一、热身练习
要求:生成一个5*5的单位矩阵
warmUpExercies 函数:
function A = warmUpExercise() %定义函数A为warmupexercise
A = eye(5); %eye()单位矩阵,该函数的功能即生成5*5的单位矩阵
end
调用:
fprintf('Running warmUpExercise ... '); fprintf('5x5 Identity Matrix: '); warmUpExercise() %调用该函数 fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue. '); pause;
输出:

二、绘图(plotting)
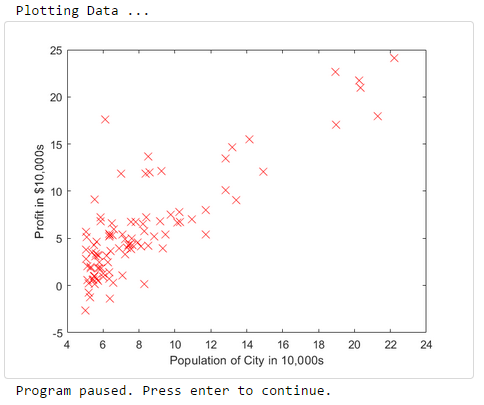
要求:根据给出的数据(第一列为所在城市的人口,第二列为对应城市的利润,负数表示亏损)绘制散点图,以更好选择餐馆的地址
plotData函数:
function plotData(x, y) plot(x,y,'rx','MarkerSize',10); ylabel('Profit in $10,000s'); % 设置y轴标签 xlabel('Population of City in 10,000s'); % 设置x轴标签 end
*MarkerSize: 标记大小,默认为6
* rx:红色的叉号
调用:
fprintf('Plotting Data ... ') data = load('ex1data1.txt'); % 加载data文件 X = data(:, 1); y = data(:, 2); % 将第一列全部元素赋值给X,第二列全部元素赋值给y m = length(y); % 定义m为训练样本的数量 plotData(X, y); % 将X,y作为参数调用plotData函数 fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue. '); pause;
输出:
三、代价函数和梯度下降
线性回归的目标是最小化代价函数J(θ):
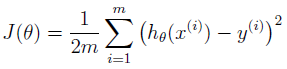 ,在这里使用平方法来表示误差,误差越小代表拟合的越好。
,在这里使用平方法来表示误差,误差越小代表拟合的越好。
其中假设 h(x) 由线性模型给出:
![]()
模型的参数是θj 通过调整θ的值来最小化成本函数,一种方法是梯度下降,在这种算法中,每次迭代都要更新θ
![]()
随着梯度下降的每一步,参数θj 接近实现最低成本J(θ)的最佳θ值
*与 = 不同,:= 代表着 同时更新(simultaneously update),简单来说就是先将计算的 θ存入一个临时变量,最后所有 θ都计算完了一起再赋值回去,例如
temp1 = theta1 - (theta1 - 10 * theta2 * x1) ; temp2 = theta2 - (theta1 - 10 * theta2 * x2) ; theta1 = temp1 ; theta2 = temp2 ;
在数据中增加一列1,因为代价函数中θ0的系数为1,且将参数初始化为0,将学习率α初始化为0.01
矩阵表示的话类似于:

X = [ones(m, 1), data(:,1)]; % 向x第一列添加一列1 theta = zeros(2, 1); % 初始化拟合参数 iterations = 1500; % 迭代次数 alpha = 0.01; % 学习率设置为0.01
==》计算代价函数J(检测收敛性)
function J = computeCost(X, y, theta)
m = length(y);
J = 0;
J = sum((X*theta-y).^2)/(2*m);
end
调用代价函数:
fprintf(' Testing the cost function ... ') % compute and display initial cost J = computeCost(X, y, theta); % 调用代价函数J fprintf('With theta = [0 ; 0] Cost computed = %f ', J); fprintf('Expected cost value (approx) 32.07 '); % further testing of the cost function J = computeCost(X, y, [-1 ; 2]); % 调用代价函数J
fprintf(' With theta = [-1 ; 2] Cost computed = %f ', J);
fprintf('Expected cost value (approx) 54.24 ');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue. ');
pause;
运行结果:

可以看到,当theta取[0;0]时的代价函数比取[-1;2]的代价函数小,说明[0;0]更优。
gradientDescent.m——运行梯度下降:
说明:验证梯度下降是否正常工作的一种好方法是查看J的值并检查它是否随每一步减少。 gradientDescent.m的代码在每次迭代时调用computeCost并打印J的值。 假设已正确实现了梯度下降和computeCost,则J的值不应该增加,并且应该在算法结束时收敛到稳定值。
在梯度下降中,每次迭代都执行下面的这个更新:
![]()
梯度下降函数:
function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) %GRADIENTDESCENT Performs gradient descent to learn theta % theta = GRADIENTDESCENT(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) updates theta by % taking num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1); for iter = 1:num_iters % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Perform a single gradient step on the parameter vector % theta. % % Hint: While debugging, it can be useful to print out the values % of the cost function (computeCost) and gradient here. % theta = theta-alpha*(1/m)*X'*(X*theta-y); % ============================================================ % Save the cost J in every iteration J_history(iter) = computeCost(X, y, theta); end end
调用梯度下降函数:
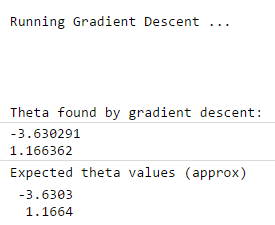
fprintf(' Running Gradient Descent ... ') % run gradient descent 运行梯度下降函数 theta = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, iterations); % print theta to screen 将theta值输出 fprintf('Theta found by gradient descent: '); % 利用梯度下降函数计算出的theta fprintf('%f ', theta); fprintf('Expected theta values (approx) '); % 期望的theta fprintf(' -3.6303 1.1664 ');
运行结果:
将得到的参数用MATLAB进行绘制并预测35000和70000人口的利润:
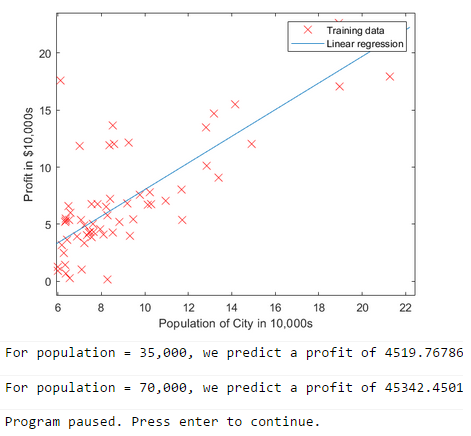
% Plot the linear fit 绘制线性拟合直线 hold on; % keep previous plot visible 指当前图形保持,即样本点仍然保持在图像上 plot(X(:,2), X*theta, '-') legend('Training data', 'Linear regression') % 创建图例标签 hold off % don't overlay any more plots on this figure % Predict values for population sizes of 35,000 and 70,000 predict1 = [1, 3.5] *theta; fprintf('For population = 35,000, we predict a profit of %f ',... predict1*10000); predict2 = [1, 7] * theta; fprintf('For population = 70,000, we predict a profit of %f ',... predict2*10000); fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue. '); pause;
运行结果:
*注意A*B和A.*B的区别,前者进行矩阵乘法,后者进行逐元素乘法
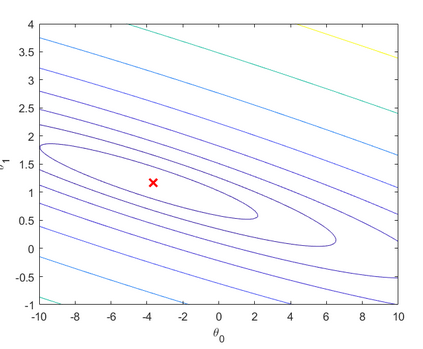
四、可视化代价函数J
这部分代码已经给出
fprintf('Visualizing J(theta_0, theta_1) ... ') % Grid over which we will calculate J theta0_vals = linspace(-10, 10, 100); theta1_vals = linspace(-1, 4, 100); % initialize J_vals to a matrix of 0's J_vals = zeros(length(theta0_vals), length(theta1_vals)); % Fill out J_vals for i = 1:length(theta0_vals) for j = 1:length(theta1_vals) t = [theta0_vals(i); theta1_vals(j)]; J_vals(i,j) = computeCost(X, y, t); end end % Because of the way meshgrids work in the surf command, we need to % transpose J_vals before calling surf, or else the axes will be flipped J_vals = J_vals'; % Surface plot figure; surf(theta0_vals, theta1_vals, J_vals) xlabel(' heta_0'); ylabel(' heta_1'); % Contour plot figure; % Plot J_vals as 15 contours spaced logarithmically between 0.01 and 100 contour(theta0_vals, theta1_vals, J_vals, logspace(-2, 3, 20)) xlabel(' heta_0'); ylabel(' heta_1'); hold on; plot(theta(1), theta(2), 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 2);
运行结果: