Python语言支持以下类型的运算符:
- l 算术运算符
- l 比较运算符
- l 赋值运算符
- l 逻辑运算符
- l 位运算符
- l 成员运算符
- l 身份运算符
- l 运算符优先级
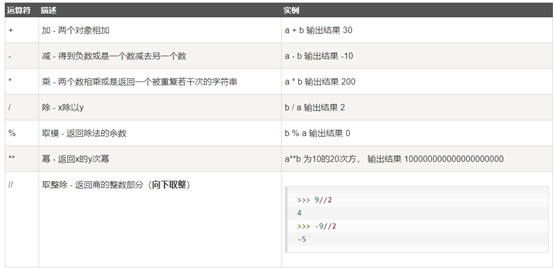
Python算术运算符
/*** arithmetic.py ***/ a = 21 b = 10 c = 0 c = a + b print "1 - c is : ", c c = a - b print "2 - c is : ", c c = a * b print "3 - c is : ", c c = a / b print "4 - c is : ", c c = a % b print "5 - c is : ", c #change the value of a,b,c a = 2 b = 3 c = a ** b print "6 - c is : ", c a = 10 b = 5 c = a // b print "7 - c is : ", c
运行结果:
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ vim arithmetic.py
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ python arithmetic.py
1 - c is : 31
2 - c is : 11
3 - c is : 210
4 - c is : 2
5 - c is : 1
6 - c is : 8
7 - c is : 2
注意:在python2.x里,整数除以整数,只能的到整数,如果想要得到小数部分,把其中一个数改为浮点数即可
/*** inter.py ***/ print 1/2 print 1.0/2 print 1/float(2)
运行结果:
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ vim inter.py
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ python inter.py
0
0.5
0.5
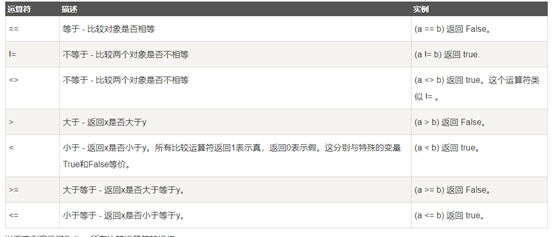
Python比较运算符

/*** comparsion.py ****/ a = 21 b = 10 c = 0 if a == b : print "a == b" else: print "a no == b" if a != b : print "a != b" else: print "a no != b" if a <> b : print "a <> b" else : print "a no <> b" if a < b : print "a < b" else : print "a no < b" if a > b : print "a > b" else : print "a no > b" a = 5 b = 20 if a <= b : print "a <= b" else : print "a no <= b" if b >= a : print "b <= a" else : print "b no <= a"
运行结果:
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ python comparsion.py
a no == b
a != b
a <> b
a no < b
a > b
a <= b
b <= a
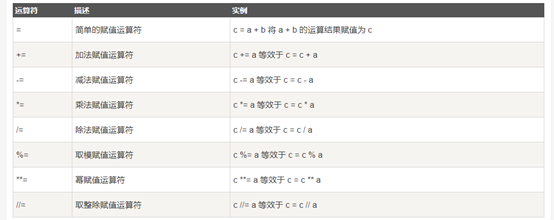
Python赋值运算符:
/*** assignment.py ***/ a = 21 b = 10 c = 0 c = a + b print "a + b = " , c c += a print "a + b = " , c c *= a print "a + b = " , c c /= a print "a + b = " , c c = 2 c %= a print "a + b = " , c c ** a print "a + b = " , c c //= a print "a + b = " , c
运行结果:
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ python assignment.py
a + b = 31
a + b = 52
a + b = 1092
a + b = 52
a + b = 2
a + b = 2
a + b = 0
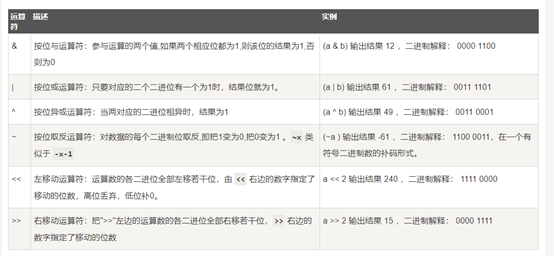
Python位运算符
Python逻辑运算符
按位运算符把数字看作二进制进行计算的。python中按位运算法则如下:
/*** bit.py ***/ a = 60 b = 13 print a,b print a & b print a | b print a ^ b print ~a print a << 2 print b >> 2
运行结果:
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ python bit.py
60 13
12
61
49
-61
240
3
Python逻辑运算符
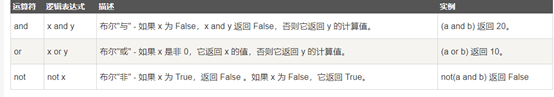
/*** bool.py ***/ a = 10 b = 20 if a and b : print "a and b is true" else : print "a and b is not true" if a or b : print "a or b is true" else : print "a or b not true" a = 0 if a and b : print "a and b is true" else : print "a and b is not true" if a or b : print "a or b is true" else : print "a or b not true" if not(a and b) : print "a and b all true" else : print "a and b not all true"
运行结果:
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ python bool.py
a and b is true
a or b is true
a and b is not true
a or b is true
a and b all true
Python成员运算符
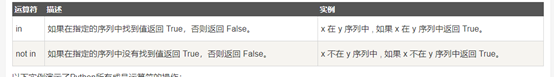
/*** member.py ***/ a = 10 b = 20 list = [1,2,3,4,5]; if ( a in list ) : print "a in list" else : print "b not in list" if(b not in list): print "b not in list" else : print "b on list" a = 2 if ( a in list ) : print "a in list" else : print "b not in list"
运行结果:
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ python member.py
b not in list
b not in list
a in list
Python身份运算符:
身份运算符用于比较两个对象的存储单元
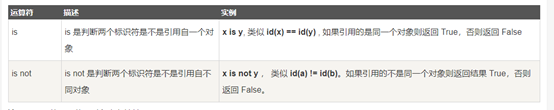
注:id()函数用于获取对象内存地址
/*** id.py ***/ a = 20 b = 20 if( a is b): print "a and b are equal id" else: print "a and b are not equal id" if ( a is not b): print "a is not b" else: print "a is b" b = 30 if( a is b): print "a and b are equal id" else: print "a and b are not equal id" if ( a is not b): print "a is not b" else: print "a is b"
运行结果:
robot@ubuntu:~/wangqinghe/python/20190821$ python id.py
a and b are equal id
a is b
a and b are not equal id
a is not b
is 和 == 的区别:
is是用于判断两个变量引用对象是否是同一个(同一块内存空间),==用于判断引用变量的值是否相同。
Python运算符优先级
|
运算符 |
描述 |
|
** |
指数(最高优先级) |
|
~、+、 |
按位反转、一元加号、和减号(最后两个的方法名位+@和-@) |
|
*/%// |
乘、除、取模、取整除 |
|
+- |
加法减法 |
|
>> << |
右移、左移 |
|
& |
与运算 |
|
^| |
异或、或 |
|
<= 、 <、> 、 >= |
比较运算符 |
|
<> 、 == 、 != |
等于运算符 |
|
= %= /= //= -= += *= **= |
赋值运算符 |
|
is is not |
身份运算符 |
|
in not in |
成员运算符 |
|
not and or |
逻辑运算符 |