最小生成树有两个算法Kruskal算法和prime算法
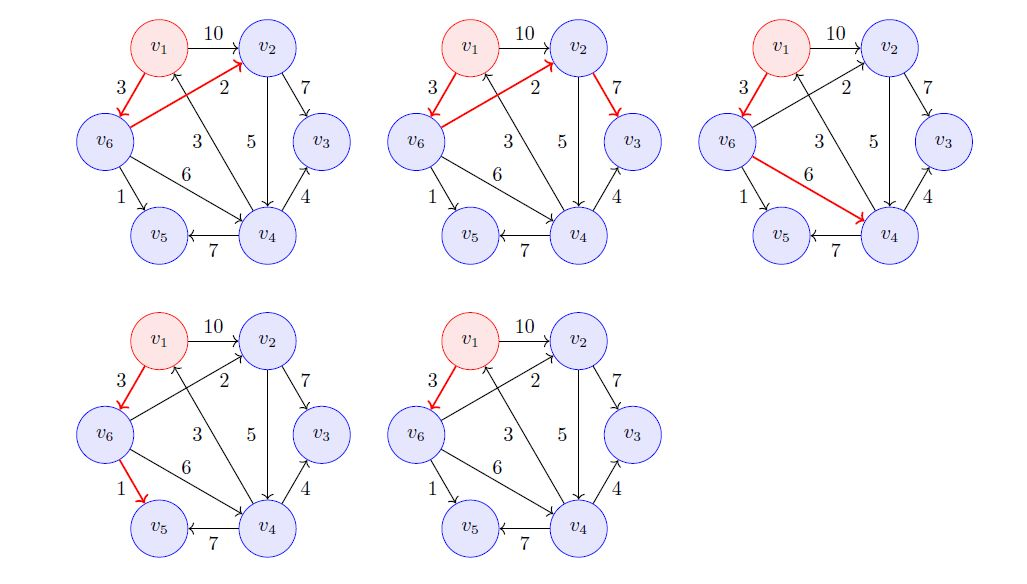
还是借用上一篇的图
public class MinimalTree { public static void main(String[] args) { WeightGraph weightGraph = buildGraph(); List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> weightEdges = buildKruskalTree(weightGraph); System.out.println("tree:"); for (WeightEdge<String, String, Integer> weightEdge : weightEdges) { System.out.println(weightEdge); } List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> weightEdges1 = buildPrimeTree(weightGraph); System.out.println("prime:"); for (WeightEdge<String, String, Integer> weightEdge : weightEdges1) { System.out.println(weightEdge); } } /** * 最小生成树之prime算法 * 基本思路: * 1.从图的所有顶点随机取出一个node,加入已知集合U,那其他节点加入未知集合V,U+V=所有节点 * 2.遍历所有已知边,找到U和V之间最短的一条,加入结果边集,同时将此边联通的未知节点从V中移动到U * 3.继续循环,指定V的集合为空 * * @param weightGraph * @return */ public static List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> buildPrimeTree(WeightGraph weightGraph) { List<String> nodes = weightGraph.getNodes(); List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> edgeList = weightGraph.getEdgeList(); //结果list List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> miniEdges = Lists.newArrayList(); //初始节点 String s = nodes.get(0); //初始化已知集合和未知集合 Set<String> knowSet = Sets.newHashSet(s); Set<String> notKnowSet = Sets.newHashSet(); for (String node : nodes) { if (!knowSet.contains(node)) { notKnowSet.add(node); } } while (!notKnowSet.isEmpty()) { WeightEdge<String, String, Integer> miniEdge = null; Integer shortest = Integer.MAX_VALUE; String newNode = null; for (WeightEdge<String, String, Integer> edge : edgeList) { String start = edge.getStart(); String end = edge.getEnd(); Integer weight = edge.getWeight(); if ((knowSet.contains(start) && notKnowSet.contains(end)) || (knowSet.contains(end) && notKnowSet.contains(start))) { if (weight < shortest) { shortest = weight; miniEdge = edge; if (knowSet.contains(start)) { newNode = end; } else { newNode = start; } } } } //更新结果边集合 miniEdges.add(miniEdge); //更新已知节点和未知节点集合 knowSet.add(newNode); notKnowSet.remove(newNode); } return miniEdges; } /** * 最小生成树之Kruskal算法 * 基本逻辑: * 1.将所有边加入到一个以边长作为优先要素的优先队列 * 2.初始化最小生成树的边数count为0,从优先队列取出一条边,判断边的两个端点是否连通 * 3.如果不连通,则将这条边加入到生成树的边集合,且count=count+1, * (如果两个节点已经联通,则再加就会构成环路,就不是最小生成树了) * 4.继续循环,知道count的数量=顶点数-1 * @param weightGraph * @return */ public static List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> buildKruskalTree(WeightGraph weightGraph) { List<String> nodes = weightGraph.getNodes(); int size = nodes.size(); List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> edgeList = weightGraph.getEdgeList(); List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> miniEdges = Lists.newArrayList(); //构造以权重为优先级的优先队列,这样可以方便从头部获取最短边 PriorityQueue<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparing(WeightEdge::getWeight)); priorityQueue.addAll(edgeList); int count = 0; //最小生成树的边一定等于顶点数-1 while (count < size - 1) { WeightEdge<String, String, Integer> edge = priorityQueue.remove(); String start = edge.getStart(); String end = edge.getEnd(); //如果start和end之前就不联通,则加入 if (!isLink(miniEdges, start, end)) { miniEdges.add(edge); count += 1; } } return miniEdges; } /** * 判断两个节点是否是联通的 * 最初的联通图是一个空map,说明没有节点是联通的 * 所以联通的条件是两个节点都在连通图中,且key相同 * * @param node1 * @param node2 * @return */ public static boolean isLink(List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> miniEdges, String node1, String node2) { System.out.println("linkMap:"); Multimap<String, String> linkMap = getLinkMap(miniEdges); System.out.println(linkMap); if (linkMap.containsValue(node1) && linkMap.containsValue(node2)) { String k1 = getKeyByValue(linkMap, node1); String k2 = getKeyByValue(linkMap, node2); if (k1.equals(k2)) { return true; } } return false; } /** * 通过图的边构造图的联通map,所有联通的节点放在一个key的value中 * * @param miniEdges * @return */ public static Multimap<String, String> getLinkMap(List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> miniEdges) { Multimap<String, String> map = HashMultimap.create(); for (WeightEdge<String, String, Integer> s : miniEdges) { String from = s.getStart(); String to = s.getEnd(); //默认from、to都不存在 boolean fromPresent = false; boolean toPresent = false; if (isPresent(map, from)) { fromPresent = true; } if (isPresent(map, to)) { toPresent = true; } //from/to都不存在,最简单,from做key,将from和to放value里 if (!fromPresent && !toPresent) { map.put(from, from); map.put(from, to); //from存在,to不存在,要区分from是key还是value } else if (!toPresent) { boolean inKey = map.containsKey(from); if (inKey) { map.put(from, to); } else { String valKey = getKeyByValue(map, from); map.put(valKey, to); } //to存在,from不存在,也要区分to是key还是value } else if (!fromPresent) { boolean toInKey = map.containsKey(to); if (toInKey) { map.put(to, from); } else { String valKey = getKeyByValue(map, to); map.put(valKey, from); } } //剩下最后一种可能,from/to都存在,那就不需要处理了 } return map; } /** * 判断一个元素是否存在于map中,需要判断两种情况 * * @param map * @param key * @return */ public static boolean isPresent(Multimap<String, String> map, String key) { return map.containsKey(key) || map.containsValue(key); } /** * 从map中反向查找value对应的key,前提条件是value存在于map中 * * @param map * @param val * @return */ public static String getKeyByValue(Multimap<String, String> map, String val) { Set<String> keySet = map.keySet(); for (String s : keySet) { Collection<String> values = map.get(s); if (values.contains(val)) { return s; } } return null; } }
两个算法的输出是一样的:
tree: WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v6, end=v5, weight=1) WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v6, end=v2, weight=2) WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v4, end=v1, weight=3) WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v1, end=v6, weight=3) WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v4, end=v3, weight=4) prime: WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v1, end=v6, weight=3) WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v6, end=v5, weight=1) WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v6, end=v2, weight=2) WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v4, end=v1, weight=3) WeightGraph.WeightEdge(start=v4, end=v3, weight=4)