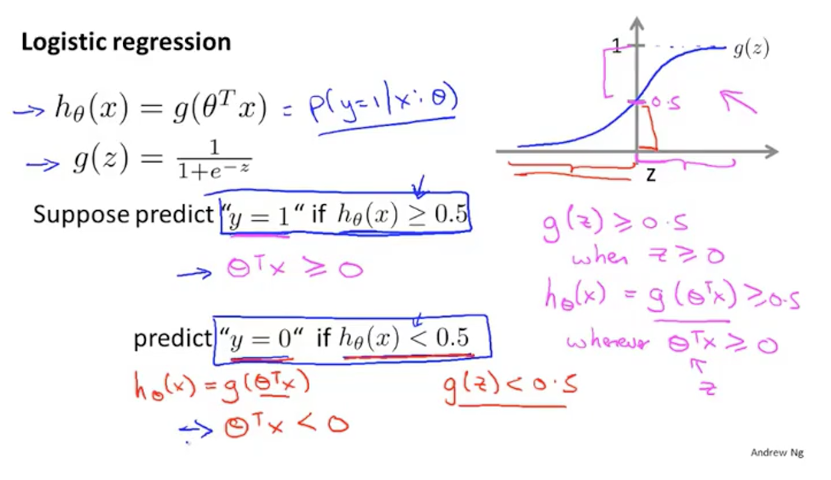
(3)决策边界:通过上面得图可以看出,当值小于0.5时判定为良性,大于0.5时判定为恶性。当函数值为0.5时,h(x)为0。也就是说h(x)大于0时判定为恶性,小于0时判定为良性(这里的h(x)就是之前线性回归的假设函数,就是theta * X)。这个边界值称为决策边界。
(4)代价函数:之前的代价函数并不是个凸函数,有很个局部最优解。用梯度下降的时候,选择不同的起始点可能得到不同的最优解。
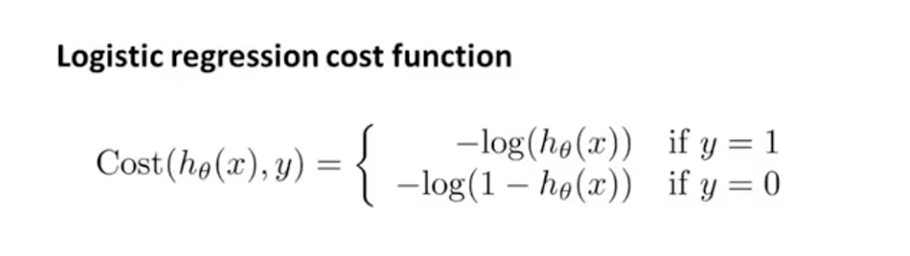
h(x)值域为0~1,所以两种情况的作用域都是0~1。y=1时是单调递减,在h(x)为1时趋近于0,h(x)为0时趋近于正无穷;y=0时单调递增,与上面相反。如果预测错误则返回一个很大的代价值用于惩罚。
为了方便计算要把两个结合到一起: - [y * (log(h(x))) + (1 - y) * log(1 - h(x))]
(5)求偏导之后

(6)代码:梯度下降之前也要进行特征缩放
1 #coding=utf-8 2 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import numpy as np 5 import math 6 import copy 7 np.set_printoptions(suppress=True) 8 9 def test(arr): 10 res = 0 11 for i in arr: 12 res += math.fabs(i) 13 return res 14 15 16 17 #读取文件 18 def readDate(path): 19 x_data = [] 20 y_data = [] 21 fd = open(path, 'r') 22 for line in fd.readlines(): 23 lineArr = line.strip().split() 24 x_data.append([1, lineArr[0], lineArr[1]]) 25 y_data.append([lineArr[2]]) 26 27 x_data = np.array(x_data).astype(np.float) 28 y_data = np.array(y_data).astype(np.float) 29 return x_data, y_data 30 31 #sigmoid 32 def h(x_data, p): 33 plus = np.dot(x_data, p) 34 for i in range(len(plus)): 35 plus[i][0] = 1 / (1 + math.exp(-plus[i][0])) 36 return plus 37 38 #特征缩放 39 def scale(arr): 40 param = [] 41 for i in range(1, arr.shape[1]): 42 col = arr[:,i] 43 mean = np.mean(col) 44 std = np.std(col) 45 46 std = 1 if std == 0 else std 47 param.insert(i, {'mean':mean, 'std':std}) 48 for j in range(0, len(col)): 49 arr[j][i] = (col[j] - mean) / std 50 return arr, param 51 52 53 54 def J(x_data, y_data, p, a): 55 global m 56 sub = h(x_data, p) - y_data 57 deviation = np.dot(x_data.T, sub) 58 return a / m * deviation 59 60 #整理参数 61 def build(p, param): 62 f = 1 #常数项 63 for i in range(1, len(p)): 64 f -= param[i - 1]['mean'] / param[i - 1]['std'] * p[i][0] 65 p[i] = format(p[i][0] / param[i - 1]['std'], '0.2f') 66 67 p[0] = format(f + p[0][0], '0.2f') 68 return p 69 70 71 #画图 72 def plotPoint(x_data, y_data, p): 73 xcordt = [] 74 ycordt = [] 75 xcordf = [] 76 ycordf = [] 77 n = len(y_data) 78 for i in range(n): 79 if int(y_data[i][0]) == 1: 80 xcordt.append(x_data[i,1]) 81 ycordt.append(x_data[i,2]) 82 else: 83 xcordf.append(x_data[i, 1]) 84 ycordf.append(x_data[i, 2]) 85 86 fig = plt.figure() 87 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 88 ax.scatter(xcordt, ycordt, s=30, c='red', marker='s') 89 ax.scatter(xcordf, ycordf, s=30, c='green') 90 91 #函数曲线 92 x = np.arange(-3, 3, 0.1) 93 y = -(p[0][0] + p[1][0] * x) / p[2][0] 94 ax.plot(x,y) 95 plt.show() 96 97 98 if __name__ == '__main__': 99 path = 'testSet.txt' 100 a = 0.5 101 x_data, y_data = readDate(path) 102 x_bak = copy.deepcopy(x_data) 103 x_data, param = scale(x_data) 104 105 m = len(x_data) 106 p = np.zeros([len(x_data[0]), 1]) 107 108 step = 2000 109 for i in range(step): 110 j = J(x_data, y_data, p, a) 111 p -= j 112 113 114 p = build(p, param) 115 plotPoint(x_bak, y_data, p)