Linux 的 touch 命令用来修改文件时间戳,或者新建一个不存在的文件,使用方式如下:
touch [-acm][-r ref_file(参照文件)|-t time(时间值)] file(文件名)
本实验基于C语言实现Linux touch命令的 [-acm]选项。
注:
touch file1.txt 更新 file1.txt 的存取和修改时间
touch -a file1.txt 改变 file1.txt 的读取时间记录
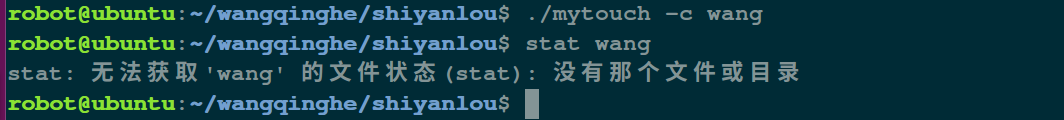
touch -c file1.txt 如果 file1.txt 不存在,不创建文件
touch -m file1.txt 改变 file1.txt 的修改时间记录
touch命令就是修改文件或者目录的时间属性,包括存取时间和更改时间。若文件不存在,系统会建立一个新的文件。
getopt函数:解决参数处理的函数。
//头文件 #include<unistd.h> //函数原型: int getopt(int argc,char * const argv[ ],const char * optstring);
函数介绍:分析命令参数。
返回值:参数字符。
open函数:
函数 open 是 UNIX 系统的系统调用函数,区别于 C 语言库函数 fopen。
//头文件: #include<fcntl.h> //函数原型 int open(constchar*pathname, int flags); int open(constchar*pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
函数作用:打开和创建文件。
返回值:成功返回文件描述符,失败返回-1。
参数说明:
对于 open 函数来说,第三个参数仅当创建新文件时(即使用了 O_CREAT 时)才使用,用于指定文件的访问权限位(access permission bits)。pathname 是待打开/创建文件的 POSIX 路径(如/home/user/a.cpp);flags 用于指定文件的打开/创建模式,这个参数可由以下常量(定义于fcntl.h)通过逻辑位或逻辑构成。
O_RDONLY 只读模式
O_WRONLY 只写模式
O_RDWR 读写模式
参数 mode 则有下列数种组合, 只有在建立新文件时才会生效, 此外真正建文件时的权限会受到 umask 值所影响, 因此该文件权限应该为 (mode-umaks).
S_IRWXU 00700 权限, 代表该文件所有者具有可读、可写及可执行的权限.
S_IRUSR 或S_IREAD, 00400 权限, 代表该文件所有者具有可读取的权限.
S_IWUSR 或S_IWRITE, 00200 权限, 代表该文件所有者具有可写入的权限.
S_IXUSR 或S_IEXEC, 00100 权限, 代表该文件所有者具有可执行的权限.
S_IRWXG 00070 权限, 代表该文件用户组具有可读、可写及可执行的权限.
S_IRGRP 00040 权限, 代表该文件用户组具有可读的权限.
S_IWGRP 00020 权限, 代表该文件用户组具有可写入的权限.
S_IXGRP 00010 权限, 代表该文件用户组具有可执行的权限.
S_IRWXO 00007 权限, 代表其他用户具有可读、可写及可执行的权限.
S_IROTH 00004 权限, 代表其他用户具有可读的权限
S_IWOTH 00002 权限, 代表其他用户具有可写入的权限.
S_IXOTH 00001 权限, 代表其他用户具有可执行的权限.
函数utimensat
//头文件 #include<sys/stat.h> //函数原型 int utimensat(int dirfd, const char *pathname,const struct timespec times[2], intflags);
作用:utimensat 是以纳秒级的精度改变文件的时间戳。utimensat()通过文件的路径(pathname)获得文件。
这个系统调用函数都是通过一个时间数组 times 来改变时间戳的,times[0] 修改最后一次访问的时间(access time),times[1] 修改最后修改的时间 (modify time)。该时间数组是由秒和纳秒两个部分组成,数据结构如下:
特别注意:
当 times[x].tv_sec = UTIME_OMIT; 相应的时间戳不变,times[x].tv_sec = UTIME_NOW; 相应的时间戳编程当前时间。
实例:
#include<stdio.h> #include<getopt.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<time.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<stdbool.h> #include<sys/time.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #define CH_ATIME 1 #define CH_MTIME 2 //定义创建文件时的模式,此处对用户,组,其他设置的权限都是可读可写。 #define MODE_RW_UGO (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH |S_IWOTH) //标志文件access time 和 modify time的改变情况 static int change_times; // 如果有(-c)选项,并且不存在命令行中输入的文件名,则不创建 static bool no_create; //当设置新的access time 和 modify time的时候使用 static struct timespec newtime[2]; //mytouch命令核心的核心模块,用于创建或者更新文件的时间戳。 static bool mytouch(const char *file) { bool ok; int fd = -1; if (!no_create) { fd = open(file, O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, MODE_RW_UGO); } //在主函数中,如果没有检测到(-a)(-m),则change_times == (CH_ATIME | CH_MTIME), 否则按照选项只用改变其中一个时间戳。 if (change_times !=(CH_ATIME | CH_MTIME)) { //只设定其中一个时间值。 /*如果change_times == CH_MTIME,即(-m),将对应的修改access time 的timespec结构的tv_nsec设置为UTIME_OMIT;参考utimensat函数的用法*/ if (change_times == CH_MTIME) { newtime[0].tv_nsec = UTIME_OMIT; } /*如果change_times == CH_MTIME,即(-a),将对应的修改modify time 的timespec结构的tv_nsec设置为UTIME_OMIT;参考utimensat函数的用法*/ else { //AT_FDCWD表示当前工作目录。 newtime[1].tv_nsec = UTIME_OMIT; } } ok = (utimensat(AT_FDCWD, file, newtime, 0) == 0); return true; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int c; bool ok = true; change_times = 0; no_create = false; //从命令行中得到命令的选项,即以'-'开头的参数。目前只支持三种选型-a, -c, -m。 while ((c = getopt(argc, argv, "acm")) != -1) { switch(c) { case 'a': change_times |= CH_ATIME; break; case 'c': no_create = true; break; case 'm': change_times |= CH_MTIME; break; default: printf("fault option!"); } } if (change_times == 0) { change_times =CH_ATIME | CH_MTIME; } newtime[0].tv_nsec = UTIME_NOW; newtime[1].tv_nsec = UTIME_NOW; //如果optind == argc,代表少输入文件名字 if (optind == argc) { printf("missing file operand "); } //针对多个文件名字调用mytouch函数 for (; optind < argc; ++optind) { ok &= mytouch(argv[optind]); } exit(ok ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE); }
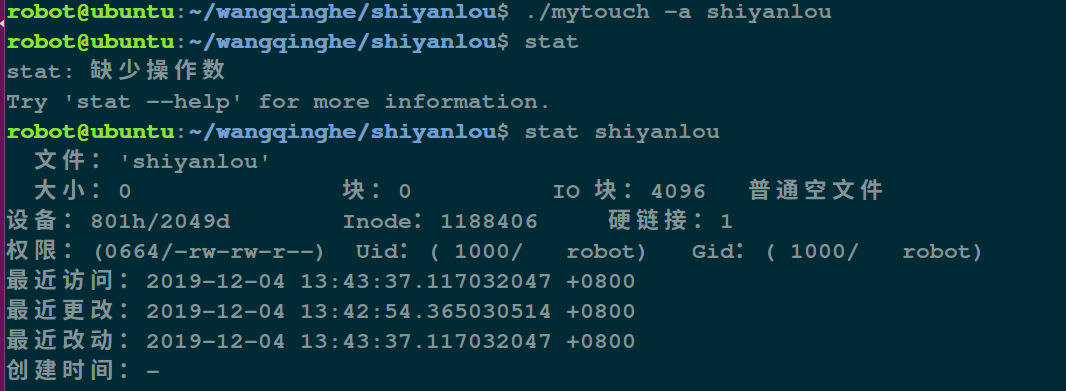
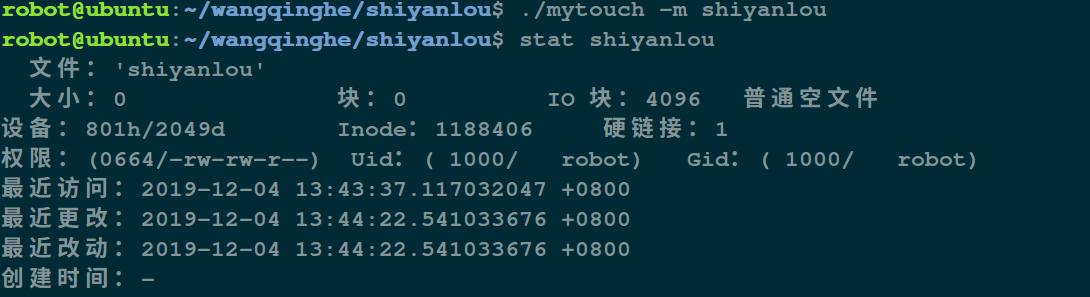
运行结果:
touch 创建文件

touch -a 命令
touch -m
touch -c