Lock:
getHoldCount(): 获取当前线程调用lock()方法的次数
1 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 2 3 public class Service { 4 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 5 6 public void serviceMethod1() { 7 try { 8 lock.lock(); 9 10 System.out.println("serviceMethod getHoldCount=" + lock.getHoldCount()); 11 serviceMethod2(); 12 } finally { 13 lock.unlock(); 14 } 15 } 16 17 private void serviceMethod2() { 18 try { 19 lock.lock(); 20 System.out.println("serviceMethod getHoldCount=" + lock.getHoldCount()); 21 } finally { 22 lock.unlock(); 23 } 24 } 25 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 */ 4 public class Run { 5 6 /** 7 * getHoldCount() 查询当前线程保持此锁定的个数,即调用lock()方法的次数 8 */ 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Service service = new Service(); 11 service.serviceMethod1(); 12 } 13 }
运行结果如下:
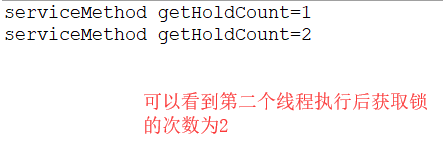
getQueueLength():获取等待获取锁的线程估计数
1 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 2 3 public class Service { 4 5 public ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 6 7 public void serviceMethod() { 8 try { 9 lock.lock(); 10 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "进入方法"); 11 Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 }finally { 15 lock.unlock(); 16 } 17 } 18 }
1 /** 2 * getQueueLength()测试类 3 */ 4 public class Run { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 final Service service = new Service(); 8 9 Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 service.serviceMethod(); 13 } 14 }; 15 16 Thread[] threads = new Thread[10]; 17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 18 threads[i] = new Thread(runnable); 19 } 20 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 21 threads[i].start(); 22 } 23 24 try { 25 Thread.sleep(2000); 26 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 System.err.println("有" + service.lock.getQueueLength() + "在等待获取锁" ); 30 } 31 }
运行结果如下:

getWaitQueueLength():获取等待与此锁定相关的给定条件的condition的线程估计数(也就是获取同一个锁的线程中于condition相关的线程数)
1 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; 2 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 3 4 public class Service { 5 6 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 7 private Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 8 9 public void waitMethod() { 10 try { 11 lock.lock(); 12 condition.await(); 13 System.out.println("被唤醒的线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 }finally { 17 lock.unlock(); 18 } 19 } 20 21 public void notityMethod() { 22 try { 23 lock.lock(); 24 System.out.println("有" + lock.getWaitQueueLength(condition) + "个线程正在等待condition"); 25 condition.signal(); 26 }finally { 27 lock.unlock(); 28 } 29 } 30 }
1 /** 2 * getWaitQueueLength(condition)测试类 3 */ 4 public class Run { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 final Service service = new Service(); 8 9 Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 service.waitMethod(); 13 } 14 }; 15 16 Thread[] threads = new Thread[10]; 17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 18 threads[i] = new Thread(runnable); 19 } 20 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 21 threads[i].start(); 22 } 23 24 try { 25 Thread.sleep(2000); 26 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 service.notityMethod(); 30 } 31 }
运行结果如下:

其他方法介绍:
1 hasQueueThread() 查询指定的线程是否正在等待获取锁 2 hasQueueThreads() 查询是否有线程正在等待获取锁 3 hasWaiters() 查询是否有线程正在等待锁有关的condition(也就是当前通过condition进行等待的线程数) 4 isFair() 判断是不是公平锁 5 isHeldByCurrentThread() 查询当前线程是否获取到锁 6 isLocked() 查询此锁是否可以由任意线程获取,也就是当前是否被某个线程获取了锁 7 8 lockInterruptibly() 如果当前线程未被中断,则获取锁,如果已中断则抛异常 9 tryLock() 仅在调用的时候锁未被另一个线程获取的情况下,才能获取该锁 10 tryLock(Long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 如果在指定时间内,没有被另一个线程获取,且当前线程未被中断,则获取锁 11 12 13 awaitUninterruptibly() 当使用该方法等待时,此时使用interrupt()中断该线程,程序不会抛异常 14 awaitUnit() 设置线程等待的时间,当等待时间到达后继续执行,此方法等待达到之前,可以被其他线程唤醒