参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/129373740
《数据结构与算法-python描述》作者:裘宗燕
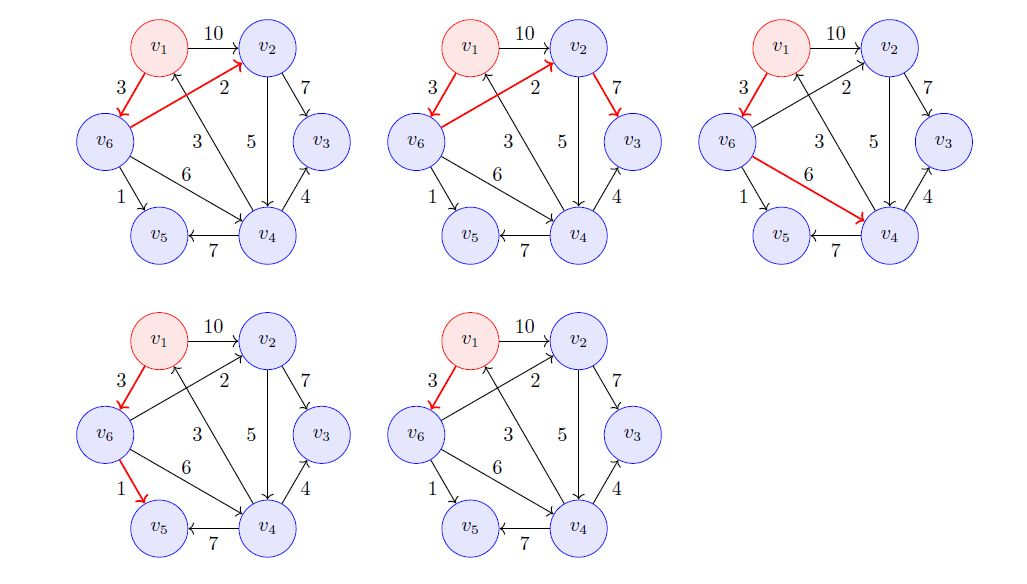
以上是原图,求V1到其余所有节点的最短路径。参考了裘宗燕教授的数据结构与算法
并未完全理解其精髓,暂且记录,后面再慢慢理解
@Data @AllArgsConstructor public class WeightGraph { private List<String> nodes; private List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> edgeList; public static void main(String[] args) { WeightGraph weightGraph = buildGraph(); Map<String, Path<String, Integer>> shortest = findShortest(weightGraph); for (Map.Entry<String, Path<String, Integer>> entry : shortest.entrySet()) { System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue().getLen()); } } /** * 初始化图结构 * * @return */ public static WeightGraph buildGraph() { List<String> node = Lists.newArrayList("v1", "v2", "v3", "v4", "v5", "v6"); List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> edge = Lists.newArrayList(); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v1", "v2", 10)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v2", "v3", 7)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v4", "v3", 4)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v4", "v5", 7)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v6", "v5", 1)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v1", "v6", 3)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v6", "v2", 2)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v4", "v1", 3)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v2", "v4", 5)); edge.add(new WeightEdge<>("v6", "v4", 6)); return new WeightGraph(node, edge); } public static Map<String, Path<String, Integer>> findShortest(WeightGraph weightGraph) { List<WeightEdge<String, String, Integer>> edgeList = weightGraph.getEdgeList(); List<String> nodes = weightGraph.getNodes(); //以路径边长做key的优先级队列 PriorityQueue<Triple<Integer, String, String>> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparing(Triple::getLen)); //初始化队列 //表示原点v1,经中间节点v1,到v1的距离是0 queue.add(new Triple<>(0, "v1", "v1")); //结果map Map<String, Path<String, Integer>> paths = new HashMap<>(); //paths初始为null,用于存储最终结果 int size = nodes.size(); for (String node : nodes) { paths.put(node, null); } int count = 0; while (count < size && !queue.isEmpty()) { //长度、中介、终点 Triple<Integer, String, String> triple = queue.remove(); String end = triple.getEnd(); //如果end已经找到,则跳过本次循环 if (paths.get(end) != null) { continue; } //如果end还为找到最短路径 Integer len = triple.getLen(); //因为从优先队列头部取出,因此<end,len>就是当前已知的最短路径 //第一次执行("v1",new Path("v1",0)),v1经v1到v1的最短距离是0 paths.put(end, new Path<>(triple.getMiddle(), len)); //遍历所有以新得到的最短路径节点做start的边,扩展可达的边界 for (WeightEdge<String, String, Integer> edge : edgeList) { if (edge.getStart().equals(end)) { String newEnd = edge.getEnd(); Integer w = edge.getWeight(); //如果新目标还未确定最短路径,则将end做中介,原end的len+weight作为新的len,并加入优先queue //优先队列保证经过这轮循环,得到了最新的最短路径节点 if (paths.get(newEnd) == null) { queue.add(new Triple<>(len + w, end, newEnd)); } } } count += 1; } return paths; } } /** * 带权重的边 * * @param <S> * @param <E> * @param <W> */ @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor class WeightEdge<S, E, W> { private S start; private E end; private W weight; } /** * 优先队列元素三元组,主要用于获取目标节点的最短路径 * * @param <L> length * @param <M> 中介点 * @param <E> 目标点 */ @Data @AllArgsConstructor class Triple<L, M, E> { private L len; private M middle; private E end; } /** * paths的元素格式 * * @param <M> 中介点 * @param <L> 最终最短路径 */ @Data @AllArgsConstructor class Path<M, L> { private M middle; private L len; }
输出:
v6:3 v1:0 v2:5 v3:12 v4:9 v5:4